The break down diode is an electronic component with two electrodes called as the anode and the cathode. Most of the diode is made up of semiconductor materials such as silicon, germanium etc. The fundamental property of a diode is to conduct electric current in only one direction and blocks the current that flows in the opposite direction. When the cathode is negative charge related to the anode at a voltage greater than minimum called as forward breaker, then the current flows through the diode. If the cathode is positive with respect to anode, is at the same voltage of a node, or is negative by an amount less than the forward breakover voltage, then the voltage doesn’t conduct current. Diode characteristic almost matches with the switch. The oldest of semiconductor devices was the crystal detector. It was used in early wireless radio. The forward breakover voltage of silicon device is 0.6V, germanium is 0.3V, selenium devices is 1V.
What is a Diode?
The current flow will be only in forward condition, not in the reverse direction. The voltage and current relationship of an ideal diode will exist only if any negative voltage produces zero current then it will be an open circuit. As long as the voltage is non-negative the diode looks like a short circuit.
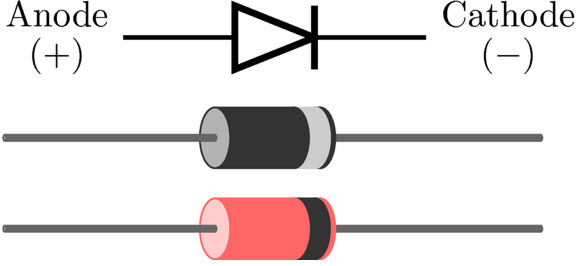
Diode Symbol
Different Types Of Break down Diodes mainly includes Signal diode, Zener diode, Tunnel diode, Gunn diode, Crystal diode, Varactor diode, Constant current diode, Light emitting diode, IR leds, Schottky diode, PIN diodes, Avalanche diode, Laser diode, Shockley diode, Photodiodes, Transient Voltage suppression diode, Super barrier diode, Point contact diode and Peltier diode.
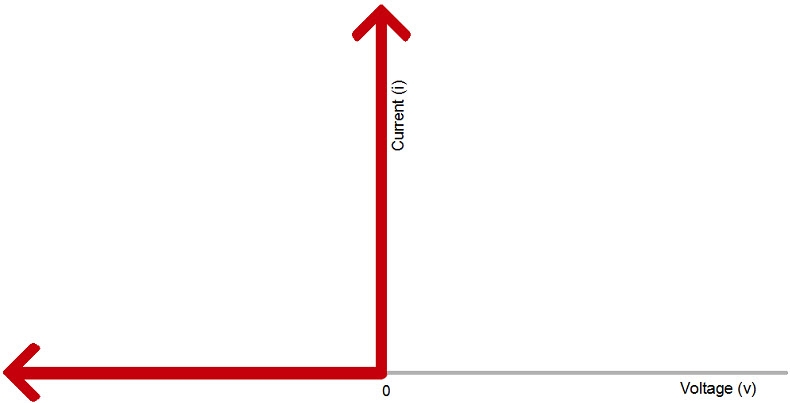
The Current-Voltage Relationship of an Ideal Diode
The table below will give brief information on the Ideal Diode Characteristics.
| Operation Mode | On(Forward Biased) | Off (Reverse Biased) |
| Current Through | I>0 | I=0 |
| Voltage Across | V=0 | V<0 |
| Diode Looks Like | Short Circuit | Open Circuit |
Types Of Break Down Diodes And Applications
The types of break down diodes include Schottky diode, Zener diode and Avalanche diode.
Schottky Diode
The Schottky diode is a semiconductor also known as hot carrier diode. It was invented by a German physicist ‘Walter H. Schottky. The forward voltage ranges from 150 – 450 mV. It resembles same as a basic diode but with additional elements to the bars across the triangle shape.
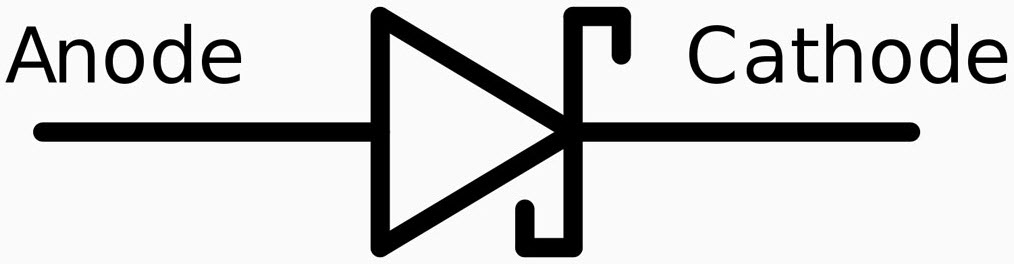
Schottky Diode Symbol
The basic problem of charge storage of PN junction can be minimized or limited with the Schottky diodes. The potential barrier is in between metal and semiconductor. Rectifying action will depend on the majority carrier. This results in the excess majority carrier to recombination. It will reverse the low level recover time. Schottky diodes are used as a rectifier at a single frequency exceeding 300 MHZ to 20 GHZ
Construction of Schottky Diode
It is a metal semiconductor junction diode without depletion layer. One side of the junction a metal like silicon, gold, platinum is used and other side of N-type doped semiconductor is used. To protect it from any external damage metal layer is surrounded by gold or silver layer. The metal film forms a positive electrode and semiconductor is the cathode.
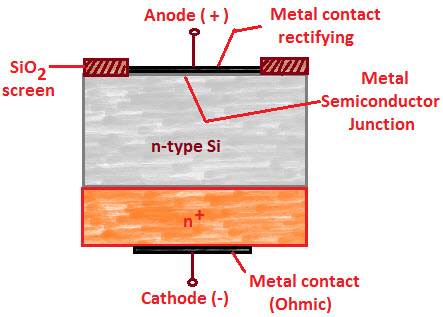
Construction of Schottky Diode
V-I Characteristics Of Schottky Barrier Diode
The VI characteristics of Schottky barrier diode are almost similar to a PN junction diode. But there are some exceptions in the forward voltage drop of the Schottky barrier diode is very low when compared with the normal PN junction diode. The forward voltage drop of Schottky barrier diode made of silicon exhibits a forward voltage drop of 0.3v – 0.5v. The forward voltage drop increase along with the increasing doping concentration of N type semiconductor diode.
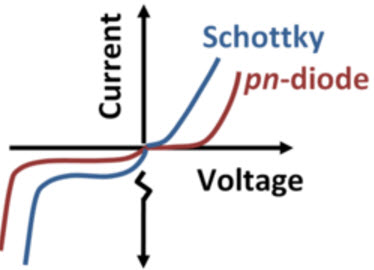
Schottky V-I Characteristics
Advantages of Schottky Diode
Low Turn On Voltage
The turn on voltage for the diode is in between 0.2V and 0.3V for silicon diode against 0.6v to 0.7v for a standard silicon diode.
Fast Recovery Time
It has a small amount of storage charge which can be used for high speed switching application.
Low Junction Capacitance
In very small active area, often as a result of using wire point contact onto the silicon, the capacitance levels are very small.
Applications of Schottky Diode
RF Mixer And Detector Diode
It has high switching speed and high frequency capability.
Power Rectifiers
Its high current density and low forward voltage drop means that less power is wasted than an ordinary PN junction diode.
Power OR Circuits
Used in the applications where a load is driven by two separate power supplies.
Solar Cell Applications
When the solar cells are connected to rechargeable batteries, often lead acid batteries this is because it may require 24 hours a day and the sun is not always available. Solar cells do not reverse the charge applied to it and therefore a diode is required in series with the solar cells. Drop in the voltage will result in the reduction of the efficiency of the diode. To limit the drop of the voltage Schottky diode is required.
Zener Diode
A Zener diode is similar to the normal diode which allows current to flow from anode to cathode. But it’s the additional application which makes distinct from normal diode is it will permit current to flow in the reverse direction when its Zener voltage is reached.
Zener Diode Symbol
Zener Diode Characteristics
Zener diode characteristics mainly deals with voltage across a Zener diode varying along with the current through it. The V-I characteristic curve of Zener diode is shown below.
In the figure right side of the characteristic curve represents the Zener diode receives forward voltage, which is positive voltage across anode to cathode terminals. In this region the diode is forward bias. In this period the current is very small for a while until it spikes exponentially up once the voltage reaches a particular point. This is called as threshold voltage.
Now the left side characteristic curves are also equally important. Here, Zener diode receives positive voltage across its cathode to anode terminals. In this region diode will be in reverse bias. Initially, when receiving reverse voltage, the current is very small. Leakage current is also called as small current which will be flowing through the diode. The moment it hots the breakdown voltage, the current increases suddenly. This current is called avalanche current. This used in the application of voltage regulation.
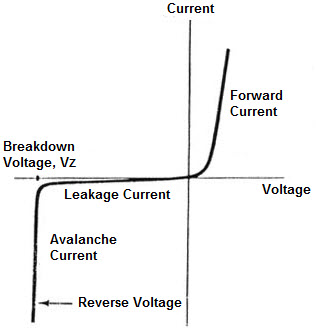
Zener Diode V-I Characteristics
Once the voltage across a Zener reaches the breakdown voltage, it is said to be Zener diode’s Zener voltage VZ. The voltage that Zener diode drops across itself will not continue to increase.
Zener Break Down Diode
When the reverse voltage is increased across the PN junction diode, then the electric field across the diode junction increases. This will result in a force of attraction on a negatively charged electron across the junction. The force from this junction will frees electron from its covalent bond and moves those free electrons to conduct the band. When the electric field increases, i.e., with the applied voltage then more and more electrons are freed from its covalent bonds.
This will result in drifting the electrons across the junction and electron hole recombination occurs. Finally, net current will be developed and it will increase with an increase in the electric field. Zener diode occurs in a PN junction diode with thin junction and heavy doping.
Avalanche Break Down Diode
Avalanche breakdown occurs in a PN junction. It is moderately doped and has thick junction. Normally Avalanche breakdown occurs when we apply a high reverse voltage across the diode. When there is an increase in applied reverse voltage then there will be an increase in the electric field across the junction. Suppose the applied reverse voltage is Va and the depletion layer width is d.
The generated electric field Ea = Va/d
The generated electric field applies force on the electronics at the junction and it frees them from covalent bonds. These free electrons will gain acceleration and will start moving across the junction with a high velocity. This will result in collision with neighboring atoms. Because of this collision very high velocity, which will further generate free electrons. Finally, these electrons will start drifting and electron hole pair recombination across the junction. The net current will increase.
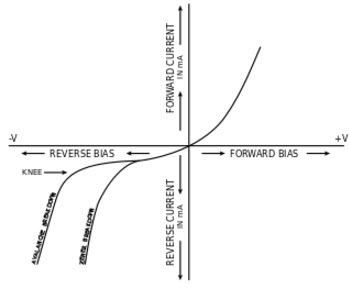
I-V Characteristics of Avalanche and Zener Breakdown
Applications Of Break down diode Diodes involves in Signal Limiter, Rectifier, Signal Modulator, Signal Mixer, Voltage regulator and Oscillators.
Please refer to this link to know more about Gunn Diode MCQs , Avalanche Photodiode MCQs.
Please refer to this link to know more about Light Emitting Diode.
Please refer to this link for Choosing resistor values for diodes.
Thus, this is all about types of break down didoes and its applications. We hope that you have got a better understanding of this concept. Furthermore, any queries regarding this concept, or electrical and electronics projects, please give your feedback by commenting in the comment section below. Here is a question for you, what are breakdown diodes?