The electric name of Silicon controlled or the semiconductor controlled rectifier (SCR) is Thyristor. These are the four-layered semiconductor devices where three terminals are known as the anode, the cathode, and the gate. Based on the triggering applied at the gate the device can be treated as a switch or used as a rectifier. These SCRs are unfit for amplifications. SCRs are responsible for conducting the flow of current in a single direction. Hence it is also a unidirectional device. It … [Read more...]
Rectifier Diode : Circuit, Biasing and Its Applications
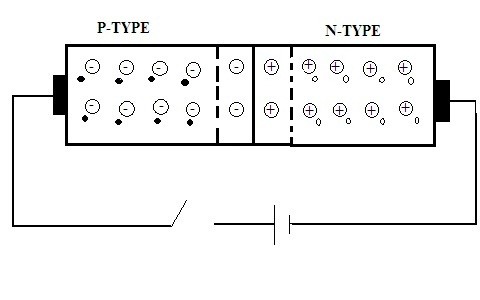
A basic semiconductor, in that there is the presence of two terminals in which one is preferred as a cathode and the other as an anode. It is formed by the two different materials referred to as p-type and n-type. Generally, it is termed as p-n junction diode. As it is application-oriented it is also referred to as rectifier diode. The main purpose of this p-n junction diode is that it is used for the conversion of the applied alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). This process of … [Read more...]
Ripple Factor for Half Wave and Full Wave Rectifiers
As already known the purpose of the rectifier is to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). It is the basic unit of any DC supply. The designing of the rectifier and its suitability for practical applications is dependent on the characteristics of that particular rectifier. Its characteristics include RMS value, average output value, ripple factor, peak inverse value and so on. After the completion of the process of rectification, the output DC generated consists of some AC … [Read more...]
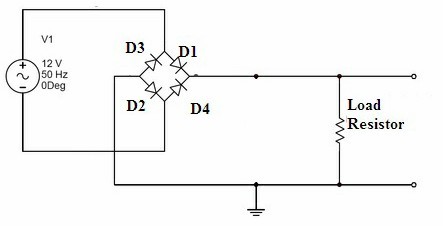
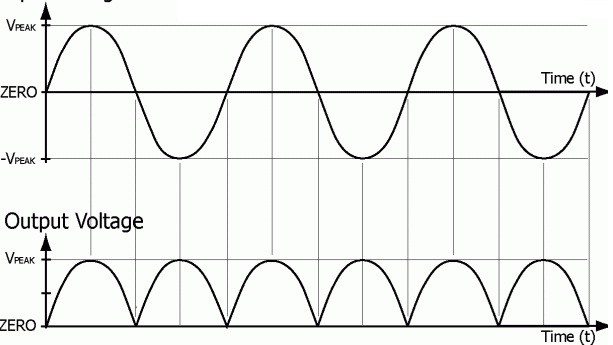
Full Wave Rectifier Working and Its Applications
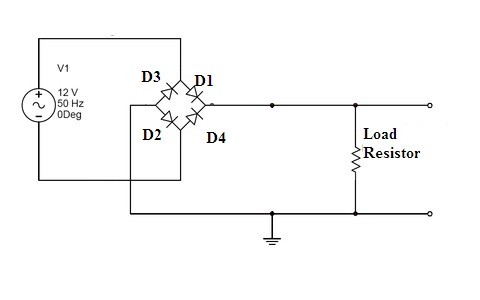
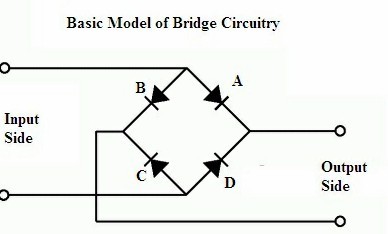
The purpose of the rectifier is to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). As in the half-wave rectifier, the rectifier output DC consists of AC components or ripples in it. To overcome this filter can be connected across the load so that the ripples can be reduced but this kind of circuitry is suitable for low power required applications. To overcome the problem of the half-wave rectifier, the model of the full-wave rectifier circuit is developed. In full-wave rectifier, full … [Read more...]
Half Wave Rectifier : Working and Its Characteristics
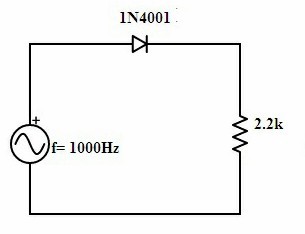
The purpose of the rectifier is to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) that is to undergo rectification. As the diode used in this process allows the flow of current in a unidirectional manner. Basing on this property of the diode the various types of rectifiers are designed. From the number of diodes used in the circuit the classification of rectifiers is done. Basically, the half-wave rectifier can be designed by using a single diode termed as single-phase rectifier. But if … [Read more...]
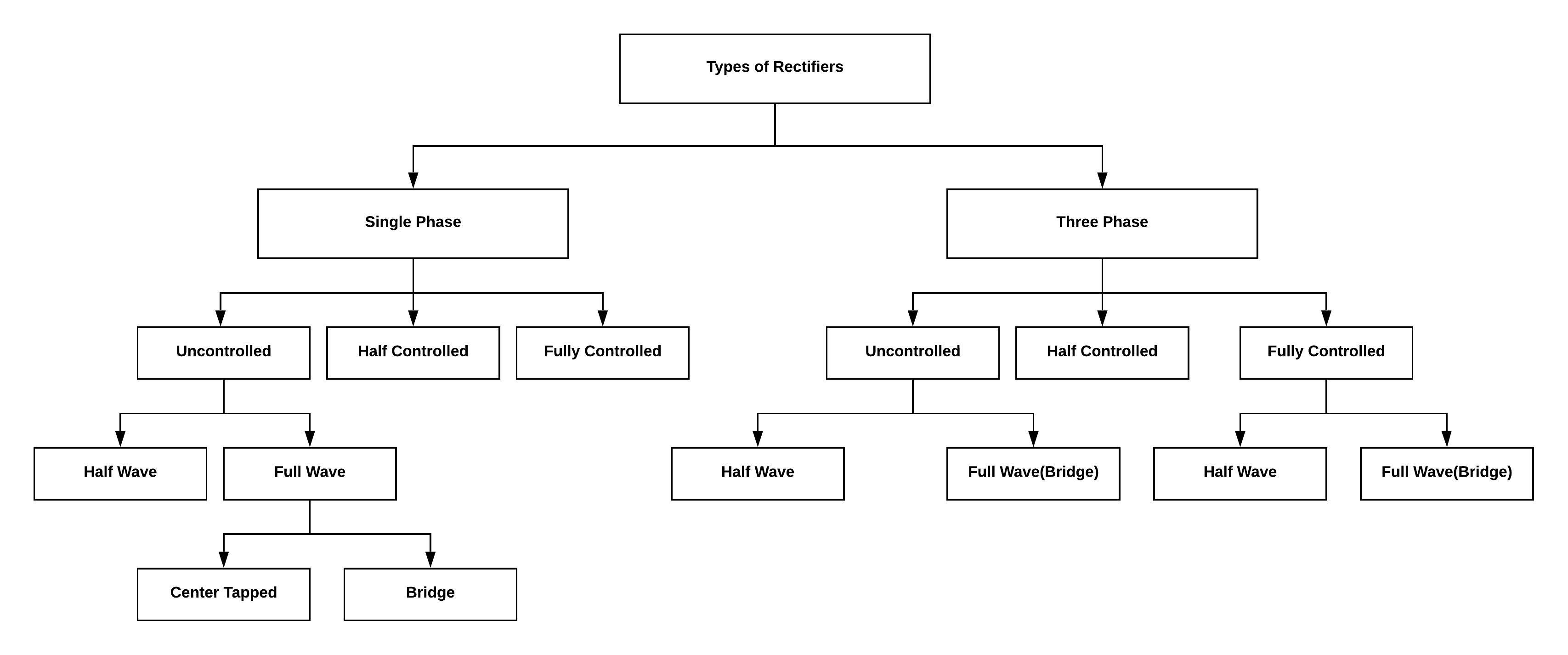
Different Types of Rectifiers & their Working Compared
The basic p-n junction diode that is used for the conversion of AC to DC can be referred to as a rectifier. This process is known as rectification. Based on its efficiency of converting AC to DC these rectifiers are chosen so that it can satisfy the essential requirements of the power supply unit in the electronic systems. Various basic electrical or electronic components are preferred in order to design rectifiers it can be diodes, MOSFET’S, etc. Considering the suitable application essential … [Read more...]
What is a Rectifier : Working and Its Applications
A basic diode has various applications it includes rectifiers in it as well. Rectification can be done through the basic diode. It may be current or voltage the AC values will be converted into DC. The basic property of the diode is that it can establish the path for the flow of current in one direction that is possible during forwarding bias. However, during reverse bias, the diode remains in non-conducting mode. It doesn't participate for the establishment of the path for the flow of current. … [Read more...]
Center Tapped Full Wave Rectifier Circuit, Working, Equations
A Rectifier is said to be center tapped if it can rectify both the positive and the negative halves of the cycle. By using a transformer with a presence of wire at the secondary winding it makes the transformer center tapped. This is the reason it is termed as a Center Tapped Full Wave Rectifier. The reason behind using this type of transformer is that it can utilize both halves of the cycle by connecting two diodes respectively. Compare to half-wave rectifier center tapped full wave has … [Read more...]