Cascode is a technique implied to improve the performance of the analog circuits. The same technique can be applied to transistors and the vacuum tubes to make the circuit better performance-wise. The word cascode is initiated in the year 1939 by Frederick Vinton Hunt’s and Roger Wayne Hickman’s article during the discussion of voltage stabilizer applications. The discussion was about to propose a method to replace the pentode by cascoding two triodes. In cascoding, two transistors are used either BJTs or FETs such that one configuration acts as an input stage whose output is provided as input to the output collecting configuration. Miller Effect can be isolated by the usage of a cascode amplifier.
What is a Cascode Amplifier?
If an amplifier comprises of BJTs then the input stage is a common-emitter configuration that feeds to the common base at which the output is collected. This type of amplifier is known as a cascode amplifier. Even FETs can be used in cascode amplifiers. In such cases, the common-emitter is replaced by a common source and a common base will be replaced by common gate configurations.
The characteristics due to the cascoding of amplifiers are:
- The impedances at input and output are high.
- The signals amplification undergoes under high bandwidths possessed by the system.
- The isolation amid input and the output is high.
As there is no direct communication or coupling from output to input because of high isolation leads to eliminate the miller effect.
Miller Effect
It is a phenomenon that occurs mainly in feedback circuits. If the voltage amplifier is inverting there is an increase in the equivalent capacitance at the input due to the capacitance effect amplification amid the terminals of input and output. This increase in the capacitance value is known as virtual capacitance and it may lead to a reduction in the bandwidth. To overcome this situation, the cascoding technique is used in amplifiers.
Cascode Amplifier Circuit Diagram
A cascode amplifier circuit can be designed by using FETs with two configurations like common source and drain. As it is of the two-stage amplification process the input stage is of common source configuration. The circuit diagram of the cascode amplifier using FETs is
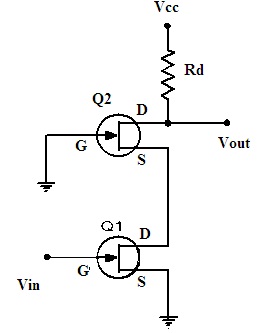
Cascode Amplifier
The input signal is applied to the terminal gate at the initial stage. The second stage that is the output stage which is driven from the output of the initial stage is of configuration common drain. The final output is collected from the drain terminal at which the drain resistor Rd is connected.
The gate of the FET at the second stage is grounded. So, the value of the source voltage of the second stage FET has remained equivalent to the drain voltage of the first stage FET.
FET at the second stage offers a low path of resistance to the first stage FET. Due to this reason for low resistance, the gain of FET at the first stage is reduced which indirectly reduces the miller effect. Hence the bandwidth is improved. The overall gain doesn’t get affected because it is compensated by the FET in the second stage.
As the voltage at the source and the drain of the first stage FET, Gate, and the source terminals of the second stage FET is almost constant. Hence their nothing to be feedback. These type of conditions leads to isolating the situation called the miller effect.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cascode Amplifier
The advantages of the cascode amplifier are:
- The bandwidth is high due to the elimination of the Miller Effect.
- Due to the cascode connection between two transistors the overall gain of the system is high.
- Even the parts of the count for both the transistors are low.
The disadvantages of these amplifiers are:
- The presence of two transistors requires a high amount of voltage supply.
- The sufficient amount of drain to source voltage must be supplied to both the transistor which strikes lesser the limit on the supply voltage.
Applications of Cascode Amplifier
The applications of these amplifiers are:
- In the RF tuners, cascode amplifiers are used.
- Amplitude modulation technique uses cascoding technique
FAQs
1). What does cascode mean?
The load in the amplifier stacked vertically and it is referred to as cascode connection. The first stage configuration is connected in parallel to the second stage configuration of the transistor. To isolate and avoid direct feedback from the output to the input. This type of connection is known as cascode.
2). What is the difference between cascade and cascode?
The cascade connection is about the series oriented connection between the transistors. In the two-stage amplification, the output of the first stage is provided as input to the second stage, and further for n-stages, this chain continues.
The cascode connection is about the parallel connection amid the transistors of the multiple stages. There is only one Common emitter configuration transistor that drives the transistor with the configuration of the common base. This is the basic difference between cascade and cascode.
3). Why do we use a cascode amplifier?
To achieve high impedances, bandwidth, overall gain, and above all to protect the amplification from the miller affect these amplifiers are used.
4). What do you mean by feedback in the amplifier?
The process in which the output generated is fed back to the input is known as feedback. This process is popular in amplifiers to make its operation stable, as well as noise, which can be reduced from the system.
5). What is Miller voltage?
When the voltage amid gate an the drain terminal comes closer to the value zero where there is a chance of transition to be at its peak. In this situation, the miller effect occurs and this type of voltage is referred to as miller voltage.
know more about Positive Feedback Amplifier MCQs.
Please refer to this link to know more about Isolation Amplifier & Audio amplifier circuit.
Please refer to this link for cascode amplifier MCQs
However, cascode amplifiers are further classified into two types. They are folded and bimos cascode amplifiers. Based on the requirement of gain, bandwidth and the impedance criteria the type of it is chosen for applications. Can you describe how gain and the bandwidth are related to these amplifiers?