Trimmer resistors are also called trim pots or variable resistors that allow you to manually fine-tune the resistance in a circuit. They’re often used for calibration in applications like amplifiers and radios to make sure that the circuit output is as close to the ideal level as possible. In this article, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about awesome little components like a trimmer resistor and how they work, how they’re manufactured, and how you can use them in your own projects.
What is a Trimmer Resistor/Definition?
A trimmer resistor is a resistor that can be adjusted or “trimmed” to an exact resistance by turning a screw. This type of resistor is often used in circuits because it allows for adjustments in circuit performance. The adjustment is made by using a tool, such as a screwdriver, to turn the dial or knob on the device. The Trimmer resistor symbol is shown below.
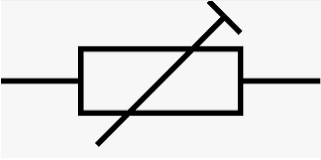
Trimmer Resistor Symbol
Trimmers are normally manufactured as single-turn or multi-turn components and may be top-adjusted or side-adjusted. Multi-turn trimmers can be used with automated test equipment (ATE) and are also available with anti-rotation features that prevent the adjustment from being changed accidentally.
Trimmer resistors are usually used in applications where adjustments need to be made during production, or where the effect of manufacturing tolerances needs to be compensated for during the operational life of a product.
Trimmer Resistor Pinout
This resistor includes three terminals where each terminal and its function are discussed in the following pinout configuration.
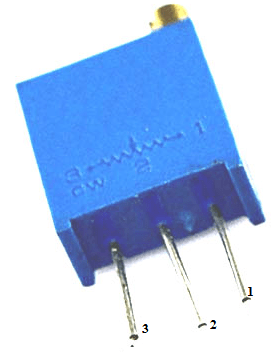
Pinout Diagram
- Pin1 (CCW): This pin is simply connected to one terminal of the resistive track.
- Pin2 (Wiper): This terminal is moved to get variable voltage.
- Pin3 (CW): This pin is simply connected to the remaining terminal of the resistive track.
Features & Specifications
The features and specifications of the trimmer resistor are discussed below.
- Trimmer resistor is a cermet/multi-turn/ sealed/industrial based resistor.
- Chevron seal design.
- The available package is tape & reel.
- The available hardware type is mounting.
- RoHS compliant.
- The typical resistance value of this resistor ranges from 10 ohms – 2 mega-ohms.
- The tolerance of resistance is ±10%.
- Insulation resistance is 500Vdc.
- Dielectric strength ranges from 350 – 900VAC.
- Effective travel is 25 turns.
- Operating temperature ranges from -55℃ to +125℃.
Trimmer Resistor Construction
The main body of the resistor contains a strip of conductive material that moves when it is turned. This movement physically changes the resistance of the resistor by increasing or decreasing the amount of contact between the conductor and the surface it rests on. This changing resistance can then be used to control the electrical signals or components within circuits.
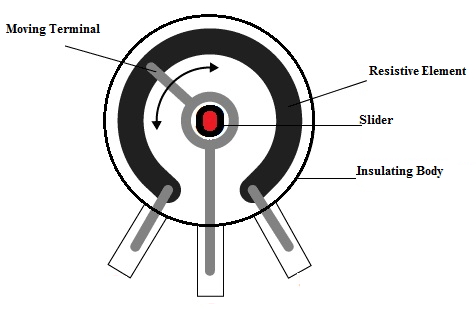
Trimmer Resistor Construction
The body of the resistor is constructed of three main parts:
Fixed Terminal
This terminal is usually anchored in place and does not move when the resistor is adjusted. It is connected to an external part of the circuit that supplies power or electrical signals.
Moving Terminal
This terminal is attached to the adjusting shaft that can be turned to make micro-adjustments. It also connects to an external part of the circuit that receives power or signals from another component in the circuit.
Resistive Element
This element is mounted inside the resistor and connects both terminals together. It provides resistance between the two terminals and can be adjusted by turning the moving terminal.
These are typically small in size and have large resistance values. Most of them are surface mount components, though some through-hole versions are still available. They may also be sealed for use in harsh environments or covered with a protective cap to prevent unwanted adjustment.
There are many different types of trimmer resistors, varying in size, resistance value, power rating, and environmental sealing abilities.
Types of Trimmer Resistor
These are the most common types of trimmer resistors:
Single-turn Trimmer Resistors
These have a screw that turns about 300 degrees in either direction in order to adjust the resistance value. This type of resistor has a resistance range of 10Ω-1MΩ and can be adjusted in increments as fine as 0.01Ω. It can handle up to 1W of power.
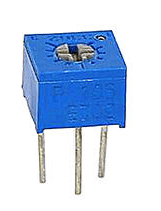
Single-turn Trimmer Resistor
Multiturn Trimmer Resistors
These work like single-turn trimmers, except they have multiple turns—usually five—to give them more adjustment range (50Ω-1MΩ). They can also be adjusted in increments as fine as 0.01Ω, but they can only handle 0.25W of power, making them less powerful than single-turn trimmers.
Multiturn Trimmer Resistor
Surface Mount Trimmers
Surface mount type resistors are a type of trimming potentiometer that has been specially designed for surface mounting onto a printed circuit board. They are used in applications where the voltage or current needs to be adjusted, and their small size makes them suitable for small electrical equipment such as mobile phones.

Surface Mount Trimmer
Generally, these resistors have three pins, which are connected to the three terminals of an adjustable resistor. As well as these three pins, there are three other pins on the resistor which can be connected to the circuit. This gives six possible ways of connecting the resistor, but there is only one way that will give the correct resistance.
Trimmer Resistor Working Principle
The working principle of this resistor is very simple. The resistance element is a thin film deposited on an insulator. If the contact end of the thin film is pressed against the external connection pin, the current can be passed through, but if it is not pressed, the current cannot flow.
How are Trimmer Resistors Used?
Trimmer resistors are used primarily when the exact resistance value of a component is unknown or cannot be determined before the circuit is assembled and powered on. For instance, if you add an amplifier to your circuit, you may need to adjust the resistance value of your resistor to get rid of any background noise or static.
Trimmer Resistor Circuit Diagram
Generally, It is a variable resistor and it is available in the potentiometer form (pot) known as trimpot. This component includes three terminals but it can be used as a two-terminal resistor by connecting the wiper to one of the remaining terminals, otherwise simply using two terminals.
The simple LED circuit diagram of the trimmer resistor or variable resistor is shown below. Once only two terminals this resistor is used as the wiper leg and an outer leg then it works as rheostat otherwise a 2-terminal variable resistor. So a potentiometer needs to be used in this circuit to change the resistance instead of using a voltage divider. So a trimmer is used as a two-terminal variable resistor in this circuit.
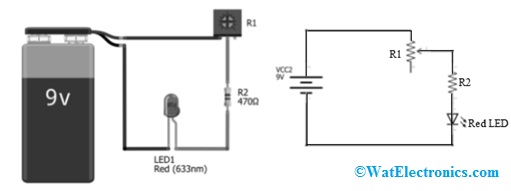
Simple LED Circuit with Variable Resistor
The required electronic components of this circuit mainly include a battery, variable resistor, backup resistor, and LED. The circuit connections can be done like the following by using these components.
In the above circuit, once we revolve the potentiometer to fewer resistance values, then extreme current will be supplied to the LED. So an additional resistor or backup resistor is used in series with the potentiometer to control the current flow toward LED. Generally, potentiometers range from 0Ω resistance to maximum,
For instance; a red color LED with a 9V battery and Vf =2V & a 9V battery. If the trimmer is set to 50 ohms, then we will have the flow of current I=7V/50Ω =140mA which is far beyond the 20 to 30mA threshold of the light-emitting diode. Similarly, if the potentiometer is set to 0ohms and the backup resistor is not used then the LED will blow.
Advantages
The advantages of a trimmer resistor include the following.
- The main advantage of these resistors is that they provide a high degree of precision.
- Small size & Highly customizable.
- The exact value of resistance can be achieved.
- High resistance tolerance values.
- The resistance value can be adjusted when the circuit is running.
- They can withstand high temperatures and have a long life expectancy.
- They do not require the use of special tools for adjustment, and the cost of trimmer resistors is low when compared with other adjustable resistor types.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of a trimmer resistor include the following.
- These are not suitable for high power applications, since the power rating is typically less than 1 watt.
- Adjustment should only be performed by trained personnel, since repeated adjustment may damage the resistor.
- In addition, there is no provision for locking the resistance once it has been adjusted.
- Another disadvantage is that they can only be adjusted by hand using a screwdriver, which may not be as convenient as using a panel control knob.
Trimmer Resistor Applications
The applications of trimmer resistors include the following.
- The most common type of trimmer resistor or Trimpot is the single-turn trimmer potentiometer. This is due to their small size and ease of use.
- Trimpots can be used to adjust the brightness of a light, volume control on audio equipment, or any other function where an adjustable electrical resistance is needed in a circuit.
- These are used as adjustable voltage dividers and are used in a variety of applications. One example is an electronic tuner for a television set. As the channel is changed, a signal generator sends a voltage to the tuner.
- Another application is in audio equipment such as stereo systems and radios. This resistor allows users to adjust the base or treble frequency so they can receive audio at their preferred tone.
- They are also used in medical equipment like dialysis machines, where they help provide precise measurements of liquid levels within the equipment.
- In radio-frequency (RF) applications, these are used to tune the resonant frequency of inductors and capacitors. They may also be used to adjust the gain or phase shift of amplifiers and oscillators.
- It can also be used to match impedances in transmission lines, such as those used in power supplies and cables.
Thus, this is all about an overview of the trimmer resistor. Sometimes, these are also called trimmer potentiometers, trim pots, or a kind of adjustable potentiometer or variable resistor. Generally, a tiny screw on the resistor is used to adjust the resistance. These components are calibrating devices, so their range of resistive is frequently very small & very precise settings can be obtained during adjustment. Here is a question for you, what is a rheostat?