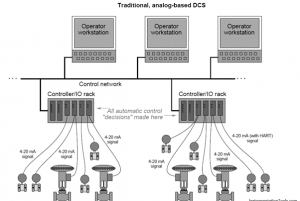
In the initial days, the process of controlling for giant industrial purposes is so difficult and developed after multiple phases. Originally, the controlling requires panels for processing of plants and this needs a huge workforce too and even this provides no exact results. And the next advancement is the transformation of all plant measurements into a permanently controlled central room where acts as the centralism of entire localized panels providing the benefit of less workforce. But seems to be uncomfortable because every control loop has its own controller-managed hardware. With the evolution of graphical displays and electric processors, the digital controllers are hosted on the array of I/O racks. This concept provided a thought for the development distributed control system. Here, the article explains its work, architecture, features, advantages, and applications.
What is Distributed Control System?
The name itself represents that DCS is a system including related computers, controllers, and sensors where all there are in a distributed format all across the plant. Every element in the system performs its own functionality like data attainment and management, process management along with the graphical display, and data accumulation. The communication between each element in the plant is done through a centralized computer which is also termed a controlling network. The crucial component of the plant is the “Distribution Control System” where is utilized for automated decision-making depending on the production updates as per reality all across the plant.
For instance, the DCS that is at the power plant spontaneously augments the steam generation ability of various turbines so as to sync with the altering demand of electricity at the time of increased temperatures and again reduces at the time of reduced temperatures. The distributed control system diagram is shown below:
Working and Operation
In a DCS system, the sensors are operated to receive data and process the information, and transfers the data to the local input/output modules where the actuators are also connected to these I/O modules. With this connection, the process parameters are exactly managed. From here, the received data is collected and sent to the process controlling section through a field bus. In the case of smart field appliances, the sensed data will get directly transmitted to the process controlling section, and the gathered data is again processed, evaluated, and generates the result depending on the control logic that is executed in the controller.
These results are now transmitted to the actuator devices through the field bus. The distributed control system alignment, authorization, and execution of control logic function at the engineering level. And the operator has the ability to look at and transmit the control actions at the functional locations.
This is the brief working of distributed control system.
Structure and Architecture of Distributed Control System
In the DCS structure, the control processing unit is distributed all across the nodes present in the system and the entire system has enhanced reliability and reduces the failure of a single processor. When a single processor gets failed the entire process will get impacted by this when there is a failure in the centralized computer unit. The dissemination of the computing power ability for the I/O field connected racks even makes sure for quick controller functionality by eliminating the probable central and network operating delays. The structure of a DCS can be clearly explained at each level.
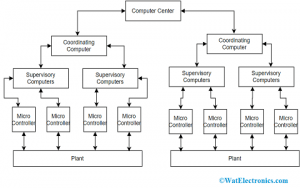
Structure of DCS
Level 0 – This level is included with field equipment like final control components like control valves, temperature sensors, and flow elements.
Level 1 – This level includes technologically advanced I/O modules and their related distributed type of electronic processors.
Level 2 – Here, regulatory computers assist in collecting data from the processor nodes present in the system and then offer the operator managed screens.
Level 3 – This is termed as the production-managed phase where it is not directly related in controlling the process but involved in examining production and monitoring targets.
Level 4 – This is termed the production scheduling phase.
Level 1 and Level 2 are considered as the operational phases of the general type of DCS where all the components come under integrated systems of a single manufacturing person. Whereas level 3 and level 4 manages to control and scheduling activities.
Whereas in the architecture of distributed control system, it has mainly three crucial characteristics which are:
- The automation of industrial procedure by assimilation of high-end control approaches.
- Arrangement of entire things as the whole system
- Multiple control functions are distributed as small sub-systems that are semiautonomous in nature. They are interrelated using high-speed communication bus and the operations consist of data management, process control, data addressing, process examination, data reporting, accumulation, and data retrieval.
The above three attributes are clearly observed in the architectural diagram of the distributed control system. Here, the 4 basic elements of distributed control system are:
Engineering Workspace
For the DCS, these elements function as the supervisory controller. This can be a computer device or any personal computer which has consistent engineering software like the ABB freelance type of DCS for control builder F engineering workspace. This element provides controlling configuration tools that permit the user to operate engineering activities like the development of new loops, forming multiple I/O points, altering control and sequential logics, the configuration of multiple devices, and formulating documentation for every I/O component and many others.
HMI or Operating Workspace
This element is employed for functionality, monitoring, and managing plant parameters. This can also be any monitoring equipment or personal computer which has a distinct software tool where the user can look at process factor values and correspondingly performs functionality. These HMI units can be of multiple or single units where single units are responsible for performing activities like alarming value and trend displays. Whereas multiple units are responsible for performing a few PC display factors, data acquisition and logging, and for trend records.
Process Controlling Unit
In a distributed control system, this element is termed the local controlling unit, processing unit, or distribution controller. A DCS might have one or more PC units that can be expanded using multiple kinds of I/O units. The process control unit is included with a potent CPU section, a communication unit having extended field bus ability, and remotely connected I/Os. The field equipment such as actuators and sensors are connected to I/O components for this unit. Few of the field equipment can have a direct connection to the field bus without connecting to the I/O module. The device which has this type of connection is called a smart field device.
The input for the PC unit is received from multiple sensors through the input section, examine and handle the received input depending on the control logic that is executed, and transmits the output through the output section in order to have regulation on relays and actuators.
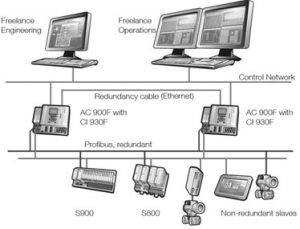
Communication Media
The communication media acts as a crucial role in the DCS. This connects the engineering workspace, process unit, operating section, and smart devices. This transmits the data across the stations. The common type of communication protocols that are utilized in the DCS consists of Profibus, DeviceNet, Ethernet, Foundation Field Bus, and others.
This is not much required to implement only one protocol for the whole DCS, few levels use only one network whereas few other levels use various networks. For example, assume that field equipment, processing station, and distributed input and output devices are interconnected using Profibus and the communication across HMI unit, processing station and engineering workspace is carried using Ethernet which is shown as follows:
The added benefit of DCS is the redundancy of few or entire levels of the controlling location. In many of the situations, complex processes are embedded with the redundant types of controllers and redundant communication networks like the issue in the major processing line show not show impact the observation and controlling activities due to the redundant processing unit.
These are the 4 fundamental elements in the distributed control system.
7 Important Features of DCS
The main features of the distributed control system are:
- Management of complicated processes
- System redundancy
- Numerous pre-defined functional blocks – DCS provides various algorithms, many standard application libraries, pre-defined and pre-tested activities to handle huge systems
- More advanced HMI design allows to manage and monitor complex systems and also this functions as a centralized system of the entire DCS.
- Enhanced scalability – The DCS structure allows more flexibility which can be used for any range of server systems
- System protection
Comparison between DCS and PLC
To know clearly on DCS, one has to know how DCS is varied from PLC.
| DCS | PLC |
| With the prevailing function blocks, custom logics are created | To create custom logic, a high level of programming languages are used |
| There is more probability of system redundancy | Redundancy is not that much required |
| The whole system acts as one complete solution | There must be provisions for the integration of functions into one single architecture |
| Most of the algorithms are complicated and there will be no variation across the applications | This requires customized routines |
| It has simple to advanced PID and even sophisticated process controlling | PLC has simple PID only |
These are the crucial differences between the distributed control systems and PLC systems.
Advantages of DCS
The advantages of the distributed control system are:
- Minimal engineering time
- DCS shows a possibility of batch management
- The system needs reduced troubleshooting
- OPC server
- The system itself drives to enhanced organization and reliability
- Included with faceplates and HMI graphics
- Superfluous functional system servers
Applications of Distributed Control System
The processors where the DCS is employed are:
- Nuclear power plants, chemical, and petrochemical, metallurgical plants
- Automobile engineering
- Food processing industries
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Water handling and sewage plants
- Environmental management systems
Please refer to this link to know more about Open Loop Control System, PLC Programming Languages.
Please refer to this link to know more about PLC MCQ’s & Control System MCQs
And this is all about the detailed concept of the distributed control system. This article has provided a clear explanation of distributed control system working, architecture, structure, advantages, features, and applications. Also, know how DCS processors are used in microcontrollers and how they work?