The Pentium processor was invented by the Intel Corporation in 1993 and it is a widely used in personal computer. This processor is also called Pentium 1, P5 otherwise Intel 80586, because it was the 5th generation of Intel microprocessors. The Pentium 1 is the first microprocessor in the Pentium series. The features of this Pentium1 processor mainly include; 32-bit processing, 16 KB – 32KB L1 cache, FSB (Fast serial bus) up to 66 MHz and base CLK speed ranges from 66HZ to 300MHZ. There are different Pentium microprocessors available in addition to the Pentium I like Pentium II, III, IV, M, and dual core. This article discusses an overview of a Pentium processor definition – working with applications.
What is a Pentium Processor?
The Pentium processor is an advanced 32-bit superscalar microprocessor from Intel’s Χ86 microprocessor family. This microprocessor includes approximately 3.1 million transistors, a 64-bit external data bus & also a 32-bit address bus that provides 4 GB of physical memory space. The highest clock rating provided by this microprocessor is approximately 60 – 233 MHz.
The Pentium processor list mainly includes; Intel Core, Pentium D, Pentium, Pentium 4, Celeron, Intel Core i3, Pentium III, Pentium II, Sandy Bridge, Intel Core 2, Pentium M, P6, Pentium Pro, i486, Intel 80286, Intel Core 2 Duo, Pentium 4-M, Silvermont, Wolfdale, Yonah, Dothan, and Pentium II OverDrive.

Intel Pentium Processor
The Pentium processor features mainly include the following.
- It is a superscalar processor.
- It has superscalar architecture.
- It has separate data & instruction caches.
- It has bus cycle pipelining & execution tracing.
- Its data bus is 64-bit.
- Internal parity checking.
- Dual processing support.
- Monitoring of performance.
- Dynamic branch prediction.
Pentium Processor Architecture
The Pentium processor architecture is shown below. This architecture includes various functional units like bus unit, paging unit, control ROM, prefetch buffer, Execution unit with 2- integer pipelines like U-pipe & V-pipe, code cache, data cache, instruction decode, branch target buffer, dual processing logic and advanced programmable interrupt controller.
The bus unit in this architecture transmits the control signal and fetches data & code from outside memory as well as I/O devices. The size of the external data bus is 64-bit through which burst read & burst write-back cycles can be attained. The page unit offers optional extensions of approximately 2 to 4 Mb page sizes.
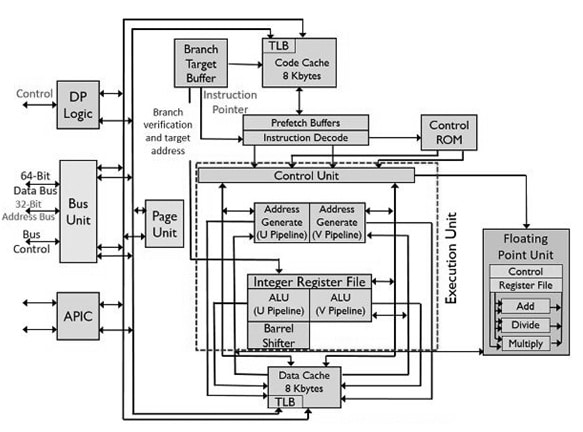
Pentium Processor Architecture
To load the instructions into the EU (execution unit), the branch target buffer code cache & pre-fetch buffers work mutually. The external memory/code cache simply holds the information from where these are obtained. Whenever the branch target buffer holds the particular branch address & the translational look aside buffer in the code cache changes the address from linear to the physical that is utilized by the cache of code.
The Pentium processor includes a set of pre-fetch buffers with a 32-byte size that function combined through branch target buffers. These buffers work independently however not all at once. When one of these buffers starts fetching the instructions in a sequential way the instruction of the time branch has not happened. But, when the branch instruction is obtained by the pre-fetch buffer, BTB will verify for the branch although once it is verified by BTB then that branch has not happened the instruction’s linear fetching will continue.
In contrast, when BTB tries to know about the branch occurrence then the additional pre-fetch buffer within the pair gets allowed & begins fetching the commands from the address of the branch target. So, the branching instructions will be fetched simultaneously and are prepared for decoding & execution.
In this processor, the execution unit includes two integer pipelines U-pipe & V-pipe where everyone includes its separate ALU. These pipelines work in five stages pre-fetch, decode1, decode2, execute and write back.
The U-pipe in the execution unit of this processor is mainly responsible for performing all the instructions like integer & floating-point whereas the V-pipe performs simple integer & some floating-point instructions.
The instruction fetch simply reads one instruction at a time & stores them within the instruction queue. In an instruction execution, this processor does not sit inactively & verifies for the further two instructions within the queue. If the two instructions are independent of each other then U-pipe & V-pipe integer pipelines are individually allocated instructions so that execution can simultaneously occur. But, the queued instructions depend on each other and are assigned to the U-pipe for execution continuously & V-pipe will remain idle.
The Pentium processor’s operations control is provided by the control ROM that has a microcode within it. The control ROM directly controls U-pipe and V-pipe. In the processor architecture, both the code and data cache is organized in two ways where every cache includes 128 sets & every set includes two lines that are 32 bytes wide. The Least Recently Used (LRU) mechanism handles the cache substitution.
In the above diagram, the code cache can make a connection by the pre-fetch buffer through a 256-bit size, therefore 32 bytes of op-code is buffered within a single CLK cycle. The data cache has two ports that are used to simultaneously deal with two data references.
The APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) chip in the architecture simply handles interrupts & provides 8259A compatibility. So, this is the basic model of the Pentium processor although, Intel released many superior processors that comprise superior features than Pentium. The different Pentium series mainly include Pentium Pro, P-II, P-III & P-IV processors.
Difference between Pentium and Pentium Pro Microprocessor
The difference between Pentium and Pentium Pro Microprocessors is discussed below.
| Pentium | Pentium Pro Microprocessor |
| The Pentium processor is normally used as a 5th-generation personal computer microprocessor invented by Intel Corporation in 1993. | The Pentium Pro processor is a 6th generation x86 silicon transistor developed by Intel in 1995. |
| This processor is represented by P5. | This processor is represented by P6. |
| This processor operates with 5V. | This processor operates at 3.1 V – 3.3 V |
| This was fabricated in a 0.8-micron BiCMOS technology. | This was fabricated in a μm BiCMOS process. |
| Pentium processor runs at 60 MHz/66 MHz. CLK frequency.
|
The clock speed of the Pentium-Pro processor runs at 150 MHz, 166 MHz, 180 MHz, or 200 MHz with a 60 MHz or 66 MHz external bus CLK. |
| This processor includes 3.1 million transistors. | Pentium-Pro includes 5.5 million transistors. |
| Pentium includes a 2×8 Kbyte L1 cache, although there is no L2 cache. | Pentium-Pro includes a 2×8 Kbyte L1 cache & a 256 Kbyte L2 cache. |
| The address bus of this processor is 32-bit. | The address bus of this processor is 36-bit. |
| This processor includes 2- instruction units. | This processor includes 6- instruction units. |
| This processor includes a superscalar pipeline, two independent integer pipelines & a floating point pipeline. | This processor includes the architecture of a 12-stage decoupled super pipeline that utilizes an instruction pool. |
Advantages & Disadvantages
The advantages of the Pentium processor include the following.
- This processor is a very good choice for a beginner in practicing programming.
- These are low-power and basic-level processors.
- These are more affordable.
- This processor’s CLK speed is higher.
- These are universal and efficient.
The disadvantages of the Pentium processor include the following.
- These processors are not suitable for gaming.
- Both the Silver & Gold sub-brands & their variations can be confusing.
Applications
The applications of the Pentium processor include the following.
- The Pentium from the Intel Corporation is a broadly used PC microprocessor.
- The Pentium devices are normally used for online use, collaboration & cloud computing.
- This processor perfectly works for tablets and Chrome books for providing strong and efficient online interaction performance.
- This processor is used in many CPUs.
- These are used in low-power embedded devices & low-end budget systems.
Thus, this is an overview of a Pentium processor – working with applications. The speed of this processor ranges from 60 MHz to 200 MHz. So this processor quickly became a recommended processor for personal computers. Here is a question for you what is a processor?