In Data Communication Systems, a network is an interconnecting point to exchange information between various communication components connected by various communication network links. If two or more network devices are connected to each other to transfer and share information and resources within a geographical area, then it is called a network. For example, a computer network is formed with multiple computers connected to transmit, exchange, share, store data, and resources. It enables communication for entertainment, business, and research. The computer network is built by using various hardware network nodes like bridges, routers, hubs, switches, etc, and communicating links like optical fiber cables, coaxial cables, wireless networks (LAN, WAN), etc. This article gives an overview of network nodes and their types in a computer network.
What is a Node in a Computer Network?
A node within a computer network is defined as, a connecting point or redistributed point or communicating point or joint, or a transfer point where the data can be stored, received, transmitted, or created. A node can be either a computer or any device that involves receiving and sending the data inside the computer networks. It is simply called a network node. The link that connects the node of a network is known as a communication channel.
The network node is either a redistribution point or an endpoint that transmits the data with a recognizing, processing, and forwarding capability to other network nodes. To form a network connection for data transmission, 2 or multiple network nodes are needed. It depends on the type of network and the referred protocol layer.
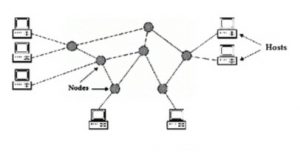
Network Nodes
To receive access each node requires an IP address for identification. Examples of network nodes include printers, computers, modems, bridges, switches, etc. A network node is any device in the network that can transmit, process, recognize and store information to other networks.
If the node is referred to as data communication equipment, then it forms a connection for modems, hubs, bridges, switches, etc. If the network node is data terminal equipment, then it acts as an endpoint for connecting printers, handsets, telephones, computers, etc.
Any device that is connected to the network contains a unique IP address or logical address, which is referred to as a node. The device manufacturers assigned a MAC address for every node on the network to a NIC (network interface controller) for data transmission and communication. The measure of several connections made by a network node with other nodes gives the degree of connectivity.
Types of Network Nodes
The network nodes concept adopted packet switching theory to transmit and receive the data through different routes in a distributed network. There are different types of network nodes based on the application and function.
End Nodes
These are referred to as the initial point or an endpoint for communication. Examples of end nodes are computers, security, cameras, printers, and many more.
Intermediary Nodes
The nodes are located in between the initial (starting) point or an endpoint of the end nodes of the computer network. Examples of intermediary nodes are bridges, routers, switches, cell towers, etc.
Data Communications
The network nodes are the physical devices that are located in between DTE (data terminal equipment) and data communication circuits. Bridges, switches, hubs, and modems are included to execute the conversion of signals, line clocks, and coding. In data communications, devices like digital telephones, host computers, printers, routers, servers act as data terminal equipment.
Internet and intranet network nodes: these types of nodes are nothing but host computers, which are identified by an IP address. Some of the data link layer devices and WLAN access points don’t contain any IP address and they are referred to as physical network nodes or LAN nodes.
LAN and WAN network nodes: these types of network nodes are the physical devices that are involved in performing particular functions and also every node contains a specific MAC address for NIC (network interface card). The examples are modems, access points of WLAN, and PCs. If the device is offline, then there would be a loss of function of the node.
Telecommunication Nodes
These types of nodes in fixed telephone networks might be private or public to exchange the information or a computer that provides intelligent network service. While in cellular networks, include base station controllers to control multiple base stations. Since the cellular network base stations are not referred to as nodes.
Cable TV Network Nodes
These types of nodes are related to fiber optic cables, which connect businesses, homes distributed by common fiber optic receivers within a specified geographical location. The fiber optic node in cable systems determines the number of businesses and homes are connected by a particular fiber node.
Distributed Network Nodes
These types of nodes are servers, clients, and peers. In distributed networks, some virtual nodes are used to maintain data transparency.
Example of Network Nodes
The best examples of network nodes are discussed below.
Switches
The network devices that operate at the data link layer of the OSI model to forward, send, and receive the data frames/packets over the entire network are called switches. A switch is a multiple port device, in which multiple computers or network devices can be plugged in. It performs error checking and examines the destination address when the data frame arrives at any port or node of the network and forwards it with efficiency to the selected port or node.
A switch can divide the Collision domain of hosts and the broadcast domain remains the same. It supports all modes of communications such as unicast, multicast, and broadcast. It uses packet-switching technology and utilizes the MAC address to send and receive the data frames from source to destination.
The mode of transmission is full-duplex and communication is bidirectional. The switches are active devices with network management capability. Error checking is done before forwarding of data. There are 4 types of switches.
- Unmanaged switches: most widely used in home networks
- Manages switches: used complex and large networks of various organizations.
- LAN switches: connects internal LAN of a business or organization
- PoE switches (power over Ethernet switches): can receive power and data frame over the same line on the Ethernet network.
Bridges
The network devices that operate at the data link layer of the OSI model and connect two or multiple LANs to form a single larger Local Area Network (LAN) are called bridges. The process of aggregating the local area networks is known as bridging the network. It connects two or multiple segments or components of the same local area network.
They are referred to as layer 2 switches. They are usually called repeaters, which can filter the data by reading the MAC address of destination and source. They are 2 port devices, that contain a single input and output port. It can interconnect two local area networks, which are operating on the same protocol.
When multiple LANs are joined together to form a single LAN, the capacity of the network will increase. The data frame is passed to the node and then discarded, if it contains a destination MAC address in the same network. The data frame will be forwarded towards the network if it contains the destination MAC address in the connected network. If the MAC address is not available, then the bridge broadcasts the data frames to every network node. There are 2 types of bridges. They are,
- Transparent bridge: unaware of the existence of a bridge in the network and performs two processes like bridge forward and bridge learn.
- Source routing bridge: source station and the data from specifies the route to be followed.
Know more about VPN.
Please refer to this link to know more about Network Theory MCQs
Thus, this is all about the network nodes in a computer network– network node definition and types of network nodes. The purpose of the network node is to transmit, receive and store the information contained in the computer network. Here is a question for you, “What are the different types of computer networks? “