In 1979, a data communication protocol called Modbus was developed by Modicon (now Schneider Electric) and it is used along with its PLCs (programmable logic controllers). It is an industrial standard protocol and it is mainly used in process and factory automation. Now it is commonly referred to as a de facto communication protocol to connect various industrial electronic components. In the electric power industry, this is used to connect a supervisory computer with RTU (remote terminal unit) in SCADA systems (data acquisition systems) and supervisory control systems. It is an open protocol and anyone can access it. The registered trademark of Modbus is Schneider Electric USA, Inc. this article gives an overview of Modbus communication protocol, architecture, versions, and implementations.
What is Modbus?
The serial communication protocol developed by Modicon in 1979 for usage with its PLCs (programmable logic controllers) is known as Modbus. That means it transmits the information or data over serial lines between multiple electronic devices. It is referred to as an open protocol so that manufacturers can utilize it without paying any royalties. It provides client/server or master/slave communication between the electronic devices connected on various types of networks or buses.
It is a request/reply type protocol and the services provided by this are specified by the function codes. It is generally referred to as application layer message protocol because it is placed at layer 7 of the OSI reference model. The specifications of various modes are testing, software, code interface, and many more.
Profibus vs Modbus
The comparison between Profibus and Modbus is given below.
| Profibus |
Modbus |
| It is a master/slave and peer-to-peer communication protocol | It is a master/slave or client/server communication protocol |
| Profibus PA, Profibus DP, Profibus FM, profinet, and profisafe are the variants of Profibus | Modbus ASCII, RTU, and TCP/IP are the variants of Modbus |
| Allows multiple masters with additional token ring protocol. For example, Profibus PA contains 256 nodes per network | This protocol contains a single master and multiple slaves. 32 slaves are connected without repeaters on RS 485 medium and 247 slaves are connected with repeaters |
| It uses a token-passing type media access algorithm | It uses a token-passing media access algorithm |
| Supports twisted pair cable | Supports twisted pair cable |
| Physical layer standard is RS 485 and IEC 61158-2 | Physical layer standard is not specified. |
| The data rate for Profibus PA is 31.25kbps and for Profibus DP 9.6kbps | The data rate is not specified |
Modbus Communication Protocol
This type of communication protocol is widely used by most manufacturers throughout many industries. It transmits signals from control devices and instruments to main data controller systems. For example, temperature and humidity values measured by the system are communicated through Modbus to a computer. It is used to connect a supervisory computer with RTU in supervisory control and SCADA systems (data acquisition systems). There are various protocol versions for both serial lines and Ethernet.
Since the Modbus is a master/slave communication protocol, one device is operated as a master and all other devices operate as a slave. The slave can’t provide information independently and voluntarily and should wait till it asks for it. The master writes the data to device registers (slave) and then reads the data from device registers (slave). The address of the register or reference of the register is usually within the context of the slave register.
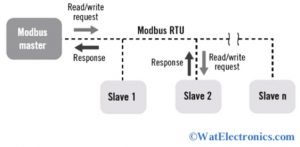
Modbus Communication Protocol
The communication protocol using master/slave or client/server transactions is shown below. The network of communication protocol is formed with one master and 247 slaves with a unique address. All the data transactions of the Modbus depend on the registered address, function code, and data.
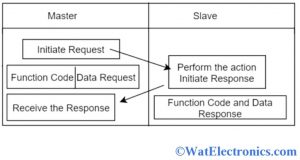
Master Slave Interaction
How does this Communication Protocol Work?
The working of Modbus communication protocol depends on the transactions between master and slave registers. It contains one master, which controls all the transactions with multiple slaves. The slave responds to the request coming from the master to read or write from/to data to the slaves.
The architecture of Modbus TCP/IP or Modbus communication protocol using TCP is shown below. This TCP/IP is implemented on an Ethernet network and all the data interactions from client/master are forwarded towards server/slave via IP address. The master/slave interactions of this protocol are a request/response type protocol. Communication always occurs in pairs. That means, one device sends or initiates a request and waits till it receives a response from another device.
The initiating devices act as a master and it is responsible for every interaction initiation. The master or client is an HMI (human-machine interface) or supervisory control or SCADA system. The slave is a PLC (programmable logic controller), sensor, or PAC (programmable automation controller). The data or information of these responses and requests and the layers of the network, where the messages are sent are determined by the different layers of protocol.
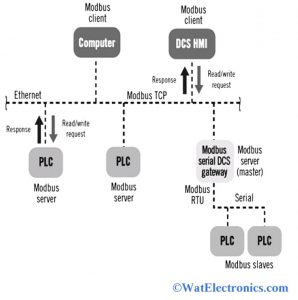
Modbus TCP IP Architecture
This communication protocol is an application layer protocol where all the data transactions are independent of the medium. But the data transactions are based on the request data from the master or write data to the slave. The master controls these data transactions with no exception data transmission. The data packet contains the device address or slave address followed by function code and all other parameters, which are required.
Please refer to this link to know more about Modbus MCQs
Versions
Protocol versions of Modbus will exist for Ethernet and serial port and other protocols that support the Internet protocol suite are discussed below.
Modbus Remote Terminal Unit (RTU)
It is used in serial communication to represent binary data for communication protocol. The format of RTU follows the data/commands with a CRC (cyclic redundancy check) checksum as a mechanism of error check that ensures the reliability of information or data. This type of protocol version is implemented most widely. Continuous transmission of Modbus RTU messages is done without any inter-character delays. The messages of Modbus are separated or framed by idle periods.
Modbus ASCII
It is also used in serial data communication. To achieve protocol communication, it utilizes ASCII characters. The format of ASCII uses longitudinal redundancy checks as a checksum. The messages of Modbus ASCII are framed by leading colon (:) and trailing newline (CR/LF).
Modbus TCP or Modbus TCP/IP
This type of protocol version is used in data communications over networks of TCP/IP by connecting through port 502. There is no need for checksum calculations because the checksum protection is provided by the lower layers of the network.
Modbus over TCP or Modbus over TCP/IP or Modbus over RTU/IP
This type of protocol version is different from Modbus TCP. The checksum mechanism is included as a payload with Modbus RTU.
Modbus over UDP
Some of the experiments had been done with this protocol version on IP networks to remove the overheads needed for TCP.
Modbus + or MB+ or MBP
This type of variant differs from other variants and acts as proprietary to Schneider Electric. Supports peer-to-peer communication between various masters. A dedicated co-processor is required to handle HDLC-like token rotation.
Every node is isolated using a transformer, which enables edge/transition triggering instead of level/voltage triggering. It required a twisted pair at 1Mb per second and special hardware to connect MB+ to a computer. A special card made for the PCI, ISA, or PCMCIA bus.
Pemex Modbus
This type of version is an extension to standard Modbus to support the flow of data. It was designed for process control in Pemex oil & Gas Company.
Enron Modbus
It was introduced by Enron Corporation to support 32-bit floating and integer variables and historical flow of data. It is an extended version of the standard Modbus where data types are mapped using standard addresses. The historical data should meet the requirements of an American Petroleum Institute (API) standard industry to store the data.
Function Codes
There are several function codes of Modbus that will access its registers. The 4 data blocks are identified by the Modbus, where the addresses or registration numbers are overlapped. Hence to define and find the data, both address and function codes are required. The most common function codes, which are identified by this protocol are given in the table below.
|
Modbus Function Code |
Type of Register |
|
1 |
Read coil |
|
2 |
Read discrete input |
|
3 |
Read holding registers |
|
4 |
Read input registers |
|
5 |
Write single coil |
|
6 |
Write single holding register |
|
15 |
Write multiple coils |
|
16 |
Write multiple holding registers |
Implementations
The Modbus protocol was introduced by Modicon (Schneider Electric) in 1979 for serial communication. It is the most widely used common protocol in the industrial sector for industrial applications. The full protocol is implemented in the NRT as a partial implementation. The initial implementation of this was a single protocol built on top of the serial and cannot divide into multiple layers.
Later on, various application data units (ADU) were developed either to change the packet format over a serial line or to allow the TCP/IP and UDP (user datagram protocol) networks.
At present, the implementation of this protocol is done using TCP/IP over Ethernet, asynchronous serial transmission over a wide range of media, Modbus plus (MB+) which is a token-passing network with high speed.
All the protocol implementations have some variations when compared to standard protocol. The most common variations are given below,
1). Data types:
- 32-bit integer
- 8-bit data types
- Mixed data types
- Bit fields in integers
- IEEE floating-point number
- Multipliers for changing data from/to integer
2). Extensions of protocol
- Slave address of 16-bit
- The data size of 32-bit
- Word-swapped data
Modbus Applications
The Modbus applications are listed below
- Used in the healthcare sector to monitor the temperature. Many IT departments of hospitals use this protocol to monitor the temperature in a single interface. The data collected from various floors is done via RS485 Modbus ADC devices.
- Used in the transportation sector to detect trafPlease refer to this link to know more aboutfic behavior. Detects the abnormal behavior of traffic by cross-referring with normal traffic obtained through transactions Modbus TCP
- Used in home automation devices to transfer the data easily and quickly. This protocol helps to transfer the data from different sensors via a single layer and it is easy when compared with other protocols.
- Used industries to connect industrial devices to provide communication with other automation devices. The industries include Oil & Gas, renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal.
- Used in various applications of client-server to monitor and program the connected devices.
- Used to provide communication between sensors, instruments, and intelligent devices.
- Used to monitor PCs and HMIs and other wireless applications.
Please refer to this link to know more about Transport Layer.
Please refer to this link to know more about PLC MCQ’s.
Thus, this is all about the basics of Modbus – definition, differences with Profibus, working of communication protocol, protocol versions, function codes, implementations, and advantages. The purpose of this is to transmit data between various electronic devices over serial lines or Ethernet and it is most widely used in industrial applications. Here is a question for you, “What is Modbus RTU?”