Karl Ferdinand Braun has researched the concept of the elastic strings of oscillations. He used the CRT (cathode ray tube) as an electron gun through a fluorescent screen. This screen emits a spark of light. So he built the first oscilloscope namely Braun’s electrometer. Karl Braun demonstrated the first model of oscilloscope in the year 1897. Since its development, the CRO (cathode ray oscilloscope) is an essential type of oscilloscope that are mainly used for measuring different electrical circuit waveforms.
The current CRO is mainly designed like a measuring device. As compared to all the electronic test devices, these are the most useful devices. The main feature of this device is versatility so we can find this instrument in every scientific laboratory. If the purchase of electronic measuring equipment is limited then the majority of skilled workers would choose an oscilloscope.
What is Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO)?
The term CRO stands for cathode-ray oscilloscope and it is one kind of laboratory instrument, used to display the analysis & measurement of waveforms. CRO is an extremely quick X-Y plotter that shows the input signal vs. time. These oscilloscopes analyze the waveforms, phenomena, transient & other quantities which change with time from an extremely low range frequency to the radio frequencies.

Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO)
The cathode ray oscilloscope is mainly functioned on voltage & also other physical quantities such as strain, current; pressure & acceleration are changed into the voltage using the transducer & display on a CRO. This instrument includes a luminous spot or stylus that rotates on the display region in response to an input voltage. This stylus can be produced through an electron beam that hits on a fluorescent display.
The typical form of the cathode ray oscilloscope employs a horizontal input voltage i.e, internally produced ramp voltage known as a time base. The horizontal voltage shifts the stylus periodically in a horizontal way from the left side to the right on the area of the screen.
Here the vertical voltage is nothing but the voltage below analysis. This voltage shifts the stylus up & down on the display. Once the input voltage shifts very quickly on the display, then it appears inactive. Therefore, this oscilloscope provides the visualizing voltage by changing with time.
Block Diagram of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope
The construction of a cathode ray oscilloscope can be done by using the following parts which are very essential parts in CRO. The parts of the cathode ray oscilloscope are shown below where each part is discussed below.
- Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
- Electronic Gun
- Deflecting Plate
- Fluorescent Screen for CRT
- Glass Envelop
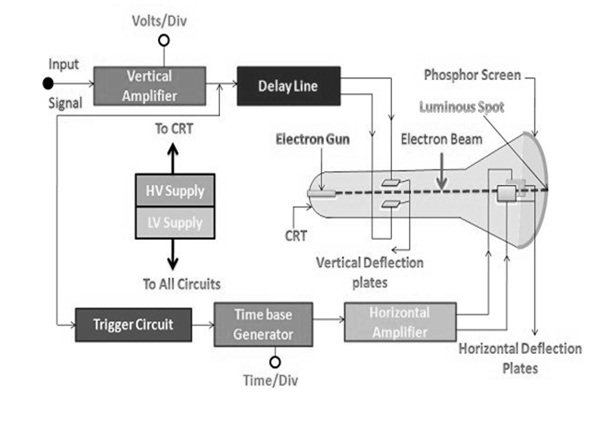
CRO Block Diagram
CRT or Cathode Ray Tube
The cathode ray tube or CRT is the vacuum tube and the main function of this tube is to change the signal from electrical to visual. The CRT mainly includes the electron gun as well as the electrostatic deflection plates like horizontal & vertical. The electron gun in the CRT will generate a focused electron ray that speeds up to high frequency.
The vertical deflection plate shifts the rays upward & downward & the horizontal plates move the electron rays from left side to right. These movements are not dependent on each other & thus the ray may be located anyplace on the display.
CRT includes different parts like heater, cathode, grid, pre-accelerating mode, focusing anode, and accelerating anode. All these parts jointly make the electron gun.
Please refer to this link to know more about Oscilloscope MCQs
Electronic Gun
The main function of an electron gun is to generate the electrons to form them into a ray. This gun can be designed with a heater, a grid, cathode, a focusing anode, an accelerating anode & a pre-accelerating anode.
For achieving the high electron emission at the normal temperature, then strontium & barium layers can be deposited on the cathode end.
After the electrons discharged from the cathode grid are done, it supplies throughout the control grid which is generally a nickel cylinder through a centrally positioned co-axial and the CRT axis. It controls the discharged electron intensity from the cathode. The electron flowing throughout the control grid can speed up a high positive potential. This potential can be given to the accelerating or pre-accelerating nodes.
The electron ray is focused on electrodes & supplies throughout the two deflection plates & goes finally on to the fluorescent lamp. Both the anodes like accelerating and pre-accelerating are connected to 1500 volts whereas the focusing electrode can be connected to 500volts
There are two focusing methods on the electron ray-like electrostatic and electromagnetic. The cathode-ray oscilloscope works with an electrostatic focusing tube.
Deflecting Plate
Once the electron ray leaves the electron gun, then it supplies throughout the two pairs of the deflecting plates. The pair of plates that emits the vertical deflection is known as a Y plate or vertical deflecting plate. The pair of plates which is mainly utilized for horizontal deflection is called an X plate or horizontal deflection plate.
Fluorescent Screen for CRT
The CRT front side is known as the faceplate and it is flat for up to 100mm×100mm sized screen. For larger displays, the CRT screen is curved a little. This plate can be formed by pushing the molten glass into a shape & then melting it. The faceplates within the surface can be covered through phosphor crystals.
The main function of phosphor is to change the energy from electrical to light. Once an electronics ray hits phosphor crystal, then it increases its energy level & thus light can be produced throughout the crystallization of phosphorous which is known as fluorescence.
Glass Envelope
The shape of the Glass envelope is an empty conical shape. The inside CRT surface among the display & neck is covered through the conducting material like aquadag. This material works as an electrode with high voltage. The covering surface is connected electrically to the anode & thus assists the electron to be the center of attention.
Operation of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope
The working of cathode ray oscilloscope is, once the electron ray is injected throughout the electron gun, and then it supplies using the control grid so that the electron intensity within the vacuum tube can be controlled. If this grid includes high negative potential, then it permits a few electrons only to supply throughout it. So, the dim spot is formed on the lightning display.
On the control grid, the negative potential is less; the bright spot can be generated. Therefore, the light intensity mainly depends on the control grid’s negative potential. Once the control grid is moved, the electron beams supply throughout the accelerating as well as focusing anodes. These anodes are at a high positive potential & they meet the ray at a specific point on the display.
Once the grid moves from the accelerating anode, then the ray comes beneath the deflecting plate’s effect. Whenever this plate is at nil potential, after that the ray will generate a dot at the center. If the voltage is applied to the vertical deflecting plate, then the electron ray focuses at the up. Similarly, when the voltage is provided horizontally then the light spot will be horizontally deflected.
Basic Controls of CRO
The basic controls of CRO mainly include position, focus, brightness, astigmatism, blanking, and calibration.
Position Control
In the oscilloscope, the knob is mainly used for controlling the bright spot position from the left side to the right. So by changing the position control knob, one can simply control the position of the spot.
Brightness Control
The intensity of the ray mainly depends on the intensity of the electron. In the electron beam, the control grids are useful for the electron intensity. Thus, by managing the voltage of the grid, we can regulate the intensity of the electron ray.
Focus Control
The focus control can be achieved by regulating the applied voltage to the center anode of the CRT. This anode & the remaining two in the region of it can form the electrostatic lens. Therefore, the lens focal length can be regulated by controlling the voltage across the center anode.
Astigmatism
In oscilloscope, astigmatism can be understood through the same incidents which exist within the eyes of a human being. In astigmatism, the dot at the middle can be moved to edges otherwise spot at edges can be moved to the middle. This entire process can be done by controlling the electron beam length.
Blanking Circuit
In the oscilloscope, the time base generator is used to generate the blanking voltage.
Calibration Circuit
In an oscilloscope, an oscillator is an essential device used for the purpose of calibration. However, it must be used in such a way that it can produce a fixed voltage square waveform.
Measurements through CRO
We can do the following measurements by using CRO.
- Amplitude Measurement
- Time Period Measurement
- Frequency Measurement
Amplitude Measurement
The cathode ray oscilloscope shows the voltage signal like a time function on its display. The voltage signal’s amplitude is stable; however, we can change the several partitions which cover up the voltage signal in the vertical route by changing the knob of volt/division on the cathode ray oscilloscope panel. So, the amplitude of the signal can be obtained which is displayed on the CRO display.
x = A sin (ωt+ϕ)
Where x is a position
‘A’ is amplitude
‘Sin’ is a sine function
‘ω’ is an angular function
‘t’ is time
‘ϕ’ is the phase difference
Time Period Measurement
The voltage signal can be displayed on the CRO like a time function on its display. The periodic voltage signal’s time period is stable, however, we can change the various divisions which cover up one whole voltage signal cycle within a horizontal way by changing the time or division knob over the panel of the oscilloscope. The time period on the CRO screen can be calculated by using this formula like T = 1/f.
Please refer to this link for Digital Storage Oscilloscope MCQs & Cathode Ray Oscilloscope MCQs
Frequency Measurement
The frequency of a signal is the mutual of the time period ‘T’. So mathematically, it can be represented as f =1/T
So, the frequency can be calculated by using two steps like the following.
First, need to find the periodic signal’s time period
From the above step, need to take the mutual of a time period for a periodic signal
Applications
The applications of cathode ray oscilloscope include the following.
- The cathode ray oscilloscope is used to examine the signal properties, testing of oscillation distortion, signals frequency response, etc.
- The CRO is used to measure the current, frequency and voltage, etc.
- These instruments are used in Radio stations for observing the transmitting & receiving properties of signals.
- CRO displays the signal properties and characteristics
- CRO helps in observing the shape of current & voltage waveform so that necessary decisions can be taken within a communication & radio station.
- These instruments are very helpful for research because if the researcher designs a new circuit, then they have to check current voltage waveforms for every part of the circuit through CRO.
- Along with the resonance circuit, the CRO is used to check the shape of signal, bandwidth, etc
- The characteristics of AM, FM circuits can be done through CRO
- The measurement of current, frequency, voltage, and phase difference can be done using CRO
Please refer to this link to know more about Sampling Oscilloscope MCQs, LIFI MCQs.
know more about Digital Storage Oscilloscope & Dual Trace Oscilloscope.
Thus, this is all about an overview of cathode ray oscilloscope and what does a cathode ray oscilloscope does, block diagram, and its applications. The CRO is the most frequently used laboratory instrument, used to provide precise time as well as the measurement of amplitude for voltage signals on a broad range of frequencies. Here is a question for you, what are the different types of oscilloscopes available in the market?