In electronics engineering, different kinds of materials are used to carry electricity. The materials like copper, aluminum, germanium Ge), silicon (si) are good conductors of electricity and have good conductivity. Such materials are called semiconductors, used in various electronic applications. These types of materials have a narrow forbidden gap of 1eV, sufficient to transfer the electrons from the valance band to the conduction band. When two types of materials like p-type and n-type are combined chemically with a fabrication method, then a p-n junction is formed. This p-n junction forms a semiconductor device called a diode. Mostly it is made up of silicon because of its good conductivity. Hence it is also called a silicon diode. It is mainly applicable for rectifier circuits. The article is about a peak inverse voltage, which gives the peak voltage rating of a silicon diode.
What is Peak Inverse Voltage?
Peak inverse voltage is also referred to as reverse breakdown voltage or peak reverse voltage, which is defined as the maximum reverse voltage that a diode or PN-junction can withstand in a non-conducting state or reverse bias condition before breakdown. If this voltage exceeds, the diode might get damaged. This maximum voltage can block the rectifier or diode in a given circuit. The value of PIV for the diode is the specified value that should be mentioned by the manufacturers in the datasheet.
PIV in the Diode
Peak inverse voltage in the diode is the peak value of the inverse voltage across the diode in reverse bias condition. Consider the circuit shown below to calculate the PIV of the silicon diode or peak inverse voltage of the diode. In the circuit, the silicon diode or pn-junction diode is used as a rectifier to convert AC to DC. Make sure that the maximum value or peak value of the AC supply should not exceed the peak inverse of the silicon diode.
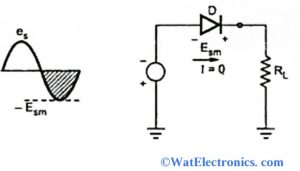
Peak Inverse Voltage in Diode
In the half-wave rectifier, the load current will be zero when the diode is in a non-conducting state or reverse bias condition. Thus the maximum value of the voltage that exists across the diode is Esm.
At the reverse bias condition of the diode, the PIV of silicon diode occurs at the peak value of each negative half cycle of the input. The peak inverse voltage formula is given as,
PIV of Diode = Esm
Peak inverse voltage of diode formula is nothing but the maximum value of the secondary voltage = π E dc|Idc =0
This is also known as the PIV rating of the diode. According to the desired circuit specifications and PIV rating, the diode must be selected for the operation.
Peak Inverse Voltage Calculation
Consider the circuit diagram shown below for peak inverse voltage calculation.
PIV of the silicon diode is calculated in reverse bias condition or non-conducting state of the diode. When the D2 diode is reverse biased, the total voltage of the secondary winding of the transformer is dropped across it. The voltage drop across the diode D1 ie in conducting diode is assumed to be zero. Here D1 will be in forward bias and D2 will be in reverse bias condition.
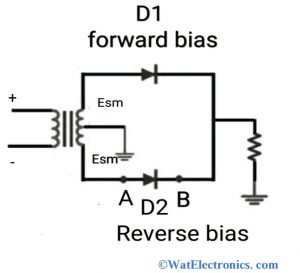
PIV Rating of Diode
Hence, the PIV or breakdown reverse voltage is the peak value of the reverse voltage to which the diode gets subjected to the secondary winding of the transformer. Let point A be the -Esm and point B be the +Esm with respect to ground. Neglect the voltage drop of the diode D1
Hence the peak value of the reverse voltage across D2 is 2Esm
Peak Inverse voltage (PIV) of diode = 2Esm = π E at DC | Idc =0
Where Esm= maximum value of the AC voltage across the half of the secondary winding of the transformer.
If the drop across the diode is assumed as 0.7V the PIV of the reverse-biased diode is given as,
PIV = 2Esm – 0.7
The above formula is used because only one diode conducts at a time.
Importance
The importance of peak inverse voltage is shown in the reverse bias condition of the diode. Because, if this value exceeds the diode might get damaged. When the diode is non-conducting, the reverse voltage gets across the diode. This peak value of the reverse voltage decides the peak inverse voltage or PIV rating of the diode. This rating is used to analyze the capacity of the diode that can withstand reverse bias condition without breakdown.
The PIV of the diode in the half-wave rectifier is equal to the maximum value of the supply voltage.
In rectifier circuits like half-wave, full-wave, center-tapped, and bridge circuits, the PIV of silicon diode is the maximum value of the AC sinusoidal supply voltage that exists across the diode in reverse bias condition, which is equal to Esm.
If the PIV exceeds across the junction of the diode in reverse bias condition beyond the specified PIV rating, then the junction gets damaged or breakdown occurs.
Thus, this is all about an overview of an important characteristic of the diode, which is peak inverse voltage of diode -definition, formula, calculation, and importance. Here is a question for you, “What is the PIV rating of the rectifier circuit? “