There are many topologies available in networking like star topology, bus topology, tree topology, and others where each type of topology has its own advantages and disadvantages. In the domain of networking, topology refers to the layout of connected devices and network topology corresponds to the layout of various nodes, connecting lines, and nodes.
There are mainly two approaches of specifying networks which are logical and physical topologies. Logical topology defines data transmission in the network in contrast to the design whereas physical topology corresponds to the way where a network is laid. Apart from these, Today, this article explains a star topology, its definition, how it works, its uses, and its drawbacks.
What is Star Topology?
The definition of star topology is defined as the networking topology where the components are connected through separate cables to a central section which is generally called HUB. There is no directions between the devices and because of this, there will be no traffic congestion in this topology.
Here, the controller functions as an exchange which means that when a device needs to have communication with other devices, the transmitting device sends information to the controller, and then it transfers the data to receiving device.
In the star topology, each device requires only one link and input-output port to connect to many others. In this, the hub/switch is even termed as server and the nodes that have a connection with the hub are called clients.
The star topology diagram is shown below:
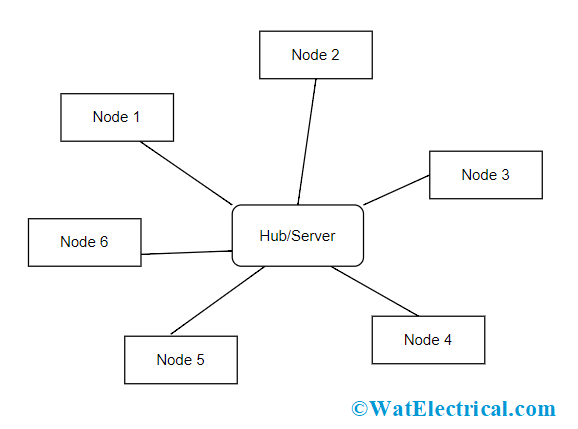
Star Topology Diagram
The nodes in a star topology are termed as hosts and the cables which are used for the connection can be optical/twisted fibers, coaxial cables, or RJ-45 connectors. The central device called a hub/switch holds the responsibility of traffic regulation in the network.
Here, the network performance is based on the ability of the hub. When the hub/switch does not have the capability of handling multiple nodes, then there should not be any addition of new nodes.
The network topology is termed STAR because the physical arrangement of nodes and hubs represents star shape. The central hub used in the star topology can be of four kinds which are of:
- Hub/Repeater
- Router/Gateway
- Computer
- Switch/Bridge
When any host device needs to transfer information to another host, then the information is initially transmitted to a central hub and from there it is transmitted to the receiver host. As discussed, the central hub can be a computer also where it operates as a server.
Every node in this topology holds a specific address which helps in the transmission and reception of the message in the network. For example: when the switch acts as a server, then it used for storing entire addresses of nodes that are connected to it. When any specific node requires to send data, then the switch understands which node has to transmit data because it holds the addresses of all nodes.
Whereas, when the hub acts as a server, then it does not have the capacity to store addresses. In that case, the hub transmits messages to all the nodes in the network and the receival device identifies the corresponding address of the transmission node and receives the information.
When there is the failure of any one of the nodes in the network, then it does not show an impact on other nodes whereas when there is a failure in the central hub, then the total network stops working.
Resetting of Hub
When no one of the star topology networks has access to network resources, then the hub is considered as either failed or overloaded. In this case, resetting the hub is to be done by pressing the reset switch.
When resetting has to be done often, then there might be the chances of hardware components failure or extended limit of network bandwidth. So, the corresponding action is to be performed based on the failure activity.
Differences between Bus and Star Topology
The major difference to be considered between the star and bus topologies are explained in below tabular column.
| Star Network Topology | Bus Network Topology |
| Here, all the network devices are connected to the central hub/switch | In the bus topology, every device has a connection with a specific cable which acts as a backbone for the network |
| Failure of central hub leads to failure of the entire network | Failure of network cable leads to failure of the entire network |
| There are no terminators in the star topology | There are terminators at both the ends of the network |
| Depending on the ability of the central hub, network performance and huge traffic are managed | Huge traffic in bus topology cannot be efficiently managed where it shows the impact on the network performance |
| In this, data transmission is speed when compared with bus topology | When compared with a star topology, the data transmission is slower |
| This network connection requires high cost because of the central hub and additional wires those are used for connection | This network connection maintenance and pricing is less |
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of star topology are explained as below:
- High reliability – Failure of one node does not show impact on other nodes and the other part of the network works perfectly. So, this topology shows high reliability
- User approachable – Here, the addition and removal of nodes can be added to the network without influencing the rest of the network. So, replacing nodes seems to be simple and easily manageable
- Extended topology – The length of the star network topology can be extended by adding multiple stars to the server. Whereas the network should have the ability to provide power for all the activities in the network
- Enhanced efficiency – As every device is connected to the server/hub using the cable, the probability of data collisions is very less. This also corresponds that performance is higher when compared with other network topologies.
- Safe to make use of – When there is any NIC failure or cut cable, it shows impact only on one node. So, the approach to disconnect all the devices is to disable the central core. As the central component is not easily accessible for everyone, so it is the safest network topology.
The disadvantages of star topology are:
- Higher cost – Usage of switch/router in the topology incurs high cost
- Increased maintenance – Installation of hub needs frequent maintenance as this is the central part of the system
- Immobile – Even there are wireless topology connections, mostly wired connections are used. This corresponds that constant cable length constricts the movements of individual persons. So, this reduces the productivity
- Minimal data transmission rates – When huge loads are to be managed by this topology, then a wired network connection performs well. And the wireless connection has slower movement which shows the risk of bottlenecks
- More damage exposure – The wires and cables that are used in the star topology create high potential damage disclosure.
Please refer to this link to know more about Bus Topology MCQs & star topology MCQs
1). Which is an example of a star topology?
The main example of star topology is an ethernet network
2). Where are star topologies used?
Star topologies are mainly used in home networks which are usually wireless connections, and the other examples are in educational institutions and in businesses.
3). What type of cable is used in star topology?
In the star topology network, coaxial cable or RJ-45 is used. It is completely based on the kind of network card that is installed on every computer.
4). What are the features of a star topology?
The crucial features of star topology are:
- All the devices are connected to the central hub
- Easy installation
- No disruption happens when adding or removal of cables takes place
- Failure of a single node has no effect on the entire network
This is all about the concept of star topology. This article has explained on star topology definition, its diagram, resetting of the hub, advantages, and disadvantages. Know, how star topology is used in video routers?