A Thermometer is a device that is used in the measurement of temperature. A resistance thermometer is a type of thermometer which can be used to give extremely accurate results. The temperature is measured by measuring the change in resistance. The thermometer consists of a platinum wire placed inside glass probes. The device is evacuated to prevent an unnecessary rise in temperature. The device is extremely fragile and hence kept within protective probes. They have extremely high accuracy and they are replacing thermocouples in the industry. It has various important applications and is being used in different industries to give accurate results.
What is Resistance Thermometer?
A resistance thermometer is used for temperature measurement. It is also called a resistance temperature detector. An RTD is basically a sensor that consists of fine wire wrapped around a glass or ceramic material and various other constructions are also used. The wire used is typically made of copper, nickel or platinum. The material which is used in the construction of this thermometer has an accurate resistance and temperature relationship which is used in the measurement of temperature.

Resistance Thermometer
Resistance Thermometer Circuit
The resistance thermometer circuit is basically a Wheatstone bridge circuit. However, it is not exactly a Wheatstone bridge but a modification of the circuit. It is connected to one arm of the Wheatstone bridge as shown in the figure:
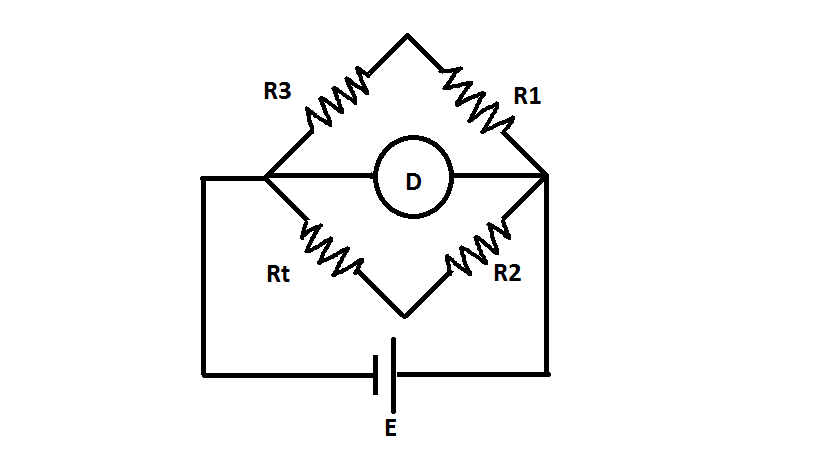
Resistance Thermometer Circuit
The resistors R1 and R2 are fixed resistances and R3 is the variable resistance. Rt is the detector resistance that is used in the circuit.
At balanced condition,
Rt = (R2 / R1 ) * R3
When R1 = R2
Rt = R3
The variable resistance which is used is nothing but an adjustable potentiometer. The resistors which we use in the circuit are made of manganin. This is because manganin has the lowest temperature coefficient and the temperature does not rise unnecessarily.
There are a few things which we must keep in mind while designing the circuit of resistance thermometer and they are as follows:
We use lead wires to connect the resistance thermometer to our circuit. So, if there is a variation in temperature, the resistance of the Wheatstone bridge circuit will also vary accordingly. In order to avoid that, we will have to maintain a proper distance between the measurement point and the point where the resistance thermometer has to be installed in the circuit.
The current flowing through the thermometer may cause heating effect leading to a considerable rise of temperature in the circuit. This is an unavoidable situation. However, in order to avoid this condition, we will have to compromise with the sensitivity of our instrument. If we reduce the current flowing through this thermometer, the heat generated will also reduce along with the sensitivity. However, we can improve the situation with proper amplification. The increase in temperature can be give represented by the formula:
∆T = P / Pd
Where ∆T = rise in temperature in ⁰C
P = power dissipated in RTD in watts
Pd = Dissipation constant of RTD in W/ ⁰C
The Equation for Resistance Thermometer
As we know, the relation of resistance with respect to that of temperature can be given by the equation:
Rt = Ro (1 + αt + βt2 + ϒt3 ———)
Therefore, from the above equation, Rt can be calculated as:
Rt = Ro (1 + αt + βt2 )
For pure platinum,
α = 3.94 Χ 10-3 /⁰C
β = – 5.8 Χ 10-7 /(⁰C)2
We can write the above equation as:
Rt = Ro (1 + C tpt)
C = mean resistance temperature coefficient between 0 ⁰C and 100 ⁰C.
tpt = platinum temperature coefficient
and is given by
tpt = [(Rt – Ro ) / (R100 – Ro)] * 100
: Rt, Ro, R100 are the resistance at t ⁰C, 0 ⁰C, 100 ⁰C
The interval of the thermometer is denoted by R100 – Ro
The equation which has been mentioned below shows the difference true temperature ‘t’ and platinum temperature ‘tpt’
(t – tpt) = δ { (t/100) ^2 – (t/100)}
δ = constant
δ lies between 1.488 to 1.498. The temperature range of a platinum resistance thermometer is between 100 ⁰C to 650 ⁰C.
Working Principle
The resistance of a conductor depends on temperature variations. When the temperature of the metal increases, it causes an increase in the vibrational amplitude of the atomic nuclei of the metal. This causes an increase in the probability of the collision of the free metals that exist on the metal surface. This leads to an increase in the resistance of the material causing subsequent temperature rise.
This is exactly how the resistance thermometer works. The temperature detector is made of copper, tungsten, nickel or platinum. However, platinum is best suited for the purpose because of its stable temperature-resistance relationship. The changes in resistance with respect to that of temperature can be represented by the formula.
Construction of Resistance Thermometer
The construction of a resistance thermometer is shown below:
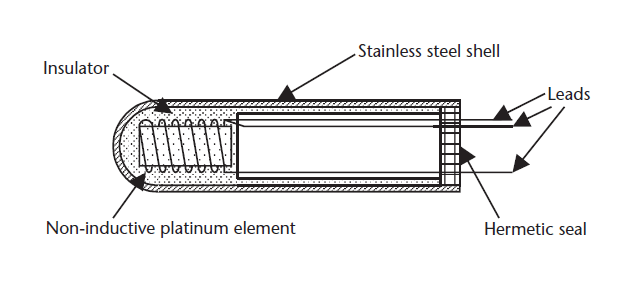
Construction of a Resistance Thermometer
A platinum resistance thermometer consists of a platinum coil that is present inside a cross frame. We place the whole arrangement in an evacuated tube which is made of stainless steel. The coil arrangement generates very little strain when there is a rise in temperature. This may cause an undesirable change in resistance. For the construction, the pure platinum wire must be used. The purity of the platinum can be confirmed using the formula R100 /Ro. In the case of pure platinum material, the value must be greater than 1.390.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages are
- It gives an accurate result
- it is used in various industrial applications
- It provides you with a vast operating range.
The disadvantages are
- The sensitivity of platinum is extremely less for a small change in temperature
- The response time is quite slow
Resistance Thermometer Applications
The applications are
- Used in automotive to measure the temperature of engine oil
- Used in communication and instrumentation to measure the temperatures of amplifiers, stabilizers, etc.
- Used in food processing, power electronics, and aerospace engineering
FAQs
1). How does the resistance thermometer measure temperature?
It measures temperature by measuring the change in resistance with respect to the change in temperature of the circuit
2). What is the range of resistance thermometer?
The temperature range is between -200 ⁰C to 1000⁰C.
3). What is the accuracy of a platinum resistance thermometer?
It provides excellent accuracy over a wide range of temperatures.
4). How does a platinum resistance thermometer work?
In a platinum type, the current is passed through a circuit and the temperature is measured by measuring the voltage across the circuit. The change in resistance is then used to measure the temperature.
5). What type of metals do we choose for making resistance thermometers?
Metals like copper, nickel, and platinum are used which are accurate temperature/ resistance relationships.
So, here we have mentioned all the important details related to an overview of the resistance thermometer. As can see it is a very important device from an industrial point of view. It has endless applications. If you know any important characteristics of this instrument, then do let us know. Here is a question for you, what are the types of resistance thermometer?