The differential amplifier is a basic operational amplifier that consists of three basic terminals. Among those, two are of input that is inverting and the non-inverting terminals. Hence, these amplifiers are the circuits that can perform various operations mainly it is the difference between the two applied input signals. The most important factor gain is applicable here for both the applied input signals. Hence this concept of application leads to the elimination of the noise quantity from the input signals.
The concept of DC offset and the way it performs subtraction over the applied signals makes it the best in the area of IC designing. These are the circuits with negative feedback which is proven beneficial in terms of performing various operations. These differential amplifiers can be designed with transistors or the Op-amps and are simple to analyze.
What is a Differential Amplifier?
The amplifier which amplifies the signal is the difference between the two applied input signals. This type of amplifier is defined as the differential amplifier.
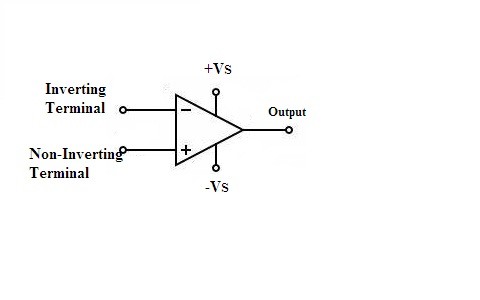
Symbol of Op-amp
The circuit of the differential amplifier can be designed by using the basic components of the semiconductors. These components can be a transistor that is it can be bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or the field-effect transistor (FET). These are also designed by using operational amplifiers.
Differential Amplifier Design using BJT
The differential amplifier designed with Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) is possible by using two transistors connected in such a way that the emitters of it are connected to the ground. The inputs are applied to the base of the transistors and the output is collected at the collector. As the emitter is common the influence of the input signals is evident at the output. The differential amplifier working is discussed below.
Once the input is applied at the base of the transistor Q1 the voltage drop is observed across the resistor. This makes the transistor Q1 with a less positive value. The drop value of the voltage is dependent on the applied input. There are two supplies present in the circuit that is at base 1 and base 2. With one supply even the circuit can function. The opposite sides of both the voltage supplies are connected to the ground or the respective constant current source.
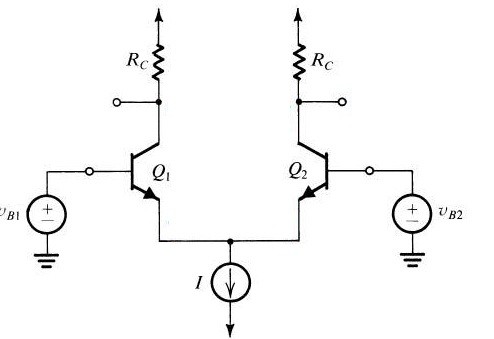
Differential Amplifier Using BJT Circuit
The conductance of the transistor T1 is based on the positive voltage applied at the input it doesn’t work if the input voltage at the base is negative.
Differential Amplifier Design using MOSFET
The basic differential amplifier can also be constructed in the same manner as BJT. The terminals sources of both the MOSFETs are connected commonly to the source of constant current. But in practice, the ideal current source is not available so that a circuit is designed and replaced with it. The circuit functionality is mainly dependent on the balance condition. This can be achieved by making the resistor’s value equal.
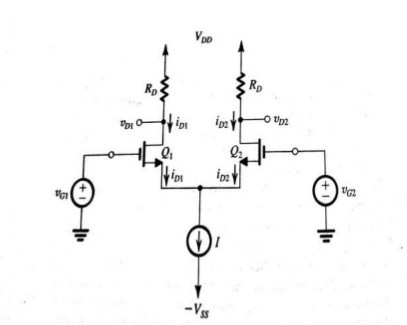
Differential Amplifier Using MOSFET
The biasing current is the sum of the currents at the drain terminal of both the transistors. In an ideal case, both the currents will also be equal. The voltage generated at the output its magnitude is dependent on the value of the current at the drain terminal.
If the applied voltage increases above the threshold value then in that case the MOSFET enters into a region called the triode. If the supposed input voltage applied at the terminal gate is increased it doesn’t affect the value of the biasing current. The biasing current is obtained by the sum of the respective drain currents.
Hence the overall current must not get affected. This is the reason if the input biasing voltage of the first transistor increases then indirectly there is a decrement in the drain current of the second transistor. This indicated the less voltage drop at the first transistor but the drop increases at the second transistor.
Differential Amplifier Design using Op-amp
The design of the operational amplifier is simple to construct. It requires two basic input terminals one is known for its inverting capabilities and the other is for its non-inverting capabilities. It has a very low input value of the impedance in comparison with other operational amplifiers.
But the drawback of this design is that the gain of these amplifiers is not in control. The amplifier without any separate feedback resistor connected to it makes it work as a differential amplifier. As for these amplifiers if the feedback type negative is applied then that results in the loss of one of the input signals.
The factor of gain can be maintained in control by connecting the resistors externally to the circuit. The resistors that are interfaced externally if they are of equal resistance value then in such cases the gain is maintained to be at unity. But this can be considered to be the most ideal case because practically it is not possible to get a gain of unit value.
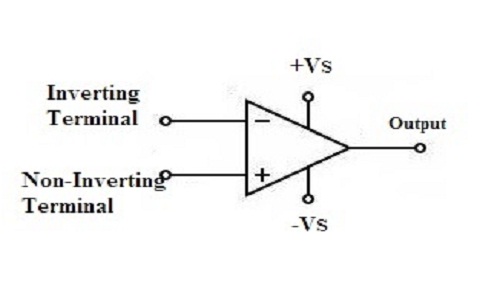
Differential Amplifier with Op-Amp
From this basic differential amplifier, two other terms called inverting and non-inverting amplifiers have been generated. In the case of inverting amplifier, the non-inverting terminal is grounded but it is not the same during non-inverting amplification. The total voltage that is generated at the output is the difference between the voltages applied at the input terminals.
However, the drawback of the gain control is improved by connecting the resistors in external ways. But still, it has the problem that it possesses low impedance values. This can be improved by the technique called buffering of the input signals.
Differential Amplifier Configurations
The way differential amplifier is configured is dependent on the inputs applied and the outputs obtained. There are four types of configurations in this amplifier. They are:
- Dual input balanced output.
- Dual input unbalanced output.
- Single input balanced output.
- Single input unbalanced output.
As the two transistors are interconnected to form the differential amplifier if it is supplied with the inputs on both the transistors it is termed as the dual input amplifier. If there is a single supply provided then it is known as a single input amplifier.
the output value of the voltage if it is collected in between the two collectors of the transistors with respect to its connection of ground is referred to as balanced output. The collection of the output from the single collector is known as unbalanced output.
These are the configurations of the differential amplifier based on the input voltages that have to be applied and the way in which the output is collected. A multiple-stage amplifier that is designed with this type of differential amplifier is connected in the form so that the required gain is obtained. As the coupling utilized here is a direct one it can remove the cut-off frequencies and make it compatible with the amplification of both the AC and the DC signals.
Applications
The differential amplifier is basically known for its difference in the applied input signals this makes it different from other amplifiers. The applications of the differential amplifier are as follows.
- Based on its way of operation its major application is that it can be referred to be used in the subtraction of the signals.
- By making it to use with an operational amplifier it can be preferred in the feedback circuit of the negative type.
- In volume control circuits these differential amplifiers are used.
- In the control circuit where the automatic gain is present these amplifiers are preferred.
- For the amplitude modulation techniques, these amplifiers are used.
The above are some of the applications of the differential amplifier.
In this way, the differential amplifier is advantageous because it can be designed with various types of basic transistors. The required gain can be obtained from these kinds of differential amplifiers. It is the best equipment designed in a simple and easy manner that possesses the characteristics of the subtraction of the signals. Hence the property of differences at the applied input signals makes it an amplifier with the differential characteristics.
Please refer to this link to know more about Class D Amplifier, Low Noise Amplifier.
Please refer to this link to know more about Differential Amplifier MCQs.
Hence it is considered to be one of the most widely used amplifiers in the platform of digital electronics. From this amplifier, one can derive inverting and non-inverting amplifiers. Now can you state one practical example where a differential amplifier was installed?