A Digital Counter is obtained by arranging the flip-flops. These are the applications of flip-flops. Other than counting, these are used for measuring the frequency as well as time. These are used to increase the addresses in memory. The operation of these devices depends on the single clock applied. These are made of flip-fops as basic elements. There are two states included in the flip-flops. The high state is represented by 1 and the low state by 0. The operation of the counter can be made possible by high state-driven flip-flops. Counters consist of modes that are represented by the number of countable states, for example a mod-8 counter. In this, the number of states countable is from 000 to 111 (that is 0 to 7). Hence eight countable states name the counter as a mod-8 counter.
What is Digital Counter?
Definition: The circuit is designed with digital logic to obtain information about the number of events that occurred. This type of digital logic device can be defined as a Counter. The design of counters can be achieved by following various steps.
- The number of Flip-Flops based on the requirement.
- Accordingly, the State diagrams/ Excitation Tables are drawn.
- Further, the expressions are minimized using various techniques.
- Finally, the logic diagram is designed.
The above steps are especially followed fro the design of the type of counter known as Synchronous Counters.
Types of Digital Counters
The interconnection of the flip-flops results in the classification of the counters. Although the single clock signal applied to the counters. There is a difference among the operation based on a single cock applied to the flip-flops in the circuit or the signal applied to the main flip-flop.
The types of counters are:
- Asynchronous Counters
- Synchronous Counters
The asynchronous counters are also referred to as Ripple counters. The simplest in design among the other counters is the ripple counter. The least quantity of hardware is required for this counter. The flip of one stage reflects the flip in another stage in asynchronous counters. These counters are further described as ‘Serial Counters’.
But in the other type of counter called synchronous counters, each flip-flop in the circuit gets triggered with the same clock at the same time. This is possible by connecting each flip-flop clock line with a single clock. The operation occurred in such types of circuits will be in coordination or synchronization with all the flip-flops present. Hence these are referred to as Synchronous Counters.
Based on the clock signal applied the counters are classified as synchronous and asynchronous counters. In the Asynchronous type, only the first flip-flop is provided by the main cock. the remaining flip-flops are powered with the output obtained in the previous stage of flip-flops. There is another category of counters referred to as Decade Counters. This counter is able to count the pulses for ten values. The counting is done from 0 to 9. Even this counting can be extended to 15 states.
What is the difference between Synchronous and Asynchronous Counters?
Based on the connections and the clock applied to the flip-flops there are certain differences between Synchronous and Asynchronous counters. Some of the differences are listed as follows:
| Asynchronous Counters |
Synchronous Counters |
|
1. In this counter, the main clock is applied to the first flip-flop. Whereas the other flip-flops are provided with the clock from the output of previous stage flip-flops. |
1. The arrangement of the flip-flops in this counter is driven by the same clock. |
|
2. The clock is not simultaneous for all the flip-flops in the circuit. |
2. The clock is simultaneously provided for all the flip-fops. |
|
3. To the more number of states, the design of this counter is simple to implement. |
3. In this counter, as the number of states is increasing the design tends to become complex. |
|
4. The propagation delay is more as the counters are not in sync. |
4. The propagation delay will be less in comparison to the asynchronous counters because of the sync among the flip-flops. |
In comparison to the asynchronous counters, the operation will be fast in synchronous counters. The frequency required for operation in the synchronous counters is high. In terms of cost, it is low in asynchronous counters.
Please refer to this link to know more about Synchronous Counter MCQs & Asynchronous Counter MCQs.
How do Digital Counter Works?
The most frequently used flip-flops in the counter design is ‘D’ and ‘J-K’. Based on the way the clock signal applied for the counter works. The working can be analyzed well with the below example of two-bit ‘Asynchronous Counter’.
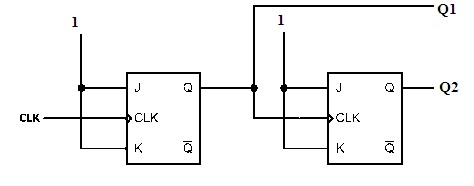
Digital Counter
The two-bit counter can count the pulses from 0 to 3. In the binary language from oo to 11. As soon as it reaches 11 it resets itself to 00. The above image is for the Asynchronous counter which is negatively triggered. Where the Q1 bits are treated as LSB and Q2 bits are granted as MSB.
At the initial state, the flip-flops are at 00.
When the initial signal of the clock is applied The first flip-flop gets affected by the negative edge. This leads to toggle the flip-flop from Low to High. After the first negative edge, the outcomes Q1= 1 and Q2=0. In this situation, Q2 has not affected because of the positive edge.
When the second signal of the clock is applied. Because of the negative edge, the toggle condition occurs. Then Q1 changes from High to Low and Q2 from Low to High. That is Q1=0 and Q2=1
Similarly, after the third pulse, the values are Q1=1 and Q2=1. As it reaches 11 further application of clock applied tends to reset that is 00. As the values are counted in an increment order. This is referred to as Up-counter.
What are Up and Down Counters?
The working or the operation of the counter is dependent on the clock signal applied. But the way these counters are used for the operations these are classified as Up and Down counters. To count the pulses in an ‘Incremental’ order referred to as Up counter. When the counting is done in the ‘Decremental’ manner these counters are referred to as Down counters.
Both these operations of counters can be done in a single circuit by using the mode in it. If the Mode is selected as ‘0’ at the input then it operates as Up counter. If the mode value is selected as ‘1’ then in such case the counter operates as Down Counter.
Digital Counter Applications
These counter circuits are the basic ones in the ‘Digital Electronics’. These counters possess various applications.
- In the conversions from Analog to Digital, these counters are used.
- In the applications of Timers for example Washings machines where we set the time. These counters are used.
- With the help of these counters, a ‘Digital Triangular Wave Generator’ can be designed.
- In the application of ‘Digital Clock’ counters are used.
- A practical example of these devices is seen in malls, stadiums, or auditoriums. In the above situations to keep the data on the number of persons. This can be made possible or it will become simple because of these counters.
The above are some of the applications of Digital Counters.
Please refer to this link to know more about BCD Counter.
Please refer to this link to know more about Digital Circuits MCQs & Digital Electronics MCQs
The counters can be designed by the arrangement of the ‘shift Registers‘. These are commonly known as Ring Counters and Johnson counters. Can you describe the basic difference between ring and johnson counter?