An amplifier is a device used to amplify the power of the output signal, although with some additional noise whereas a preamplifier is a device used to change a weak electrical signal into a noise-tolerant clear output signal. These two amplifiers utilize voltage to enhance the power of sound signals, and although they perform it in different ways & they have different functions. When preamplifiers are normally used to increase the microphone recordings level without increasing its noise floor significantly whereas amplifiers are utilized to boost sounds that are audible already such as; speakers & electric guitars. This article discusses an overview of a preamplifier – working with applications.
What is Preamplifier?
A preamplifier or preamp is an electronic amplifier used to change a weak electrical signal to a strong electrical signal which is strong enough to send it to a power amplifier as well as a loudspeaker. These are normally used to amplify the signals from analog sensors like microphones. So, this amplifier is located frequently to the sensor very closely to decrease the noise effects & interference.

Preamplifier
An ideal preamplifier will be linear and it has high input impedance & low output impedance. So this amplifier is mainly used for boosting the signal’s strength to make the cable without degrading the SNR( signal to noise ratio) significantly to the main instrument. A preamplifier generally follows low-level output transducers like microphones, recorder-reproducer heads & hearing-aid pickup devices. The main preamplifier characteristics are the noise factor, the I/O impedances & the necessary frequency response.
Functions of Preamp
The functions of a preamplifier include the following.
- The pre-amplifier is used to perform two main functions in home theatre systems; it handles switching between different line-level sources & increases the signal before transmitting it to the amplifier. And very weak electrical signal turns into a strong signal for extra processing and prevents noise & offers cleaner output.
- The main function of a preamplifier is to remove the signal from the detector without corrupting the intrinsic S/N signal to noise ratio. So, this amplifier is placed near the detector.
- This amplifier prepares the audio signal to avoid overload within the amplifier & other components within an audio system.
- Sometimes, this amplifier has tone controls where these controls are used for adjusting the treble and the bass frequencies once they need to be boosted.
- This amplifier increases a weak excitation signal’s strength.
- The preamplifier removes distortion, and noise and amplifies raw electronic signals which come from transducers, analog sensors, etc.
- The preamplifier first removes the noise and interference from electronic signals and after that, it amplifies those signals.
How to Build a Preamplifier?
Generally, a preamplifier circuit pre-amplifies extremely small signals to some particular range that can be amplified further through an attached power amplifier circuit. So basically it works like a buffer stage between a power amplifier & the input small signal source. This amplifier is used mainly in applications wherever the input signal is very small & a power amplifier is not capable to notice this small signal without a preamplifier stage.
A preamplifier design is very simple by using two transistors as well as some resistors as shown below. The required components to design a preamplifier are; resistors like R1-22K, R2-220Ohms, R3-100K, R4-4K7, R5-1K, capacitors like C1-1uF/25V, C2-10uF/25V and two BC547 transistors as T1 & T2.
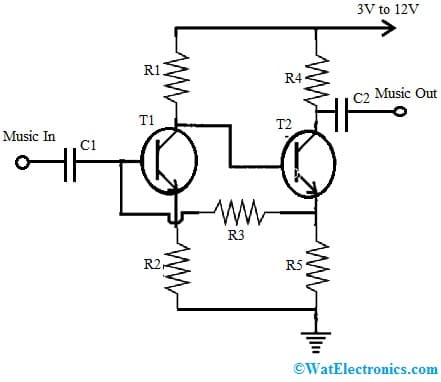
Preamplifier Circuit
The above preamplifier circuit is very simple to design with two transistors through a feedback loop to improve the amplification.
We know that any music is in the form of consistently changing frequency, so when that changing input is given across the specified C1 end terminals then the same signal is generated across the T1 transistor and GND. Generally, the high amplitudes are normally processed & regenerated by a potential that is approximately equivalent to the voltage supply. But for the low misc amplitudes, the second transistor ‘T2’ is simply allowed to perform at the high ratio which is allowable for supplying to its emitter terminal.
At the moment, once the actual improvement of the music is executed by transmitting this accumulated high potential back to the T1 transistor’s base terminal that equally saturates at a much optimal speed. So ultimately this push-pull act will result in an overall amplification of slightly small music otherwise input data into a larger output significantly.
This simple preamplifier circuit simply allows the user to boost very small otherwise least frequencies to noticeably higher outputs which can be next utilized for feeding big amplifiers.
Actually, this circuit was commonly used in old cassette-type playback recorders within their preamp stages to boost the small signals from the tape head, thus this small amplifier’s output will become well-matched for the connected high-power amplifier.
Types of Preamplifier
There are different types of preamplifiers; current sensitive, parasitic capacitance & charge sensitive which are discussed below.
Current Sensitive Preamplifier
This type of amplifier uses transistors for amplifying the audio signal’s current. The handling of these signals is quick although they have some problems with impedance. These amplifiers are not effective at low frequencies.
These amplifiers are often found within old vacuum tube amplifiers. The sound generated by this amplifier is not natural because of the distortion it can generate. These amplifiers are extensively used in front-end electronics within data acquisition systems because of their capability to directly amplify signals. The energy resolution optimization needs these amplifiers with appropriate parameters like low noise, bandwidth, gain, etc.

Current Sensitive
Parasitic Capacitance Preamplifier
The parasitic capacitance type preamplifier uses vacuum tubes and these amplifiers are very effective at less frequency. Although, these are very slow as compared to current sensitive type preamplifiers. These types of preamplifiers are often utilized within home audio devices. These amplifiers have a natural sound that is musical & warm however they are expensive compared to other types of preamplifiers.
Parasitic-capacitance preamplifier has high input impedance. Thus, the generated current pulse through the detector is incorporated into the merged parasitic capacitance available at the output of the detector & the preamplifier input. So this combined capacitance normally ranges from 10 to 50 pF.

Parasitic Capacitance
These amplifiers are not utilized with semiconductor detectors because the gain of this amplifier is sensitive to little changes within the parasitic capacitance. Parasitic capacitance preamplifiers like the ORTEC Model 113 provide good performance through photomultiplier tubes, scintillation detectors, or microchannel plate PMTs.
Charge Sensitive Preamplifier
Charge-sensitive preamplifiers utilized transistors for amplifying the audio signal’s voltage. These are very quick while handling signals but they have some problems by means of impedance. These types of amplifiers are very effective at low frequencies. The applications of charge-sensitive preamplifiers mainly involve audio equipment and home sound systems. These are costly & generate a normal sound. These types of amplifiers are mainly chosen for most energy spectroscopy-based applications.

Charge Sensitive Preamplifier
Amplifier Vs Preamplifier Vs Receiver
The difference between the amplifier, preamplifier and receiver are discussed below.
|
Amplifier |
Preamplifier |
Receiver |
| An amplifier helps in boosting the signal that can be played throughout speakers. | The preamplifier helps in boosting a microphone signal to a certain range throughout an amp. | A receiver helps in connecting input & output devices. |
| An amplifier contains up to seven channels | These are always found in AV receivers or integrated amps. | It includes an amplifier & preamplifier with other functionality. |
| Its cost is low to moderate. | Its cost is low. | Its cost is moderate to high. |
| An amplifier has one input & several outputs. | This amplifier has normally several inputs & only one output. | A receiver typically has a minimum of four or above HDMI inputs & minimum of one output. |
| An amplifier does not contain a set gain. | A preamplifier contains a fixed gain setting. | It has variable gain. |
| The amplifier has fixed or adjustable i/p impedance. | This amplifier has fixed input impedance. | The receiver input impedance is static. |
| The amplifier has tone controls like bass & treble. | The preamps don’t have tone controls. | The receiver allows a user to adjust the tone of the sound generated by an audio system. |
Importance of Preamplifier
Preamplifiers are very important due to many reasons like the following.
- The preamplifier has huge control over the sound quality which you get from the audio devices. So it is very significant to note that all these preamps are designed equally.
- Compared to low-quality preamps, high-quality preamps will generate better sound.
- This is the first amplifier within an audio chain. Once the signal is properly prepared then it will generate good-quality sound.
- This amplifier changes certain audio signal characteristics and it can also increase or decrease the volume before other components process it.
Advantages
The advantages of a preamplifier include the following.
- Preamplifiers have high bandwidth.
- The noise level of this amplifier is low.
- The dynamic range is high.
- They have high gain.
- Installation & troubleshooting are very easy.
- Low-voltage audio signals can be easily transformed.
- These are readily available.
- Less expensive.
- These are highly responsive.
- It provides a particular attitude or characteristic to your sound.
- It helps in boosting the microphone’s signal & also monitors audio on the fly.
- These amplifiers have high input impedance & low output impedance.
- They have stable gain & linear in nature.
- Generally, these are charge sensitive & current-sensitive within nature.
Drawbacks
The drawbacks of the preamplifier are discussed below.
- These amplifiers do not permit too much control
- They have a limited number of inputs & outputs.
- This amplifier is a critical component in gyro meter electronics
- It is heavier.
Applications
The uses or applications of preamplifiers include the following.
- The preamplifier is used to change a low-voltage, high-impedance signal into a high-voltage, low-impedance signal which is vulnerable to signal degradation.
- This preamplifier is used to amplify the electronic signals by enhancing the S/N ratios before the signals go into a cable important to an amplifier.
- These amplifiers are applicable where the input signal is very small & a power amplifier is not capable to identify this small signal exclusive of a preamplifier stage.
- A preamplifier is mainly used for high-fidelity audio which supports stereo channels & switches among inputs of audio like a CD player, digital media player& FM tuner.
- This amplifier provides RIAA equalization for the recording & playback of phonograph records.
- This is applicable in home theaters to support various audio channels.
- The preamplifier is utilized in any audio system for preparing the input audio signal for amplification in the next stage.
- These are used at the receiver end of the communication system to eliminate noise and interference from the obtaining signals.
- These are used with transducers, analog sensors like proximity sensors & microphones to increase their output.
- These are utilized in some devices like Equilizer Machines, Sound cards, DJ Mixers, etc.
Thus, this is all about an overview of the preamplifier (preamp) – types, working with applications. The main function of this amplifier is to remove the signal from the detector without degrading the intrinsic S/N ratio significantly. Here is a question for you, what is the function of an amplifier?