Generally, lighting systems operate with lighting control devices by switching on & off the lights. So there are thousands of lighting systems used in offices and commercial buildings but the operation cost of lighting systems is more so every year many organisations insure losses by paying to work on lighting systems even when there is no one in the office to work. To overcome this problem, the best solution is to adopt an automatic lighting control switch that controls the light by turning ON and OFF based on the person’s occupancy in the room using an occupancy sensor. These sensors are automatic switching devices that are used to detect human occupancy & control the lighting system accordingly. This article discusses an overview of an occupancy sensor – working with applications.
Occupancy Sensor Definition
An occupancy sensor is a motion-detecting device used to detect motion & identifies when a person enters a room so that it controls lights or ventilation systems or the temperature of the room. There are different occupancy sensing technologies, although the most frequently used technology is PIR, microwave, and ultrasonic. These sensors are very easy to use and operate so, by installing these sensors in your home or office, we can conserve energy, decrease maintenance costs & improves the efficiency of the home.

Occupancy Sensor
Occupancy Sensor Working Principle
The working principle of the occupancy sensor is to detect the presence of a person’s movement in its specified range. Once the motion is detected then this sensor sends the signal to the control unit. If there is no movement of a person detected after a specific time period set by the user, then the controller decides the space in the room is not occupied, so turns off the light in the room. From the occupancy sensor, the control unit will process the signals to increase/decrease power toward the light fixture. Signal repeaters are mounted if the signal has to be transmitted above 50 feet from the occupancy sensor to the controller.
Specifications
The occupancy sensor specifications are listed below.
- Power Supply 24 VDC/24 VAC.
- Maximum VA Load 0.72 VA @ 24 VDC, 0.88 VA @ 24 VAC.
- The nominal input voltage is 230V AC.
- The time delay is from 10 sec to 30 secs.
- The detection angle is 360 degrees.
- Operating temperature ranges from 32°F to 131°F.
- Consumption of power is 0.45W.
- The speed of detection is 0.5 to 1.6m/sec.
- Storage temperature ranges from -22 to 176°F.
- The effective coverage area is 1200 sq ft.
- The effective coverage radius is 22 feet.
- The material used for housing is ABS plastic.
- Weight is 200 grams.
- The height of the installation is up to 3 meters.
Occupancy Sensor Wiring Diagram
The occupancy sensor wiring diagram is shown below. The required components for this wiring mainly include an ODS10-ID wall switch PIR occupancy sensor, light as load, and connecting wires. The wiring connections of the occupancy sensor are shown in the following diagram.
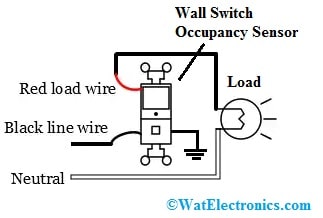
Wiring Diagram
The occupancy sensor switch has two black wires or one red & one black wire and green color ground wire. One of the black color line wires is connected to the line voltage using the panel whereas another red or black color load wire is connected to the light. Each black wire can be a line or a load. Red is always the load wire. An occupancy sensor requires a good GND connection to work properly.
The ODS10-ID occupancy sensor uses PIR detection technology to check a room for occupancy through a segmented Fresnel lens. This particular lens separates the visual field into sensor zones. Once a person moves in or out of a sensor region, then this sensor detects motion & turns ON the light. This light will remain ON if there is an occupant passes through the sensor regions
Occupancy Sensor Circuit Diagram
The occupancy sensor can be generally mounted on the ceiling. The circuit diagram of the occupancy sensor is shown below. The required components to build this circuit are ceiling mounted occupancy sensor, battery, light, and resistor. Connect the circuit as per the circuit given below.
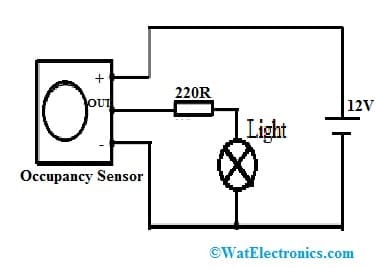
Occupancy Sensor Circuit Diagram
This occupancy sensor is ceiling mounted with PIR sensing capabilities. This sensor will turn on the light automatically to the set dimming level once the occupancy of a person is detected & turns off the light after a person moves away from the detection.
These sensors can easily detect motion within the room & control light automatically. If no motion of a person is detected after a set amount of time, then lights will be turned off. When a person occupies the room, the sensor detects the person’s motion, and the switch of the sensor is closed and turns on the lights.
This sensor works with 12 to 24VDC power. For good results, these sensors need to be installed within 30 feet distance from the target. These sensors are normally used in classrooms, homes, offices, etc.
Types of Occupancy Sensors
There are different types of occupancy sensors which are classified based on the detection of motion & the people’s presence in the room and the sensor technology it is used. There are different sensors as well as sensing technologies; however, the most common sensing technologies utilized in these sensors are PIR, microwave, ultrasonic & dual technology. Every technology has its own advantages and disadvantages and also each technology has specific techniques for the detection of motion.
PIR Sensors
PIR sensors or Passive infrared sensors are mainly used for detecting the infrared signals produced by people to inform whether they are in action or not. These sensors utilize two pyroelectric sensors, which are responsive to IR signals to identify the IR radiation within the surroundings.

PIR
Whenever a warm body like a person or any animal crosses the detecting area, then it first interrupts one slot and after that, the remaining slot of the sensor causes a positive differential change between the two infrared signals. These types of sensors observe this change as an indication of motion, thus they know the space is now occupied. Once the person from the room leaves, then the sensor knows that the room is unoccupied.
So, depending on how the sensor detects motion, it is more sensitive or less sensitive to people walking or moving away from the PIR sensor. This characteristic is very significant while installing & adjusting these sensors to acquire the best performance.
Please refer to this link to know more about PIR Sensor and its interfaces
Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors produce high-frequency-based sound waves to detect motion. The sound wave range is above the range of human hearing throughout a region. These sensors include transducers with a transmitter & a receiver.

Ultrasonic Sensor
The sound waves which are transmitted from the transmitter reflect objects within the area & reflect back to the receiver. If there is a change within the reflected sound wave frequency, then the change is known as a motion. So, by measuring the time between transmitting & receiving the sound wave, these sensors determine the main distance between the target & the sensor. This is an active sensor that continuously transmits and receives ultrasonic sound waves for detecting motion, so they need to use a sufficient amount of power to function the sensor.
Please refer to this link to know more about Ultrasonic Sensor and its interfaces.
Microwave Sensors
Microwave sensors produce low-power electromagnetic radiation & get the reflected microwave to detect motion. The microwave signal produced by the sensor reflects objects within the room & reflects back to the sensor’s receiver. If the microwave signal is changed within the reflected microwaves, then the change is known as motion.

Microwave Sensor
They can also inform whether the objective is moving to or away from the microwave sensor or randomly within the room by evaluating the waves so that they can also be arranged to notice different types of actions. Microwave signals can enter into the walls & holes due to more wide detection coverage for both inside & outside usage. These sensors are very flexible, so used almost in any environment.
Dual-Technology Sensors
Dual technology sensors merge ultrasonic & PIR sensing technologies to detect motion. These merged technologies will increase the overall reliability of sensors for high-sensitivity & complex applications.
In inactive mode, only the PIR sensor works to detect motion, whereas the ultrasonic sensor reduces energy consumption in sleep mode. Once the PIR sensor notices a motion, the ultrasonic sensor wakes up to confirm the same motion. Whenever both sensors detect the same motion the dual-technology sensor will be activated.

Dual-Technology Sensor
As long as either ultrasonic/PIR sensor detects motion continuously, then the dual-tech sensor will be kept activated. Once these two sensors cannot detect the motion, then the dual-tech sensor will think that room is empty. So this dual technology design can reduce the chance of false-off. These sensors are also self-adaptive to change automatically sensitivity & timing.
Occupancy Sensor Vs Motion Sensor
The difference between the occupancy sensor and the motion sensor is discussed below.
| Occupancy Sensor | Motion Sensor |
| An occupancy sensor is a sensor used to detect the movement of people and also detect if they are not moving around. | The motion sensor is a sensor that is used to detect the motion of a person.
|
| These sensors don’t need significant motion to work. | These sensors need significant motion to work. |
| The detection range of the occupancy sensor is up to 35 feet in particular directions within ideal conditions. | The motion sensor detection range is up to 80 feet.
|
| Sometimes, an occupancy sensor is also known as a presence sensor/vacancy sensor. | The motion sensor is also known as a motion detector. |
| The technology used in the occupancy sensor is IR, microwave, and ultrasonic. | The technology used in motion sensors is ultrasonic sensor technology. |
| These sensors are expensive. | Compared to occupancy sensors, these sensors are not expensive. |
Benefits of Occupancy Sensors
The advantages of the occupancy sensor include the following.
- These sensors automatically turn off the lights within unoccupied spaces.
- These sensors reduce energy costs.
- These sensors reduce light pollution by turning ON/OFF lights indoors and outdoors.
- This sensor data help you in understanding exactly how occupants utilize your building, verify underutilized spaces, and also capture the occupant’s flow throughout a space.
- Occupancy sensor data assists you in creating the best working conditions for your workers by simply providing insights into how employees interact through the space you give them. So this will help your business stay flexible & also easily adjust once new challenges occur.
Drawbacks
The drawbacks of occupancy sensors include the following.
- If there are a few occupants only in a region, then this sensor will need to activate the sensor periodically by moving in the detection region.
- There is a chance that the lifespan of luminaries can be reduced because of the switching frequency.
- These sensors are expensive.
- If you want to switch on or off the lights you have to activate them manually and leave the room.
Applications
The applications of occupancy sensors include the following.
- The occupancy sensor data provides valuable information about how efficiently using available space and how your building operates.
- Advanced occupancy sensors gather data on the correct number of persons in a room and how long a space is engaged.
- The uses of these sensors are; lighting and climate control in commercial settings by automatically turning off the light and adjust the temperature settings within the HVAC system.
Know more about Door Sensor.
Thus, this is an overview of an occupancy sensor – working with applications. So, connecting a light system through an occupancy sensor is an easy solution to reduce the usage of lighting energy. Once this sensor detects an individual in the room then the load will be active whereas the load will deactivate once an individual exists from the room. Here is a question for you, the technology used in the occupancy sensor is?