In electromagnetism, magnetic flux is defined as the number of magnetic lines of forces observed at the surface of a magnetic material. Magnetic flux is denoted with ‘Φ’. The SI unit of magnetic flux is derived as volt-seconds, also known as Weber and Maxwell as CGS unit. To measure the amount of flux generated from a magnetic surface an instrument called ‘Fluxmeter’ is used. Fluxmeter consists of measuring coils placed between permanent magnets known as Helmholtz coil arrangement. The change in the voltage level of measuring coils is used to calculate the amount of magnetic flux generated by the permanent magnet. This article discusses an overview of the flux meter and its working.
What is a Fluxmeter?
Fluxmeter is the device used to measure the magnetic flux of a permanent magnet. This device is in use since the 19th century to measure the magnetic properties of the earth’s magnetic field. There have been considerable improvements in its design and today there are also digital flux meters available in the market. Flux meters are an advanced form of the ballistic galvanometer. This device requires very low controlling torque and has heavy electromagnetic damping.
Working Principle
The working principle of flux meter is based on Faraday’s law. According to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, when a conductor is placed between changing magnetic fields, a voltage will be induced in the conductor. Similarly, when a moving conductor is placed between stable magnets, a voltage will be induced in the conductor.
This induced voltage will be equal to the rate of change of flux. Thus, the flex meter consists of a moving coil placed between the magnetic field of stable permanent magnets. The voltage change observed in the coil is calculated using a calibration meter. This reading gives the amount of flex present in the field.
Construction and working
The circuit of a flux meter is shown in the figure given below.
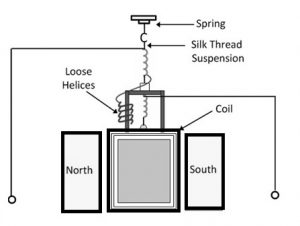
Flux Meter Construction
As the flux meter works on the principle of Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, it consists of a moving coil and permanent magnets. The coil is freely suspended between the poles of a permanent magnet with the help of a spring and silk thread. This coil moves freely between the poles. Very thin annealed silver strips are used to make helices. Helices are used here to transfer current into the coil. This applied current is used to reduce the controlling torque. Here, the damping caused by air friction is negligible.
Working
The search coil is connected across the terminals of the flux meter. This coil is either removed from the magnetic field or the field is reversed to cause changing magnetic field conditions. Reversing the magnetic field can be done by flipping the coil. With the change in the magnetic field, according to faraday’s law, an EMF is induced in the coil. This emf causing current flow in the coil. This induced voltage is sent to the flux meter. Depending on the value of induced voltage the pointer of the flux meter deflects.
This deflection of the pointer is directly proportional to the change in the value of flux. After showing the value the pointer again returns to its initial position. The low resistance circuit caused between flux meter and search coil gives rise to high electromagnetic damping conditions. These high electromagnetic damping stops the movement of the coil when there is a reduction in variation of flux.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Flux meter
Some of the advantages of flux meter are as follows:
- This is a portable instrument that can be carried anywhere easily.
- Flexmeter’s scale is calibrated in Weber units, so it is easy to take readings as no unit conversion is required.
- The deflection of the pointer depends only on the integrated flux value and does not show or depends on the time taken by the flux to change.
- The ability of the flux meter to integrate flux over a wide area makes them useful for characterizing magnets.
- Flux meter gives information about the overall degree of magnetization of the material.
- Digital flux meters can directly give information about magnetic characteristics independent of the magnetic size of the magnet under test.
The only disadvantage of flux meter is that these are less sensitive compared to other methods used for calculating flux values.
Applications of Flux Meter
Some of the applications of flux meter are as follows:
- These are used for measurements of magnetic fields.
- Flux meters are used for plotting of hysteresis loop.
- These can be used in voltage integration circuits.
- Flux meters are also used as ferromagnetic detectors.
- Flux meter is also useful for iron testing where its property of independence on the time taken to change in flux is used.
- Due to easy measurements, flux meters are used in performing inspections and quality control tasks.
Please refer to this link to know more about Measurement and Instrumentation MCQs.
Flux meters can be placed between NMR and ESR when precision values are compared. This device covers a wide range of fields, second to none. These are very flexible instruments but comes with a price as it is a relatively complex device. Different scenarios for using a coil in flux meter are moving coil, flip coil, moving wire, static coil/AC field, moving wire map, rotating coil map, etc. With the increase of ADC, digital voltage integration is used in flux meters to digitize the values. The use of ADC decreases the size, less noise, no leakage current, low-temperature dependence, etc. Digital meters also have their own limitations line dependence on ADC linearity, etc. What technique is used to reduce the controlling torque in flux meters?