An ideal diode is one kind of electronic component that includes two terminals and allows the flow of current in only one direction because it has less zero resistance in one way and infinite resistance in another way. The most frequently used type of diode is a semiconductor diode. It is a crystalline part of semiconductor material that includes a PN junction and it is connected to two electrical terminals.
The first semiconductor electronic devices are semiconductor diodes. At present, most of the diodes are designed with Si material, but materials are also used like germanium & gallium arsenide. This article discusses an overview of an ideal diode and its working.
What is an Ideal Diode?
A diode is a perfect diode because the working of this diode mainly depends on the type of biasing. When this diode is connected in forward bias then it works like a perfect conductor including zero voltage across it. Likewise, once this diode is connected in reversed bias, then it works as an ideal insulator including zero current.
Ideal Diode
How does an Ideal Diode act as a Switch?
An ideal diode works as a switch because it works like a closed switch when it is connected in forward bias whereas it works as an open switch when it is connected in reverse bias.
The main function of this diode is to control the current flow direction because the current flow in the diode is in one direction only which is called the forward direction. And, the flow of current in the reverse direction is blocked.
These diodes do not exist but the VI characteristics of the diode are mainly used to examine the diode circuits by contrasting them through the ideal diode. The designing of this diode is not possible because it works as an ideal diode. But, a diode with perfectly designed mainly performs approximately like an ideal diode.
Symbol
This includes two terminals namely positive & negative which are also known as anode & cathode. The flow of current direction is always from the anode terminal to the cathode terminal. The ideal diode symbol is shown below.
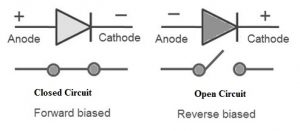
Ideal Diode Symbol
An ideal diode is said to be forward-biased when the p-type semiconductor is connected to the batteries’ positive terminal and the negative terminal is connected to the N-type semiconductor. Similarly, the diode is said to be reverse-biased, if the connection of the diode is quite opposite to forward bias.
This diode works as a closed circuit in forward biased condition whereas, in reverse biased condition, it works as an open circuit. This diode does not include a junction barrier or depletion region, which oppose the current flow. Thus, this diode has no voltage drop or voltage loss.
Difference between Ideal Diode and Real Diode
The main difference between these two diodes includes the following.
| Ideal Diode |
Real Diode |
| This is a two-terminal device that controls the flow of current in the reverse direction and allows the flow of current only in one direction that is forward | The real diode includes two terminals, which permit most of the current flow in forward bias & blocks in reverse bias. |
| The ideal diode resistance of this diode is zero when it is connected in forwarding bias whereas it is infinite when connected in reverse bias. | A real diode conducts forward bias through zero resistance otherwise it offers infinite resistance within the reverse direction. |
| The forward resistance of this diode is ‘0’ Ohm, reverse resistance is ∞ Ohm & cut in voltage ‘0’ | Real diodes forward resistance a few 10 Ohms, reverse resistance is several mega Ohms & cut-in voltage is a few one tens volts |
| When this diode is connected in forwarding bias then it acts like a perfect conductor through ‘0’voltage across it. | A Real diode is connected in forward biased & conducts a forward current through it to cause a voltage drop within the forward resistance. |
| These diodes work like perfect insulator & conductor | These diodes cannot work like perfect conductors & insulator |
| When this diode is connected in reverse bias, then it doesn’t draw current | It draws less current when it is connected in reverse bias. |
Ideal Diode Equation
We know that a PN junction diode will generate the following current. In reverse bias, there is a stable, small reverse current whereas, in forward bias, the forward current will increase through voltage. For an ideal diode, the current-voltage function is
i(v) = IS[exp(v/ηVT)−1], v>VZ
Where ‘IS’ is the reverse saturation current,
‘v’ is the applied voltage
VT = T/11,586 is the volt equal to the temperature
‘η’ is the emission coefficient
Here, the diode equation is extremely helpful like a formula for current & a function of voltage. But, sometimes the opposite relation may be more helpful; if the equation of this diode is reversed & solved for voltage like a current function, then we can find
v(i) = ηVTln [ (i/IS) + 1]
Ideal Diode Bridge Controller
For 9volts to 72volts systems, a bridge controller changes every diode within a full-wave bridge rectifier through a less-loss N-channel MOSFET. Here, how MOSFET as ideal diode works is discussed below.
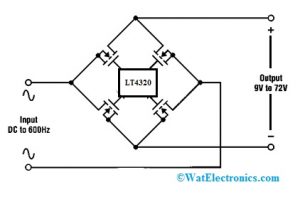
Ideal Diode Bridge Controller Circuit
An ideal diode IC like LT4320 from Linear Technology is used for 9 V-72 V that changes every diode in a full-wave bridge rectifier by using N-channel MOSFET so that power dissipation & increase accessible voltage can be reduced. The size of the power supply can be decreased because the improved power efficiency can remove large heat sinks.
An incorporated charge pump can provide the gate drive for the exterior low on-resistance MOSFETs without needing outside capacitors. Here, the bridge controller is accessible in two options like the LT4320 & LT4320-1. The LT4320 is mainly designed for voltage rectification from dc to 60 Hz whereas the LT4320-1 rectifies from dc to 600 Hz. S
For a fixed industrial temperature range like -40°C to 85°C, the package offered by a bridge controller is a 3 x 3 mm, 8-pin DFN package & a 12 lead MSOP package through improved high voltage pin spacing.
Please refer to this link for Ideal Diode MCQs
Please refer to this link for Choosing resistor values for diodes.
VI Characteristics
The VI characteristics of an ideal diode mainly depend on the two biasing conditions like forward & reverse bias.
- If the forward voltage is applied to the diode is equivalent to zero or above zero & then forward electric current within the diode enhances infinitely.
- In contrast, if the reverse voltage is applied to this diode is low or above zero, then no forward electric current & reverse electric current supplies within the diode.
know more about PN Junction Diode MCQs & Varactor Diode MCQs.
Please refer to this link to know more about Crystal Diode and Tunnel diode.
Thus, this is all about an overview of an ideal diode, working, characteristics, equation, and differences. Here are a few questions for you, what are the benefits of using this diode? What is a laser diode? What is Rectifier diode?