IR technology is used in a wide range of wireless applications which includes remote controls and sensing. The infrared part in the electromagnetic spectrum can be separated into three main regions: near IR, mid-IR & far IR. The wavelengths of these three regions vary based on the application. For the near IR region, the wavelength ranges from 700 nm- 1400 nm, the wavelength of the mid-IR region ranges from 1400 nm – 3000 nm & finally for the far IR region, the wavelength ranges from 3000 nm – 1 mm.
The near IR region is used on fiber optic & IR sensors, the mid-IR region is used for heat sensing and the far IR region is used in thermal imaging. The range of frequency for IR is maximum as compared to microwave and minimum than visible light. This article discusses an overview of the IR sensor and its working.
What is IR Sensor?
The IR sensor or infrared sensor is one kind of electronic component, used to detect specific characteristics in its surroundings through emitting or detecting IR radiation. These sensors can also be used to detect or measure the heat of a target and its motion. In many electronic devices, the IR sensor circuit is a very essential module. This kind of sensor is similar to human’s visionary senses to detect obstacles.

IR Sensor
The sensor which simply measures IR radiation instead of emitting is called PIR or passive infrared. Generally in the IR spectrum, the radiation of all the targets radiation and some kind of thermal radiation are not visible to the eyes but can be sensed through IR sensors.
In this sensor, an IR LED is used as an emitter whereas the photodiode is used as a detector. Once an infrared light drops on the photodiode, the output voltage & resistance will be changed in proportion to the received IR light magnitude.
IR Sensor Working Principle
An infrared sensor includes two parts namely the emitter & the receiver (transmitter & receiver), so this is jointly called an optocoupler or a photo-coupler. Here, IR LED is used as an emitter whereas the IR photodiode is used as a receiver.
The photodiode used in this is very sensitive to the infrared light generated through an infrared LED. The resistance of photodiode & output voltage can be changed in proportion to the infrared light obtained. This is the fundamental IR sensor working principle.
The type of incident that occurred is the direct otherwise indirect type where indirect type, the arrangement of an infrared LED can be done ahead of a photodiode without obstacle. In indirect type, both the diodes are arranged side by side through a solid object ahead of the sensor. The generated light from the infrared LED strikes the solid surface & returns back toward the photodiode.
IR sensors use three basic Physics laws like Planck’s Radiation, Stephan Boltzmann & Wein’s Displacement.
- Planck’s Radiation Law defines that the temperature of any object is not equivalent to Zero
- Stephan Boltzmann Law defines that the whole energy which is generated at all wavelengths through a black body is associated with the total temperature.
- Wein’s Displacement Law defines that the temperature of different objects emits spectra that are maximum at various wavelengths and inversely proportional with temperature.
IR Sensor Module
The IR sensor module includes five essential parts like IR Tx, Rx, Operational amplifier, trimmer pot (variable resistor) & output LED. The pin configuration of the IR sensor module is discussed below.

IR Sensor Module
- VCC Pin is power supply input
- GND Pin is power supply ground
- OUT is an active-high o/p
The main specifications and features of the IR sensor module include the following.
- The operating voltage is 5VDC
- I/O pins – 3.3V & 5V
- Mounting hole
- The range is up to 20 centimeters
- The supply current is 20mA
- The range of sensing is adjustable
- Fixed ambient light sensor
Types of IR Sensor
The classification of IR sensors can be done based on the application which includes the following.
- Active Infrared Sensors
- Passive Infrared Sensors
Active IR Sensor
This type of sensor includes both the emitter & the receiver which are also known as transmitter & receiver. In most situations, a laser diode or LED is used as a source. For non-imaging infrared sensors, LED is used whereas laser diode is used for imaging infrared sensors.
The working of an infrared sensor can be done through radiating energy, detected and received through the detector. Further, it is processed through a signal processor to fetch the required data. The best examples of active infrared sensors are reflectance & break beam sensors.
Passive Infrared Sensor
Passive Infrared Sensor (PIR) includes detectors only and this kind of sensor uses targets like infrared transmitters or sources. Here, the object will radiate the energy & detects it through infrared receivers. After that, a signal processor is used to understand the signal to obtain the required data.
The best examples of PIR sensors are bolometer, Pyro-Electric Detector, Thermocouple-Thermopile, etc. PIR sensors are available in two types like thermal IR sensor and quantum IR sensor.
Thermal Infrared Sensor
These types of sensors are independent of wavelength and they utilize heat-like energy sources. These are slow along with the response time as well as detection time.
Quantum Infrared Sensor
These types of sensors depend on wavelengths and the response time and detection time they have are high. These kinds of infrared sensors need repeated cooling for exact measurement.
IR Sensor Circuit
The application circuit of the IR sensor is an obstacle detecting circuit that is shown below. This circuit can be built with a photodiode, IR LED, an Op-Amp, LED & a potentiometer, The main function of an infrared LED is to emit IR light and the photodiode is used to sense the IR light. In this circuit, an operational amplifier is used as a voltage comparator and the output of the sensor can be adjusted by the potentiometer based on the requirement.
Once the light generated from the infrared LED can be dropped on the photodiode once striking an object, then the photodiode’s resistance will be dropped.
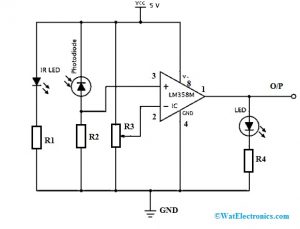
IR Sensor Circuit Diagram
Here, op-amp’s one of the input at threshold value can be set through the potentiometer whereas other inputs can be set by using the series resistor of the photodiode. Once the radiation on the photodiode is more, then the voltage drop will be more across the series resistor. In the operational amplifier, both the voltages are evaluated.
If the series resistor’s voltage is higher than the threshold voltage then the IC output is high. When the IC output is given to an LED then it will blink. So using a potentiometer, the threshold voltage can be adjusted based on the conditions of surroundings.
In this circuit, the arrangement of the IR receiver and the IR LED is a very essential factor. Once the infrared LED is placed directly ahead of the infrared receiver, then this arrangement can be known as Direct Incidence.
So in this case, nearly the whole radiation from the infrared LED will drop on the infrared receiver. Therefore there is a row of view contact among the IR Tx & Rx. If a target drops in this row, it blocks the emission while approaching the receiver by reproducing or absorbing the radiation.
Please refer to this link to know more about IR Sensor MCQs
Advantages
The advantages of the infrared sensor include the following.
- Low power consumption
- Noise immunity is strong
- Detects motion when the light is present or absent
- These sensors are not affected by rust
- They do not need to get in touch with objects for detection.
- No data leakage because of the directionality infrared radiation of ray
- These are more modest in size and are more moderate.
- It responds very quickly as compared to thermocouples.
- It provides high reliability
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of the infrared sensor include the following.
- Line of sight is necessary
- It can be affected based on the conditions of the environment like fog, rain, pollution, dust, etc
- These sensors can be blocked with common objects.
- The data rate transmission is not fast
- Range is limited
- High force IR signals can harm human eyes
Applications
The applications of the infrared sensor include the following.
- Rail Safety
- IR Imaging Devices
- Infrared Astronomy
- Optical Power Meters
- Night Vision Devices
- Sorting Devices
- Moisture Analyzers
- Missile Guidance
- Flame Monitors
- Remote Sensing
- Climatology
- Gas Analyzers
- Meteorology
- Rail safety
- Photobiomodulation
- Exploration of Petroleum
- Flame Monitors
- Testing of Anesthesiology
- Gas detectors
- Moisture Analyzers
- Water analysis
Know more about Spectrum Analyzer and Wave Analyzer.
Thus, this is all about an overview of the Infrared Sensor or IR sensor. This kind of sensor is most frequently used in wireless technology wherever surrounding objects detection, functions of remote controlling, etc. The main features of this sensor are motion & heat sensing. The infrared region is not noticeable to human eyes. Here is a question for you, what are the different types of sensors available in the market?