In a computer network, the representation of data can be done through computers & telecommunication devices with the help of signals. The transmission of signals can be done in an electromagnetic energy form from one device to another device through the air, vacuum, and otherwise other transmission mediums. Electromagnetic energy includes voice, power, radio signals, light, gamma rays, UV light, etc. The data which is transmitted from one location to other is transmission media. In the OSI model, the first layer like the physical layer is dedicated to the transmission media which is a physical path among the sender & the receiver, used to transmit data from one place to another. This article discusses an overview of transmission media and its types.
What is Transmission Media in Computer Networks?
A communication channel that is used to carry the data in the form of bits from the sender to the receiver using LAN is known as Transmission media. Here, the transmission of data can be done using electromagnetic signals. In data communication, transmission media acts as a physical lane among transmitter & receiver. The form of bits varies based on the type of network like for copper-based network; the bits are in electrical signals form whereas, in a fiber network, the bits are in the light signals form.
Transmission Media
Transmission media can be classified into two types such as wired media & wireless media. The medium characteristics in wired media are essential whereas the signal characteristics are essential in wireless media. The properties of transmission media mainly vary based on the type of transmission media like delay, bandwidth, cost, maintenance, and simple installation. In the OSI model, the transmission media is available in the last layer which is called the physical layer.
Different Types of Transmission Media
Transmission media can be classified into two types wired and wireless which is also known as guided media and unguided media.
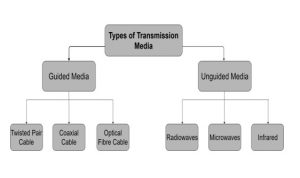
Types of Transmission Media
Guided/Wired Transmission Media
Wired transmission media is also called guided transmission media. In this type of media, the signal transmission can be done directly & restricted in a narrow path through physical links. The main features of this media are, very secured, high speed, and used for mainly short distances. Further, this type of media can be classified into five types which are discusses below.
Twisted Pair Cable
The most popular network cable that is used for data transmission is the twisted pair cable. These types of cables are lightweight, inexpensive, simple to install and support 100 Mbps data speed. This cable includes two conductor wires which are separately insulated where every pair of cables can be twisted together to make a single media. The main function of these two wires is, the first wire is used to carry the actual signal whereas the other wire is used as ground.
These two cables are color-coated so that cables can be easily identified. A twisted cable reduces the noise as well as cross-talk. These cables are used in telephone networks to provide voice & data transmission. Again, twisted pair cable is two types like unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP)
Unshielded Twisted Pair
In this type of cable, there is no metal foil or shield. As compared to STP, this cable is very common so, it is easily used in LANs & telephone connections. The main benefits of UTP are; less cost, simple installation, high speed, etc. The drawbacks are; as compared to STP, this has less performance, less capacity, transmission can be done up to a short distance because of attenuation.
Shielded Twisted Pair
This type of cable covers a special jacket to block exterior interference. STP is used in data, voice channels of telephone lines & in an Ethernet with fast-data-rate. The main benefits of STP as compared to UTP are, it gives better performance at a high data rate, cross talk can be eliminated, faster, etc. The disadvantages are expensive and bulky.
Coaxial Cable
The coaxial cable has an external plastic jacket with two parallel conductors where each conductor has an individual insulated protection cover. By using this cable, the data transmission can be done in two ways like baseband mode & broadband mode. These cables are widely used in analog TV networks, cable TVs, etc.
The main benefits of coaxial cable are; high bandwidth, noise immunity is better, low cost. The drawback of this cable is, the failure of a single cable can disturb the whole network.
Optical Fiber Cable
The concept used by the optical fiber cable is the reflection of light through a core that is made up of plastic or glass. The core can be covered with a less dense glass/plastic called the cladding. This cable is mainly used for transmitting large volumes of data. The OFC can be bidirectional or unidirectional where the wavelength division multiplexer (WDM) supports these two modes like unidirectional & bidirectional.
The advantages of optical fiber cable are lightweight; signal attenuation is less, high capacity & bandwidth, etc. The disadvantages are high cost, fragile, maintenance and installation is difficult.
Stripline
Stripline is a TEM (transverse electromagnetic) transmission line medium that was invented in the year 1950 by Robert M. Barrett from Air Force Cambridge Research Centre. It is the initial type of transmission line that works with a conducting material that is used to send high-frequency signals. This material can be sandwiched among two ground plane layers which are generally shorted to give EMI immunity.
Microstrip Line
In a microstrip line, the separation of conducting material can be done from the ground plane through a dielectric layer.
Unguided Transmission Media
Unguided transmission media is classified into three types which are discussed below.
Radiowaves
Radiowaves or EM waves are very easy to produce and they can easily penetrate throughout buildings. The wavelength of these waves ranges from 1mm and 10k kilometers whereas its frequencies range from 300 GHz to 30Hz. If the wavelength is 1 millimeter then the frequency will be 300 GHz. Similarly, if the wavelength is 10k kilometers then the frequency is 30Hz. Radio waves are mainly used for transmission in AM, FM radios & cordless phones.
Microwaves
Microwave is one kind of radio wave that has high frequencies which range from 300 Mhz to 300 GHz. In radio waves, the microwave is the subpart where the transmitting & receiving antennas must be connected properly through each other. The distance covered through the signal can be directly proportional to the antenna’s height. Microwaves are used in television distribution and mobile phone communication.
Infrared
In wireless transmission, IR signals are a part where these signals are used in the communication of extremely short distances. These waves cannot penetrate through obstacles and it prevents interference among systems. The frequency range of these waves ranges from 300GHz to 400THz. The applications of infrared waves mainly include a wireless mouse, TV remotes, printer, keyboard, etc.
Factors
For designing the transmission media, the following factors need to consider.
Bandwidth
Once the bandwidth of a transmission medium is high then the signal’s data transmission rate is also high.
Interference
Interference is the procedure to interrupt a signal once it travels on a communication medium by adding some unwanted signal.
Transmission Impairment
When the transmitted signal is not equal to the received signal because of the transmission impairment, then the signal quality will be destroyed. Transmission impairment can be caused due to attenuation, distortion, and noise.
Attenuation is the loss of energy that means the signal’s strength can be decreased by increasing the distance which can cause energy loss.
Distortion can occur once there is a change within the signal outline. This kind of distortion can be examined from various signals which have different frequencies. Every frequency component includes its own propagation speed, thus they arrive at a different time so they can cause a delay in distortion.
Noise
Once data is traveled on a transmission medium, then some unwanted signal can be included toward it which makes the noise.
Please refer to this link to know more about Transmission Media MCQs
Characteristics
The transmission media characteristics include the following.
|
Type of Media |
Performance |
Bandwidth |
|
Fiber Cable |
Performance rate is from 10–11 to 10–13 |
75THz |
|
Microwave |
Performance rate is 10–9 |
100GHz |
|
Coaxial |
Performance rate is from 10–7 to 10–9 |
1GHz |
|
Satellite |
Performance rate is ranges 10–9 |
100GHz |
| Twisted Pair | Performance rate is 10–5 |
1MHz |
Thus, this is all about an overview of transmission media and its types. In data communication, transmission media is a physical pathway that carries the information from the transmitter to the receiver and connects computers, other devices, etc. Generally, the transmission of data can be done using cables otherwise waves through electric signals or electromagnetic signals. Each transmission medium uses particular network hardware which is well-matched with that medium. In the OSI model, transmission media work at Layer-1 and they include the physical unit to describe the kinds of highways on which data & voice can travel. Here is a question for you, what are the examples of transmission media?