A protocol can be defined as a set of rules in a computer network used to process and format the data. For computers, these protocols work like a common language which may use very different hardware as well as software to allow them to converse with each other. The communication between two computers can be done only if they use IP (Internet Protocol).
But if any one of the computers uses internet protocol then they will be incapable to converse. There are different types of protocols available on the internet which are used for different purposes. This article discusses an overview of Network Protocol and its working.
What is a Network Protocol?
Network protocols are nothing but a set of rules, data structures & conventions which are used to determine how devices exchange data in the same network. These protocols allow two different devices to converse with each other apart from any dissimilarities in their inside processes, design, or structure.
In present digital communications, network protocols play a key role, and also these are the main reason that we can converse easily with people in the world. Communication between two devices can be possible with these protocols because of the inbuilt preprogrammed rules into the hardware and software of devices.
Network Protocol Working
Before understanding the concept of network protocols, we have to know the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model first. The model of Open Systems Interconnection splits the process of communication among two network devices into seven layers. In the 7 layers in an OSI model, a task can be assigned to each layer where seven layers are independent, so each task can be independently executed.
In an OSI model, seven network layers are separated into two groups namely upper layers like 7, 6 & 5 whereas lower layers like 4, 3, 2, & 1. Here, the upper layers mainly deal with the issues of application whereas the lower layers mainly deal with the issues of data transport.
In every layer of the OSI model, the functioning of network protocols is discussed below.
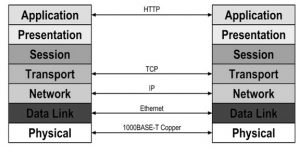
Network Protocols in OSI
Layer 7 (Application Layer Network Protocols)
This is the human and computer interaction layer where the network services can be accessed by the applications.
Layer 6 (Presentation Layer Network Protocols)
This layer ensures that the format of data is usable or not and where encryption of data occurs
Layer 5 (Session Layer Network Protocols)
This layer handles connections and it controls sessions as well as ports
Layer 4 (Transport Layer Network Protocols)
This layer sends the data through transmission protocols like UDP & TCP
Layer 3 (Network Layer Protocols)
This layer will decide to take the physical lane by the data
Layer 2 (Data Link Layer Network Protocols)
This layer will define the data format over the network
Layer 1: (Physical Layer Network Protocols)
This layer sends a raw bitstream on the physical medium
The functions of networking are possible through protocols. For instance, the (IP) is responsible for routing the data by representing data packets source and destination. Internet protocol will make communication possible in network-to-network. So, this protocol is considered a layer 3 or network layer protocol.
TCP or Transmission Control Protocol ensures that the moving of data packets across networks transmits effortlessly. So, TCP is considered as a layer 4 or transport layer protocol. A packet is a tiny part of data where all data that can be transmitted on a network can be separated into packets.
Network Protocols List
There are several network protocols that perform the following three main actions. Each type is essential to utilize network devices quickly and securely.
- Communication
- Network management
- Security
Communication
These protocols are responsible to allow a variety of network devices to interact with each other. The applications of communication protocols mainly include both analog & digital communications for different purposes like transferring files among different devices for internet access. Communication protocols are classified into different types like
- Automation
- Internet Protocol
- Instant messaging
- File Transfer
- Routing
- Bluetooth
Network Management
Network management protocols define the different methods required to operate a computer network effectively. These types of protocols will affect several devices over a single network like servers, routers & computers to make sure each one executes optimally. The main functions of these protocols mainly include
- Connection
- Aggregation of Link
- Troubleshooting
Security
Security protocols or cryptographic protocols mainly work to make sure that the computer network & the data transmitted over it are secured from illegal users. The main functions of security network protocols are;
- Encryption
- Entity Authentication
- Transportation
Network Protocol Example
Network protocols can be identified while using some electronic devices. The most commonly used network protocol examples are listed below.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
HTTP is an Internet Protocol that defines how data can be transmitted on the internet & decides how browsers, as well as web servers, must react to commands. This kind of protocol comes into view at the opening of URLs.
SSH (Secure Socket Shell)
This SSH protocol gives safe access to a PC, even it is using an unsafe network. This protocol is used mainly by network administrators who require handling various systems distantly.
SMS (Short Message Service)
This type of protocol was formed to transmit & receive text messages on cellular networks. This kind of protocol refers completely to messages based on text. For videos and pictures, we need MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service).
Types of Network Protocol
Network protocols used by different network layers are discussed below.
Network Protocols in Application Layer
The network protocols used in the application layer mainly include DHCP, DNS, FTP, IMAP, HTTP, POP, SMTP, Telnet & SNMP.
DHCP
The communication protocol like DHCP stands for “Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol” which allows the network administrators to computerize the task of internet protocol addresses within a network
In an internet protocol network, each device connecting to the internet needs an exclusive IP.
A protocol like DHCP allows the admins of the network to distribute addresses of IP from a middle point & routinely send the latest IP address once a device is connected from different locations within the network. This kind of protocol functions on a client-server model.
DNS
The DNS or Domain Name System Protocol is used to assist in mapping or changing hostnames toward IP addresses. This kind of protocol mainly works on a client-server model and uses a distributed database over a hierarchy of name servers.
Hosts are identified based on their IP addresses, but memorizing an IP address is difficult due to its complexity. IPs are also dynamic, making it all the more necessary to map domain names to IP addresses. DNS helps in resolving this issue by converting the domain names of websites into numerical IP addresses.
FTP
The File Transfer Protocol or FTP allows file sharing among remote & local hosts which works on top of transmission control protocol. This kind of protocol mainly creates two TCP connections namely data and control. The data connection is used for transferring the real file whereas the control connection transfers control information such as instructions, secret codes, etc. While transferring the entire file, these connections will work parallel.
IMAP – Version4
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) is an e-mail protocol that allows end-users to access & control messages which are stored on a server.
IMAP protocol tracks a client-server model to allow access messages of different clients on a general mail server concurrently. This type of protocol comprises different operations for deleting, renaming mailboxes & creating; verifying for latest messages; deleting messages permanently; flag setting and removing, etc. The present IMAP version is 4 revisions 1.
POP – Version3
The POP or Post Office Protocol is also one kind of email protocol. This protocol is used to download emails by the end-user from the e-mail server to their own email client. When the e-mails are downloaded then they can be examined without an internet connection. In addition, when the e-mails are moved nearby, then they can be removed from the server. This protocol is not designed to execute wide manipulations through the messages on the server, not like IMAP4. The new version of this POP is 3.
SMTP
SMTP or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is mainly designed for transmitting e-mail consistently as well as efficiently. This kind of protocol is used to send the e-mail, while other protocols like IMAP & POP are used for retrieving e-mails on the side of the end-user.
This protocol plays a major role in transmitting and notifying incoming e-mails in between systems. By using this protocol, a client can send an e-mail to a new client on a similar network through a relay otherwise gateway entrée that is accessible to both networks.
Telnet
An application layer protocol like Telnet or Terminal emulation allows a user to converse with an isolated device. The installation of a Telnet client can be done on the user’s machine. It allows the interface of a command line of one more remote machine to run a Telnet server program.
Telnet protocol is typically used through network administrators for accessing & managing remote devices. A remote device can be accessed by entering the IP address otherwise remote device’s hostname by a network admin.
SNMP
SNMP or Simple Network Management Protocol is an application layer protocol. The main function of this protocol is to handle different nodes such as workstations, routers, servers, switches on an internet protocol network. This kind of protocol enables the administrators of the network to observe the performance of a network, recognize network faults & troubleshoot them. This protocol includes three components namely an SNMP agent, a managed device & an SNMP manager.
The agent of SNMP can be located on the managed device. Here, the agent is nothing but a software module that includes the information of management & decodes that information into other forms that are well-suited through the manager of SNMP. This manager presents the obtained information from the agent of SNMP, administrators of helping the network to handle nodes efficiently.
At present, different SNMP versions are available like SNMP v1, v2 & v3. The first two versions include some common features, except version 2 gives extra protocol operations. This version 3 provides safety & remote configuration capacities to the earlier versions.
Presentation Layer Network Protocol
The network protocol used in the presentation layer in the OSI model is LPP or Lightweight Presentation Protocol. This type of protocol provides support for OSI application services within networks. LPP is mainly designed for a specific class of OSI applications which includes simply an ACSE (Association Control Service Element) & a ROSE (Remote Operations Service Element).
This protocol is not applicable to an individual whose application context is wider that is, it includes a Reliable Transfer Service Element.
Session Layer Network Protocol
The network protocol used in the session layer in the OSI model is RPC or Remote Procedure Call Protocol. This kind of protocol requests a service from a program within a remote computer using a network that is used without understanding the basic network technologies.
RPC protocol employs UDP or TCP for holding the messages among communicating programs. This kind of protocol also performs on the client-server model where the client is the requesting program & the server is the program for providing service.
Transport Layer Network Protocols
The network protocol used in the transport layer in the OSI model is TCP & UDP
TCP
TCP or Transmission Control Protocol is used in a transport layer to provide a consistent flow delivery as well as fundamental connection service to different applications by using sequenced acknowledgment. This protocol is connection based but before transmitting data, it needs a connection in-between applications.
This protocol provides wide error checking through flow controlling & acknowledgment of data. In this protocol, the packets of data can arrive in sequence at the end of the receiver. By using this protocol, retransmission of data packets that are lost can also be possible.
UDP
UDP or User Datagram Protocol is a connectionless protocol in the transport layer that offers a simple message service. As compared to TCP, this protocol includes flow control, no reliability otherwise functions of error recovery.
This is suitable in conditions where the reliability mechanisms of transmission control protocol are not required. So, there is not a possibility for lost data packets retransmission.
Network Layer Protocols
The protocols used in the network layer are IP, IPv6 & ICMP
IP
The Internet Protocol or IP is used in the network layer that includes the data of control and addressing. This data is very helpful in packet routing within a network. This protocol functions in the cycle through TCP to transmit data packets across the computer network.
Beneath this protocol, every host is allocated with a 32-bit address including two main parts like the host and the network number. Here, the network number recognizes a network that is allocated through the internet, whereas the host number recognizes a host on top of the network that is assigned through an admin of the network. This protocol is accountable for transmitting the data packets & the TCP assists in placing them back in the correct order.
IPv6
IPv6 or Internet Protocol version 6 is the new version of the network layer protocol. The main function of this protocol is to possess addressing as well as control data for allowing packets to be routed within the network. This kind of protocol was created to interact with IPv4. It enhances the size of the IP addresses from 32 – 128 bits for supporting high addressing levels.
ICMP
ICMP stands for Internet Control Message Protocol which supports through different network devices for transmitting error messages as well as operational data.
ICMP messages which are transmitted within IP data packets are mainly utilized for out-of-band messages associated with the operation of the network. This kind of protocol is used to declare network faults, blocking & helps in troubleshooting.
Data Link Layer Network Protocols
The network protocols used in the data link layer are ARP & SLIP.
ARP
The ARP or Address Resolution Protocol is used to assist from map the addresses of internet protocol to physical machine which are identified within the local network.
An ARP cache is a table mainly used to handle a connection among every internet protocol address as well as its equivalent MAC address. This type of protocol provides the laws to make these connections, & assists in converting addresses within both ways.
SLIP
SLIP or Serial Line IP is mainly used for serial connections of point-to-point through TCP/IP. This kind of protocol is mainly used for specific serial links as well as dial-up purposes. This protocol is responsible for enabling routers and mixes of hosts for communicating with others.
The common network configurations of SLIP protocol are host to host, host to router & route to router. This is a packet framing protocol and it defines a series of characters that structure IP data packets over a sequential line. It does not offer packet type identification, addressing, correction & detection of an error, etc.
The selection of the right protocol mainly depends on the applications. So after discussing and verifying all the protocols within computer networks, the best protocols can be selected based on the requirement like the following.
- A communication protocol like TCP/IP is used for startup businesses.
- FTP protocol is used for the quick transfer of efficient files.
- HTTPS is used for security purposes and that transfers the data over the network.
Once SNMP and managing networks are still widely used then it is made more efficient whenever they working in combination with UDP.
Network Protocol Standards
The set of rules used in data communication for exchanging the data among different devices is known as standards of network protocols. These standards are created by different standard organizations like ISO, IEEE, ANSI, and many more. The standards used in network protocol are two types which include the following.
- De Facto Standard
- De Jure Standard
In De Facto Standard, the term De Facto is nothing but “By Fact or By Convention”. These standards have been not accepted by any Organization, however, they adopted Standards due to their extensive use. Occasionally, these are frequently founded by Manufacturers.
For instance, multinational companies like Google and Apple have established their own policies on their products. For the manufacturing of their products, they use some network protocol standards.
In De Jure Standard, the meaning of “De Jure” is “By Regulations or By Law. These standards are approved by recognized companies like ISO, ANSI, IEEE, etc. These standards are essential to follow if it is necessary.
For instance, all the standard protocols in data communication are essential to follow and use when requiring like UDP, SMTP, TCP, IP, etc.
Please refer to this link to know more about Network Interface & Transmission Media in Computer Networks.
Please refer to this link to know more about Transmission Media MCQs, Computer Networks Question & Answers
Thus, this is all about an overview of network protocol, types & network protocol uses. These protocols are classified into three types namely network management, network communication & network security. Communication protocols mainly comprise fundamental data communication tools such as HTTP and TCP/IP. Security protocols comprise SFTP, SSL & HTTPS. Management protocols handle & rule the network by using different protocols like SNMP & ICMP. Here is a question for you, what is the network protocol error?