When integrating a voltage supply to any other equipment, we may encounter certain unwanted voltage variations. These variations at the voltage supply level can cause severe damage to the devices. So, there is a need to maintain a constant voltage at the supply level. This is where ‘Voltage Regulator‘ comes into the picture. Voltage regulators are the devices that maintain a stable output voltage irrespective of the changes at the input voltage and load. Based on their design there are various types of voltage regulators invented over time. One such voltage regulator is the ‘ Low-Dropout Regulator’ also popularly known as ‘LDO’.
What is an LDO?
LDO stands for Low-Dropout Regulator. It is a DC Linear voltage regulator. Invented by Robert Dobkin in 1977, LDO has a simple and inexpensive design. As its name ‘Low Dropout’ suggests, this regulator can operate stably at as low as 1V. This minimum potential difference between input and output voltage necessary for the operation of the regulator is known as ‘Dropout Voltage’. When the potential difference is less than the dropout voltage, the regulator operation becomes unstable.
Working
For working of LDO input voltage is supplied to a component known as ‘Pass element’. Pass element is usually an N channel FET. Pass element operates in the linear region and reduces the given input voltage level to the required output voltage level. This voltage next is passed to an element called ‘ Error Amplifier’. This error amplifier compares the output from the Pass element to a reference voltage. This error amplifier then changes the operating point of FET’s gate to remove the error between the reference voltage and the pass element’s output voltage. Thereby maintaining a required steady output voltage at the regulator’s output end.
Elements of LDO Regulator
The below diagram shows the circuit of an LDO Regulator
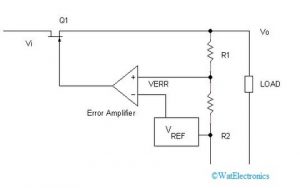
LDO Regulator Circuit Diagram
To understand the working of LDO we must understand the meaning and configurations of certain elements of the LDO regulator. Some of the important elements of LDO are Voltage reference, Error Amplifier, Feedback, Pass Element, and Output Capacitor.
Pass Element
Pass Element is one of the main components of LDO. This is usually an N channel or P channel FET. LDO uses an open-collector topology instead of an emitter follower topology. Hence, a transistor can be easily driven into saturation using the available voltages of the regulator. The use of FET for the pass element reduces the power consumption of the device.
Feedback
Feedback is a process where a fraction of output is feedback into the circuit as input. To regulate the power supply and remove unwanted voltage negative feedback loop is used in the regulator. Here the output voltage is feedback to the Error Amplifier. This amplifier compares the output voltage with a reference voltage. Any error obtained is used to change the operating point of the FET’s gate until a constant output voltage is obtained.
Error Amplifier
A differential amplifier is used as Error Amplifier in the LDO regulator. The differential amplifier amplifies the difference between two voltages. This error amplifier has two inputs. One of the inputs is supplied with a fraction of output voltage determined by the feedback voltage divider circuit. The second input of the error amplifier is supplied with a stable reference voltage.
The error amplifier calculates the difference between its two input voltages. This error voltage is used to control the power supply of FET so that a constant output voltage is obtained. If the feedback voltage is lower than the reference voltage, the gate of FET is pulled lower. Thereby increasing the output voltage by allowing more current to pass.
Voltage Reference
This voltage stays fixed irrespective of variations in power supply, temperature, load, or time. As one of the inputs of the differential amplifier, this voltage reference is highly useful to get steady output values. Here, we use bandgap voltage reference. It has a voltage value of around 1.25V.
Output Capacitor
For stability of the LDO regulator output, the capacitor is used. The ESR value of the output capacitor highly affects the stability of this device. It also affects the transient response to changes in the load current. Any good quality capacitor that has minimum capacitance and maximum ESR values can be used.
Parameters of LDO Regulator
Some of the important parameters of the LDO Regulator are Dropout Voltage, Quiescent Current, Efficiency, Transient Response, Line Regulation, and Load Regulation.
Dropout Voltage
The potential difference between input and output voltage, below which no regulation occurs is known as the Dropout voltage of a regulator. For the LDO regulator, the dropout voltage is very low, which means it can operate at levels very close to the required output voltage. Regulators with lower dropout voltages have higher efficiency.
Quiescent Current
Quiescent current is also known as Ground current. It is the difference between input current and output current. To maximize the current efficiency of the circuit lower quiescent current has to be maintained. It is the current collected by the device when no load or a very light load is connected. The value of the quiescent current is determined by
the pass elements, temperature, etc…
Efficiency
The efficiency of the LDO regulator highly depends on its quiescent current, input voltage, and output voltage. The efficiency of LDO is calculated as:-
Efficiency = (IoVo/([Io + Iq]Vi) * 100
Here, Io is the output current, ‘Iq’ is the quiescent current, ‘Vi’ is the input voltage and Vo is the output voltage.
The decrease in dropout voltage and quiescent current increases the efficiency of the regulator. This also decreases the power dissipation of the circuit.
Transient Response
The maximum output voltage variation allowed for the step change of load current is known as Transient Response. Transient voltage variation is calculated as :
ΔV tr, max = (Io, max/Co+ Cb)Δt1 + ΔVESR
Where Δt1 = closed-loop bandwidth of LDO regulator, ΔVESR = voltage variation due to ESR of the output capacitor. Co = output capacitor value, Cb = Bypass capacitor, usually added to output capacitor, Io, max = Maximum load current.
Line Regulation
The circuit’s ability to maintain the specified output voltage with varying input voltage is known as Line Regulation. It is determined by the ratio of variation in output voltage to the variation in input voltage. Increasing the open-loop gain improves the line regulation of the circuit.
Line Regulation = ΔVo/ΔVi
Line regulation is a steady-state parameter. Hence, all frequency components are neglected.
Load Regulation
The ability of the circuit to maintain the specified output voltage under varying load conditions is known as Load Regulation. An increase in the open-loop gain improves the load regulation of the circuit.
Load Regulation = ΔVo/ΔIo
Like Line regulation, Load regulation is also a steady-state parameter.
Please refer to this link to know more about Voltage Regulators, Precautions while Connecting a Constant Current Regulator
LDO regulator has a smaller device size. Unlike other DC-DC regulators, LDO does not have switching noise as no switching takes place. It has a very simple design. LDO regulator is used in cellular telephones, Battery-powered equipment, laptops, notebook computers, various consumer electronics, Linear power supplies with High efficiency, etc…In addition to functioning as a regulator, LDO is also used as a Filter to removes ripples caused in the output voltage when switchers are used in the circuit. LDO is also affected by thermal noise, bipolar shot noise, and flicker noise. When does the worst case of output voltage variation occur in the LDO regulator?