The concept of IMPATT diode was actually invented in the year 1954 by William Shockley. So, he expanded the idea for producing a negative resistance with the help of a mechanism like transit time delay. He proposed the injection technique for charge carriers within a PN junction is forward biased and published his thought in the Technical Journal of Bell Systems in 1954 and titled with the name ‘Negative Resistance Occurring from Transit Time within Semiconductor Diodes.
Further, the proposal was not extended until 1958 as Bell Laboratories implemented his P+ N I N+ diode structure and after that, it is called Read diode. After that in the year 1958, a technical journal was published with the title name “a proposed high-frequency, negative resistance diode.” In the year 1965, the first practical diode was made and observed first oscillations. The diode which is used for this demonstration was constructed through silicon with a P+ N structure. Later, the Read diode operation was verified & after that, a PIN diode was demonstrated in the year 1966 to work.
What is IMPATT Diode?
The full form of IMPATT diode is IMPatt ionization Avalanche Transit-Time. This is an extremely high-power diode used in microwave applications. Generally, it is used as an amplifier and oscillator at microwave frequencies. The operating frequency range of the IMPATT diode ranges from 3 – 100 GHz.
Generally, this diode generates negative resistance characteristics so works as an oscillator at microwave frequencies for generating signals. This is mainly because of the transit time effect and impact ionization avalanche effect. The classification of IMPATT diodes can be done by two types namely single drift and double drift. Single drift devices are P+NN+, P+NIN+, N+PIP+, N+PP+.
When we consider the P+NN+ device, the P+N junction is connected in reverse bias then it causes an avalanche breakdown that causes the region of P+ to inject into NN+ with a saturation velocity. But the holes injected from the region of NN+ do not drift which is called single drift devices.
The best example of double drift devices is P+PNN+. In this kind of device, whenever the PN-junction is biased close to an avalanche breakdown, then the electron drift can be done through the NN+ region whereas the holes drift through the PP+ region which is known as double drift devices.
Features
The main features of the IMPATT diode include the following.
- Operating frequency ranges from 3GHz to 100GH
- The working principle of the IMPATT diode is avalanche multiplication
- Output power is 1w CW & above 400watt pulsed
- Efficiency is 3% CW & 60% pulsed under 1GHz
- More powerful as compared to GUNN diode
- The noise figure is 30db
IMPATT Diode Construction and Working
The construction of the IMPATT diode is shown below. This diode includes four regions like P+-N-I-N+. The structure of both the PIN diode and IMPATT is the same, but it works on an extremely high voltage gradient of approximately 400KV/cm to generate an avalanche current. Usually, different materials such as Si, GaAs, InP, or Ge are mainly used for its construction. But, material like GaAs is mostly preferred due to its less noise behavior.
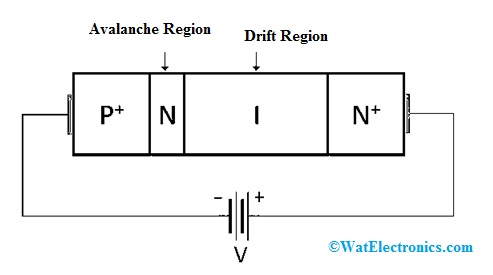
IMPATT Diode Construction
As compared to a normal diode, this diode uses a somewhat different structure because; a normal diode will break down in an avalanche condition. As the huge amount of current generation causes the heat generation within it. So at microwave frequencies, deviation in structure is mainly used to generate RF signals. Generally, this diode is used in microwave generators. Here, a DC supply is given to the IMPATT diode to generate an output that oscillates once an appropriate tuned circuit is used within the circuit.
The output of the IMPATT circuit is consistent & comparatively high as compared to other microwave diodes. But it also produces a high range of phase noise, which means that it is utilized in simple transmitters more commonly than local oscillators within receivers wherever the performance of phase noise is normally more significant.
This diode works with fairly high voltage like70 volts or above. This diode can limit the applications through phase noise. Nevertheless, these diodes are mainly attractive alternatives for microwave diodes for several regions.
IMPATT Diode Circuit
application of IMPATT diode is shown below. Generally, this kind of diode is mainly used at above 3 GHz frequencies. It is noticed that whenever a tuned circuit is given with a voltage in the region of the breakdown voltage toward the IMPATT then oscillation will occur.
As compared to other diodes, this diode uses negative resistance and this diode is capable of generating a high range of power typically ten watts or above based on the device. The operation of this diode can be done from a supply using a current limiting resistor. The value of this restricts the flow of current to the value necessary. The current is supplied throughout an RF choke to separate the DC from the RF signal.
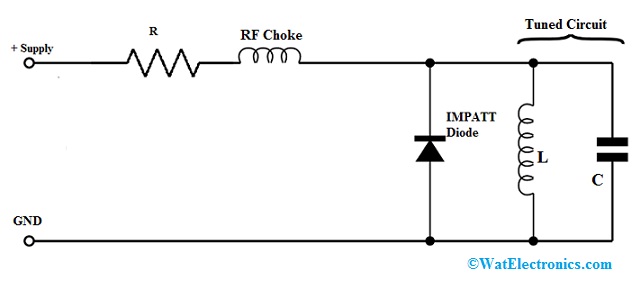
IMPATT Diode Circuit
The IMPATT microwave diode is arranged beyond the tuned circuit but normally this diode may be arranged within a waveguide cavity that gives the necessary tuned circuit. When the voltage supply is given then the circuit will swing.
The main drawback of the IMPATT diode is its operation because it generates a high range of phase noise due to the mechanism of avalanche breakdown. These devices use Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) technology which is much better as compared to Silicon. This results from the very quicker ionization coefficients for charge carriers.
Difference between IMPATT and Trapatt Diode
The main difference between IMPATT and Trapatt diode based on different specifications is discussed below.
| Specifications | IMPATT Diode | TRAPATT Diode |
| Operating Frequency |
0.5 – 100GHz | 1 – 10GHz |
| Bandwidth | 1/10th of RF Center Frequency | – |
| Efficiency | 60% in pulsed mode & 3% in CW | Pulsed mode is 20 – 60% |
| Output power | 1Watt(CW) 400Watt(Pulsed) | Above 100 Watt |
| Noise Figure | 30 dB | 60 dB |
| Basic semiconductors | Si, InP, Ge, GaAs | Si |
| Construction | N+PIP+ reverse bias PN Junction | P+ NN++ or N+ P P+ Reverse Bias PN Junction |
| Harmonics | Low | Strong |
| Ruggedness | Yes | Yes |
| Size | Tiny | Tiny |
| Application | Oscillator, Amplifier | Oscillator |
IMPATT Diode Characteristics
The characteristics of the IMPATT diode include the following.
- It operates in reverse bias condition
- The materials used to manufacture these diodes are InP, Si & GaAs.
- These are compact & reliable
- It generates a negative resistance area because of the effects of an avalanche as well as transit time.
- As compared to Gunn diodes, these provide high o/p power and noise also, so used in receivers for local oscillators.
- The phase difference between current and voltage is 180 degrees. Here phase delay with 90 degrees is mainly because of the avalanche effect whereas the remaining angle is because of transit time.
- These are mainly used where the high output power is necessary like oscillators & amplifiers
- The output power provided by this diode is in the range of millimeter-wave frequency.
- At fewer frequencies, the output power is inversely proportional to frequencies whereas, at high frequencies, it is inversely proportional to the square of the frequency.
Please refer to this link for Choosing resistor values for diodes.
Advantages
The advantages of the IMPATT diode include the following.
- It gives a high operating range.
- Its size is small.
- These are economical.
- At high temperature, it gives reliable operation
- As compared to other diodes, it includes high power capabilities.
- Whenever it is used as an amplifier, then it works like a narrow band device.
- These diodes are used as excellent microwave generators.
- For the microwave transmission system, this diode can generate a carrier signal.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of the IMPATT diode include the following.
- It gives a less tuning range.
- It gives high sensitivity to various operating conditions.
- In the avalanche region, the rate of electron-hole pair generation can cause a high noise generation.
- For operational conditions, it is responsive.
- If proper care is not taken then it may get damaged because of the huge electronic reactance.
- As compared to TRAPATT, it provides less efficiency
- The IMPATT diode’s tuning range is not good like the Gunn diode.
- It generates spurious noise through higher ranges as compared to Gunn & klystron diodes.
Applications
The applications of IMPATT diode include the following.
- These types of diodes are used like microwave oscillators within modulated output oscillators & microwave generators.
- These are used in continuous-wave radars, electronic countermeasures & microwave links.
- These are used for amplification through negative resistance.
- These diodes are used in parametric amplifiers, microwave oscillators, microwave generators. And also used in telecommunication transmitters, intruder alarm systems & receivers.
- Modulated Output Oscillator
- CW Doppler Radar Transmitter
- Microwave Generator
- Transmitters of FM Telecommunication
- Receiver LO
- Intrusion Alarm Network
- Parametric Amplifier
Know more about Clippers and Clampers & Dual Trace Oscilloscope.
Know more about Clipper Circuit MCQs.
Thus, this is all about an overview of IMPATT diode, construction, working, differences & its applications. These semiconductor devices are used for generating high-power microwave signals at a 3 GHz to 100 GHz range of frequencies. These diodes are applicable to fewer power alarms and radar systems. Here are a few questions for you, what is a TRAPATT diode? What is a laser diode?