Fiber optic sensor is a new branch in fiber optics in competition with the existing communication system. This is a very interesting and also well-known topic in the research field. Fiber optic sensors play a key role in developing the communication system to sense & measure the change within phase, data transmission rate, wavelength, intensity, noise, uneven environmental conditions, extreme heat, high vibration, etc. These sensors are available at less cost, in small size and their fabrication is easy so replaced normal sensors that were normally used before the invention of fiber optic sensors . This article discusses an overview of a fiber optic sensor – working with applications.
What is a Fiber Optic Sensor?
A sensor that uses optical fiber as a detecting element is known as a fiber optic sensor. In remote sensing, fibers play a key role but based on the requirement, fibers may be used. These sensors are available in small size and it doesn’t need electrical power. At the remote place, several sensors can be simply multiplexed along the length of fiber by using light wavelength shift for every sensor, otherwise by sensing the delay of time when light passes along the fiber throughout every sensor. Here, the time delay can be decided by using a device namely an optical time-domain reflectometer & wavelength shift is measured to implement optical frequency domain reflectometry.
Fiber-optic sensors are resistant to electromagnetic interference & they do not conduct electricity thus they are applicable in some locations where there is flammable material like jet fuel or high-voltage electricity. These sensors are also designed to resist high temperatures.
Fiber Optic Sensor Block Diagram
The block diagram of the fiber optic sensor is shown below. The parts of fiber optic sensors mainly include an optical source like laser diode, laser and LED, optical fiber, sensing element like transducer, optical detector & electronic processing unit like wave analyzer, Optical spectrum analyzer & oscilloscope.
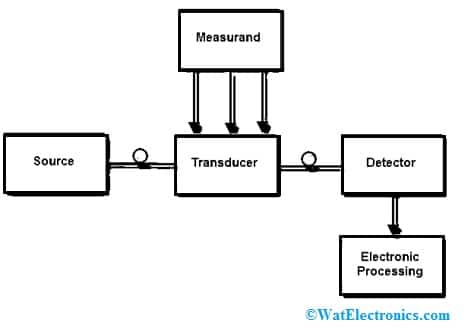
Fiber Optic Sensor Block Diagram
The fiber optic sensor working principle is that transducer changes some optical fiber system parameters like wavelength, intensity, phase, polarization, etc. This gives an increase in modifying the optical signal’s characteristics at the detector.
A fiber optic sensor works on the principle of light from a superluminescent source or a laser transmitted through an optical fiber then it experiences changes within its parameters either in the fiber Bragg gratings or optical fiber & reaches a detector that measures these changes.
Types of Fiber Optic Sensors
There are different types of fiber optic sensors are available based on different factors like sensing location, operating principle, and application.
Based on Sensing Location
Fiber optic sensors are classified into two types based on sensing location like intrinsic and extrinsic type fiber optic sensors.
Intrinsic Type Fiber Optic Sensors
In intrinsic fiber optic sensors, the sensing mainly occurs within the fiber itself. These sensors mainly depend on the optical fiber properties to change an environmental action to a modulation of the light signal throughout it. Here, the light signal physical property is available in the form of phase, frequency, intensity, polarization, etc. The main feature of this sensor is, it gives distributed sensing above long-range distances.
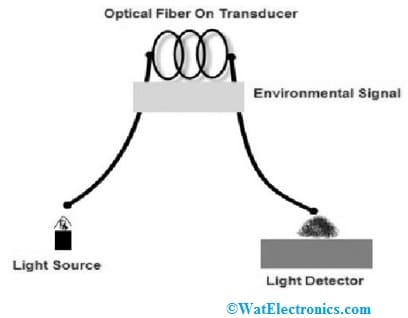
Intrinsic Type Fiber Optic Sensor
Extrinsic Type Fiber Optic Sensors
The fiber in this sensor is used as an information carrier that shows the method to a black box. Once the information arrives at the black box, then it produces a light signal. So this box may be designed with gas, mirrors, or any other device that produces an optical signal. The main function of these sensors is to measure velocity, revolution, vibration, displacement, torque, acceleration & twisting. These sensors are capable of reaching not reachable places.
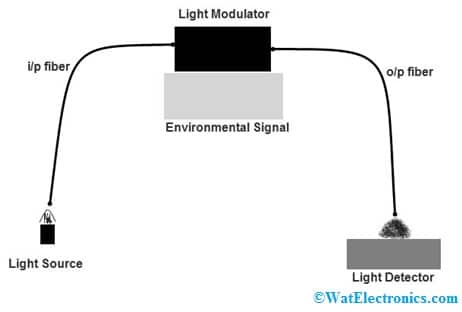
Extrinsic Fiber optic Sensor
This sensor is used in the temperature measurement of the aircraft engine that transmits an emission into a radiation pyrometer that is arranged on the engine’s outside. Likewise, these types of sensors are used for measuring the transformer’s inside temperature. These sensors offer outstanding protection from noise corruption for measurement signals.
Based on Operating Principles
Fiber optic sensors are available in three types based on operating principles as discussed below.
Intensity-based Fiber Optic Sensor
The intensity-based fiber optic sensor uses multimode fibers which have large core sizes so that it gathers more light. In the following circuit, two optical fibers are arranged very close to each other.
Once a light ray is infused into one of the optical fibers, then it will enlarge into a funnel of light whose position mainly depends on their difference.
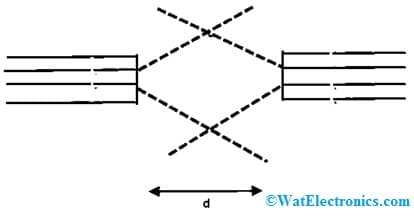
Intensity based FOS
These kinds of sensors have several limitations concerning different losses like micro bending losses, losses due to splices & connectors, misalignment of light sources & detectors, and macro bending losses. To defeat these losses, fiber optic sensors based on intensity are used with dual-wavelength. So, one of the wavelengths is utilized for calibration of all the faults because of the not preferred intensity differences by bypassing the detecting areas.
Polarization-based Fiber Optic Sensor
These sensors are normally used in different communication, signal processing & measurement applications. The optical setup of this sensor is shown in the following figure. It is designed by polarizing the light ray from the source of light using a polarizer. So, this polarized light is simply established at 45 degrees to the preferred axes of a length of birefringent polarization defending fiber.
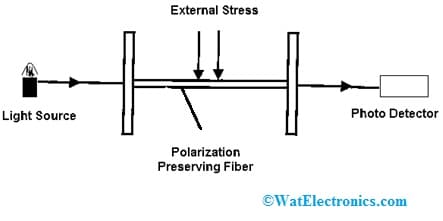
Polarization based FOS
So this part of the fiber is served as sensing fiber. After that, the phase variation between the two polarization conditions is adjusted for any external disturbances like strain or stress. So based on the external trouble, the polarization output is changed. Hence, by simply considering the output polarization condition at the second ending of the fiber optic, the outside disturbances can be simply detected.
Phase Modulated Fiber Optic Sensor
These kinds of sensors are very useful in changing emitter light on data signal where the signal is monitored by this sensor. Once a light signal is transmitted throughout the interferometer, next the light signal will divide into two signals where one signal is exposed to the sensing environment and the other one is isolated from the sensing environment, which is used as a reference. The most frequently used interferometers are; Mach Zehnder, Michelson, Sagnac, and polarimetric interferometers. In the following figure, the interferometers like the Mach Zehnder & Michelson are shown.
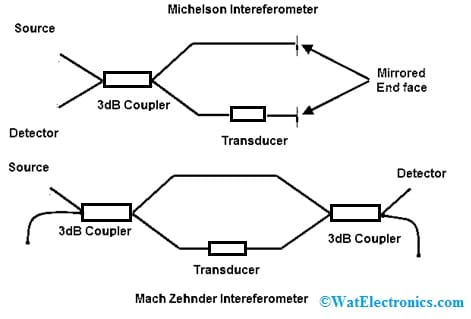
Phase based Fiber Optic Sensor
In the above two interferometers, there are mainly two similarities & differences between them. The Michelson Interferometer is commonly considered a folded Mach Zehnder interferometer and the configuration of this Michelson interferometer simply needs only one optical fiber coupler because the light supplies twice throughout the sensing & reference fibers and the optical phase shift for each unit length of the fiber optic is doubled. Therefore, the Michelson Interferometer can fundamentally have superior sensitivity.
One more benefit of the Michelson Interferometer is that this sensor is interrogated by simply a single fiber in between the source as well as a source-detector module. However, a good-quality reflection mirror is needed for this interferometer
Based on Application
Fiber optic sensors based on application are classified into three types which are discussed below.
Physical sensors
These sensors are mainly used for measuring physical properties such as stress, temperature, etc.
Chemical sensors
These sensors are to measure pH, spectroscopic studies, gas analysis, etc.
Bio-medical sensors
These types of sensors are used in different bio-medical applications like glucose content, blood flow measurement, etc.
Fiber Optic Sensor Interfacing with Microcontroller
The fiber optic sensor interfacing with the PIC microcontroller is shown below. This is used to detect Nitrate, Phosphate & Potassium in soil. To develop crop yield fertilizers including mainly
N, P & K are very important. But, the quality of these three mainly depends on the type of crop as well as plant growth conditions. In addition, the required nutrients are in macro and the main amount thus an exact control is a must and it should be maintained during the duration of the crop, which is simply the solution to get high yield and quality.
The required components of this system mainly include a fiber optic sensor, temperature sensor, humidity sensor, sunlight sensor, PIC 16F877A Microcontroller, control device, and LCD.
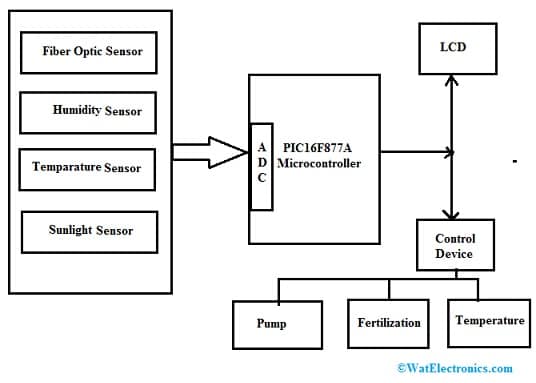
Fiber Optic Sensor Interfacing with Microcontroller
The proposed system deals with the NPK values of the soil with a multimode fiber optic sensor. The system working is shown in the above figure which includes two modules. The first module includes a crop parameter sensing unit where different sensors are used for determining the N, P, and K contents, temperature, light intensity & humidity. Here, to detect the contents of N, P, and K within the soil, a fiber optic sensor is used.
The second module includes a control device. The PIC microcontroller is used to control all the functions or operations of the various sensors used in the system. This PIC includes an inbuilt analog to a digital converter where the data from different sensors will be provided to this microcontroller.
The PIC microcontroller in this system evaluates the resulting data by necessary data and finally, the data will be displayed on the LCD. If the required data and resulting data are not matched then it will be transmitted to the control device, so that it will control all the system functions.
So, by using a fiber optic sensor, we can obtain different samples & measured transmission values in this method. As a result, we can simply detect NPK present within samples. This proposed system is very helpful in the agriculture field for detecting Phosphate, Nitrate, Potassium, detection of temperature level, Light intensity & Humidity of Agricultural surroundings. So with the help of this system, the crops’ productivity will be increased & efficient water use throughout sensor data, and the product quality is also increased by using fertilizer efficiently.
Advantages
The advantages of fiber optic sensors include the following.
- Fiber optic sensors are less costly and perform like real distributed sensors, implementation is very simple, the possibility of being multiplexed, etc.
- These sensors have unique benefits like small size, high sensitivity, resistance to electromagnetic interference & radio frequency interference, robustness, lightweight, flexibility & the ability to provide distributed or multiplexed sensing.
- The inherent benefits of fiber optic sensors include small size, low attenuation, passive, wide bandwidth, etc.
- Easily integrated into a wide range of structures.
- Not capable of conducting electric current.
- Strong and more resistant to harsh environments.
- Remote sensing capacity.
- They have multifunctional sensing capacities like pressure, strain, corrosion, acoustic signals & temperature.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of fiber optic sensors include the following.
- It is expensive.
- Detection systems are complex.
- It is different for the user and thus it needs fundamental training before they use it.
- It needs exact installation procedures/methods.
- It is difficult to develop measurement systems with fiber optic sensors.
- Once we face any difficulty with the fiber optic sensor we need special test equipment.
- Fiber optic communication is expensive compared to other broadband connection costs.
- In rural areas, the usage of these sensors is very less.
Applications
The applications of fiber optic sensors include the following.
- These sensors are used to transmit light for accuracy marking & cutting.
- These are used all over from tunnels, railways & bridges to waste-disposal systems & industrial ovens.
- These are used in environmental & industrial sensing applications.
- These are used in communications networks.
- Physical properties can be measured like temperature, displacement, pressure, strain, velocity, & acceleration within structures of any size or shape.
- In real-time, it monitors the physical strength of structures.
- It is used in tunnels, bridges, buildings, and heritage structures.
- Optical fiber sensors are used for temperature & pressure measurement within oil wells.
- These sensors are used to monitor the performance of civil infrastructures like bridges, buildings, pavements, pipelines, dams, piles, tunnels, etc.
Know more about Optical Sensor, Magnetic Sensor.
Please refer to this link to know more about Digital Image Processing MCQs.
Thus, this is all about an overview of fiber optic sensors, working with applications. This is one kind of sensing device that utilizes fiber optic technology to measure different physical quantities like pressure, temperature, voltages, acceleration, and strain. Here is a question for you, what is optical fiber?