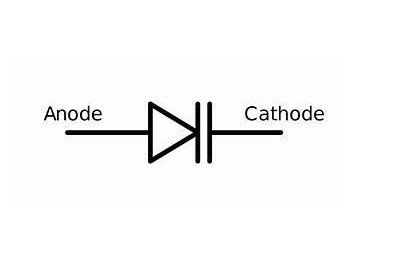
A basic diode consists of two terminals. This terminal is referred to as anode and cathode. It has a property of conducting the flow of current in a single and unified direction. This basic property of the diode makes it as a basic building block in the power supply units. because there it is preferred in the process of rectification.
It is used during the modulation of the signals. There exist many uses for the diodes based on the requirements in various fields of electronics as well as electrical. Generally, the diodes are made from the semiconductors such as silicon or germanium based on the necessity the type of semiconductor material is preferred.
Various Types of Diodes
Firstly, it started with a basic diode that consists of a p-n junction. Further developments and the increase in the needs and the demands for various subsystems paved the way in the formation of various types of diodes. Each diode has its own significance coming to the area of the electronics.
The usage of the diode in the electronic modules is vast. However, the special cases of the diodes have been constructed so that it can operate in reverse bias as well as to satisfy the respective terminologies.
Let us see the various types of diodes that are used in basic electronics. They are
1) P-N Junction Diode
This is the basic diode formed with the interaction of p-type and n-type materials. It deals with the concept of biasing. This biasing make it classify into various operating modes.
This diode conducts only during forwarding bias. In reverse bias, there is no evident flow of the current. It indicates that current gets blocked during reverse bias.
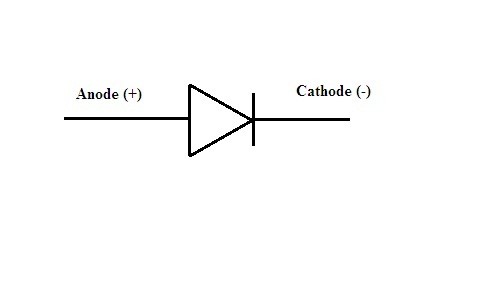
Symbol of P-N Junction Diode
These are utilized where the applications are preferred for low currents such as signal diodes. one of the basic application of this as the rectifiers.
2) Zener Diode
It is the diode designed in such a way that it can operate in the reverse bias mode. For the applied forward bias the operating characteristics will be similar to that of normal diode with the basic p-n junction.

Zener Diode
When the diode is in reverse bias mode after it reaches the minimum Zener voltage there we can see the increment in the values of current but the voltage remains constant after that point.
This makes it applicable to making use of it in the regulation of voltages. The specialty of the diode lies when it starts conducting during reverse bias. The more zen voltage of this type of diode is fixed by the manufacturers. Because of this reason, more zen diodes with various more zen voltages can be manufactured
3) Schottky Diodes
A diode that can operate with fast switching times in it is referred to as Schottky diode. The voltage drop that is considered to be forward is very low.
Schottky Diode
The applications of this type of diodes can be seen as evident in clamping circuits that are fast enough. This type of diodes can be seen operating in the range of gigahertz. That is it can be preferred during high-frequency applications.
4) Shockley Diodes
These are another type of diodes that are also utilized for the applications of switching. It is having some basic voltage that is referred to as trigger voltage.
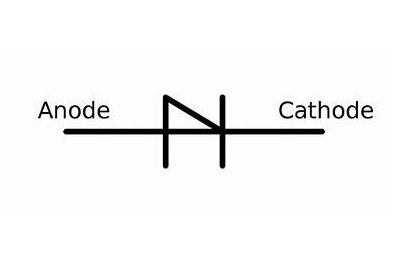
The symbol for Shockley Diode
If the voltage applied to this is less than the basic trigger value it cannot switch because it remains in high resistance mode. As the applied voltage exceeds the basic trigger value the low resistance path will be established. In this way, the Shockley diodes operate.
5) Varactor or Varicap Diode
This is another special category of the diode where the application of reverse voltage varies the capacitance at the junction. As it is variable capacitance diode it can be abbreviated as varicap.
The symbol for Varicap Diode
The applied value of the reverse voltage can affect the junction width. These are directly proportional to each other. But these are inversely related with capacitance at the junction.
This is the main reason that makes them applicable in the oscillators. The change in the value of capacitance makes the circuit to work as a tuner.
6) Barrett Diode
BARITT stands for barrier injection transit time. In this type of diode, the emission is due to thermal energy. This consists of less noise compare to another type of diodes.
These are applicable in various devices such as mixers, it can be amplifiers based on the small-signal capability or it may be oscillators.
7) Gunn Diode
It is a basic diode that has two terminals. It doesn’t possess the junction of P-N like various other diodes. The oscillators made from Gunn diodes are used during radio communications.

Gunn Diode
These are also utilized in military areas. The basic tachometers consist of this diode in it. Nowadays in the monitoring systems for opening the doors sensors are required this can be made possible by the Gunn diodes. In the intruder alarms circuitry also this diode is preferred.
8) Light Emitting Diode(LED’s)
This is the types of diodes that operate during forwarding bias operating region. As the diode starts conducting during this region there is a flow of the current. This current is referred to as forwarding current. During this process, the light gets emitted from the diode.

Light Emitting Diode
These include various types in LED. Namely blinking one that can act as on and off for a certain amount of time. They can be tricolor leads more than two colors get emitted based on the amount of received a positive amount of voltage.
Further, there are LED’s that emits infrared light. The practical application of it can be seen in remote controls. The above discussed are some of the types present in LED.
9) LASER Diode
It cannot be referred to as the same as that normal LED. Because other than normal light is emitted from this type of diode is termed as coherent light. This light is focused as a spot that consists of diameter less than one micrometer.

LASER Diode
As the response time is faster in this type of diodes these are used as optical storage devices as well as in CD players. Nowadays one can see bar code scanners these are one of the applications of LASER diode. These are also seen in the printers of LASER’s, Fax machines, etc…
10) Photo Diode
As the name suggests when the diode gets interacted with the light current gets generated. That means during the stage of darkness there cannot be any flow of the current indicating that it is an open circuit condition.
When the diode comes in contact with the light it gets interacted and the amount of current flows in the circuit making the diode bright. The functionality of photodiode resembles more zen diode because it can also conduct during reverse bias.

Photo Diode
The current value and the value of the intensity of the light are directly proportional to each other. These also have the response times that are fast enough that is in nanoseconds. This type of diodes can also have the capacity of generating electricity.
11) PIN Diode
This diode gets characterized during its construction itself. In this type of diode, it has both standards of p-type and n-type. But the junction formed due to its interactions here will be having no doping concentration in it referred to an intrinsic semiconductor.
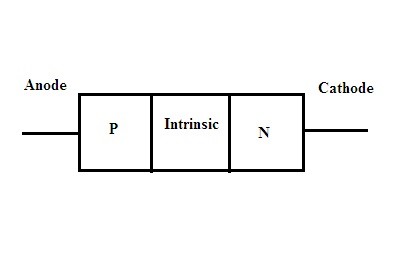
The symbol for PiN Diode
This region is helpful during applications like switching.
12) Fast Recovery Diode
As per the title, the diode will possess faster recovery time. During rectification, AC is applied as the input signal. This has positive and negative levels in it. For the change in the polarities from the positive to negative or from negative to positive, the recovery time must be fast.
During high-frequency applications, this becomes mandatory to possess the fastest recovery times. Hence this diode is preferred in such cases. This results in the representation must be in an accurate manner and maintain signal integrity.
13) Tunnel Diode
It is a diode with a basic junction of p-n that does has the property of negative resistance. In this type of diode voltage and current values are inversely related to each other.
Tunnel Diode
In the range of ultra-high-speed, these tunnel diodes have used switches. The switching time will be in nano or picoseconds. Because of the concept of negative resistance involved in it, this is used in the terminology of relaxation oscillator circuitry.
Please refer to this link for Choosing resistor values for diodes.
14) Step Recovery Diode
It can be referred to as a part of the microwave diode. During the high-frequency range, this tends to generate pulses. These diodes are dependent on the type of diodes that have the characteristics of turning-off fast based on their operation.
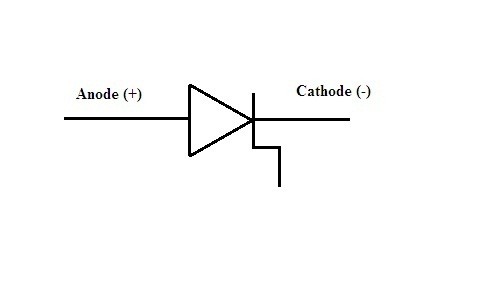
Symbol of Step Recovery Diode
Hence the various types of diodes along with there applications are discussed above. Each diode is unique in its way of representation as well as application. The above we discussed various types in a diode with respect to its applications. Can you describe the functionality of the various types of diodes and Diode Approximation?