In the initial days of electronics manufacturing, engineers and designers have realized that sometimes designing a temporary circuit needs without soldering the components. So, an engineer took cardboard and arranged several rows into it to place nails. As per the circuit diagram, they placed components and nailed them through short wire pieces. The electrical connection can be provided by wrapping wire or soldering around the nails, and then components could be soldered to the wires. But by using cardboard, some resistive features may cause power loss. So, to overcome this process, at present breadboards were implemented by the scientists. Breadboards are one of the most essential rectangular pieces, used to build different circuits without soldering. This article discusses an overview of what is a breadboard, working, types and applications.
What is a Breadboard?
As the name suggests, the term breadboard can be derived from two terms namely bread & board. Initially, this was used to cut the bread into pieces. Further, it was called a breadboard & it was used in electronics projects and electronic devices in the year 1970. A breadboard is also known as a solderless board because the component used on the breadboard does not need any soldering to connect to the board, so it can be reused.
Breadboard
The arrangement of different components on a breadboard can be done by inserting their terminals into the breadboard, so it is frequently known as a plugboard. Breadboard definition is a plastic board in rectangular shape that includes a lot of small holes in it to allow you to place different components to build an electronic circuit is known as a breadboard. The connection on the breadboard is not permanent but they can be connected without soldering the components.
If you make any mistake while connecting the components, you can place or remove the components effortlessly. For beginners of electronics, this device is very helpful to make mini-projects. If a designer builds a simple circuit that they desire to analyze, then a breadboard gives a quick solution. The breadboard diagram is shown below.
The material used to make the breadboard is white plastic. At present, most of the breadboards are solderless types, so we can directly plug in the components directly and connected them through the exterior power supply. The different kinds of breadboards are accessible according to the specific point holes. For instance 400 point type, 830 point type, etc.
Specifications & Features
The specifications & features of a breadboard, include the following.
- Distribution Strips are two
- Wire Size is 21 to 26 AWG wire
- Tie Points are two hundred
- Withstanding Voltage is 1,000V AC
- Tie points within IC are 630
- Insulation Resistance is DC500V or 500MΩ
- Dimension is 6.5*4.4*0.3 inch
- Rating is 5Amps
- ABS plastic through color legend
- ABS heat Distortion Temperature is 183° F (84° C)Hole or Pitch Style is 2.54mm
Types of Breadboard
Breadboards are classified into two types like a solderless breadboard and a solder-able breadboard.
Solderless Breadboards
This is the most commonly used breadboard for prototyping as well as testing electronic circuits without soldering the components. These are available in different shapes, sizes as well as ratings.
The circuits on these breadboards are not permanent so we can check & test the functionality of a circuit before confirming its design onto a PCB. These breadboards include rows & columns with holes that allow the leads of components & wire gauges.
If the terminal of the component does not place into the hole of a breadboard, then a connecting wire can be soldered to the lead of a component that will insert in the breadboard hole.
Advantages
The advantages of solderless breadboards include the following.
- It doesn’t require soldering to connect the components on board.
- If the circuit is not working properly then, we can easily check and rectify them by taken out the components & replace them easily.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of solderless breadboards include the following.
- Components that are connected to the breadboard can come loose once the breadboard is pushed or moved.
- This kind of breadboard is available with high parasitic capacitances because of the capacitances among different components which are being close to each other.
- These breadboards are restricted to below or 10 MHz frequencies.
Solderable Breadboards
These types of breadboards offer a permanent setup for your electronic circuits. This kind of breadboard gives a stronger setup. It includes holes for electronic components including copper tracing. These components can be soldered using soldering iron for soldering the components to the breadboard so that an electrical connection can be formed through the copper tracing.
For designing a circuit, jumper wires are needed for soldering separately in between these components to make a lane to permit the flow of current. These types of breadboards are available in different sizes based on the requirement.
Advantages
The advantages of solderable breadboards include the following.
- These breadboards are robust and your circuit will be very secured on this type of breadboard.
- This kind of breadboard gives your project a more specialized look.
- Less cost and saves time while designing a circuit.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of solderable breadboards include the following.
- If there is any error occurs in the circuit then de-soldering may cause damage to components
- This board cannot be reused.
Selecting the breadboard from these two types will depend on the requirement as well as application. We have already discussed the pros and cons of these types of breadboards, so you can select accordingly
A solderless breadboard is suitable when you want to check a circuit without soldering the components. Similarly, if you want to check your circuit below some conditions that involve several movements similar to a robot then a solderable breadboard is the best option.
Breadboard Connections/Layout
Breadboards include several holes which are called tiny sockets. The arrangement of these can be done on a 0.1 grid. Most of the terminals of components can be placed directly into the holes on the board. Integrated circuits (ICs) are arranged across the middle gap through their dot or notch to the left. The designing of wire links can be done using a wire coated with plastic and single-core and the diameter of the wire is 0.6mm. Here, each connection on the breadboard is discussed below.
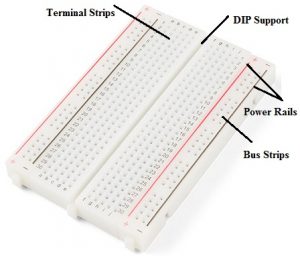
Breadboard Layout
Different electronic components are compatible with breadboards like resistors, capacitors, switches, diodes, etc. These components which include lengthy metal legs are known as leads whereas components that include shorter metal legs are known as pins. All the electronic components including different sizes of leads will function through a breadboard.
Breadboards are mainly designed with holes to insert the components in the holes tightly, so they cannot fall out but they can drag them to detach them. The appearance of a breadboard includes rows, column, numbers, letters, blue & red lines
Letters
Letters on the breadboard are printed at the top & bottom that ranges from A to J that runs horizontally & the holes can be divided consistently into vertical lines.
Numbers
The horizontal rows can be identified through 1 to 30 numbers which are printed on the right and left edges on half-size breadboards, whereas in full-size boards 60 or 63 numbers are printed. Both the numbers & letters together will direct you to place a specific hole simply while designing complicated circuits.
Terminal Strips
In the breadboard connection, the metal rows include small clips under the holes of a breadboard. The arrangement of every socket and metal strip can be spaced through a typical pitch with 2.54mm. These clips give support to connecting wires as well as leads of components to stick into the breadboard holes.
When any component is placed on a breadboard then the power supply can also be provided to any hole in that row because these are conductive & permits the flow of current from any end in that strip. Each strip in the breadboard includes five clips so we can connect simply five components within one specific section in the breadboard.
The row in the breadboard includes ten holes where each row can be separated through a crevasse or ravine in the center of the breadboard. This ravine separates both sides of rows & they are not connected electrically.
Power Rails
In the breadboard, there are horizontal and vertical rows, where the horizontal rows can be known as power rails and vertical rows are known as terminals. These are mainly useful in connecting the power supply toward the breadboard.
On this board, the red lines are positive rails whereas the blue lines are the negative rails. Usually, breadboards have different connections like power rails which are known as metal strips.
While connecting a circuit on a breadboard, we need power in various places, so power rails can provide you easy access wherever you require it within your circuit. Here, power rails (red/black or blue strips) are labeled with positive (+) and negative (-) symbols for indicating the +ve & -ve sides.
It is significant to be alert that the power rails on each side are not connected, thus if you want a similar power source on two sides, then you have to connect the two faces through some jumper wires.
Rows and Columns
In breadboards, we can notice that rows and columns are marked through letters. These are very helpful while designing a circuit on the board. If the component on this board is misplaced by mistake then the circuit can get quickly complicated otherwise it will not work at all. If you identify the row number in the breadboard for the connection then it is very easy to place the component into the board.
On the breadboard, the connection of the circuit doesn’t have to be in the correct location as shown in the circuit. Actually, it doesn’t even have to look similar. If all the circuit connections are being completed, you can design your circuit in your way.
Terminal Strips
Terminal strips in breadboards occupy most of the place. These are made up of small holes, where you can insert your components. The connection of these strips can be done in a specific way depending on their columns & rows. It is essential to recognize the terminal strip layout on the breadboard. Check the breadboard labeling before inserting components.
Metal Clips
In every breadboard, metal clips will hold an electronic component once it gets plugged in. The arrangement of these clips can be done in lines that respond to the rows as well as columns on the terminal strips of the breadboard. So that you can notice & control which components are inserted on the board
Binding Posts
Some kinds of breadboards are designed on a stand that includes binding posts by attaching to it. These posts permit you to attach all types of power sources to your board. In some types of breadboards, binding posts are used to connect exterior power sources. The primary step to use these posts is to attach them to the board through some jumper wires.
By using these posts, we can simply connect wires toward the posts to attach them to the board. Usually, you have to attach a power as well as the ground wire from the posts toward the breadboard. If you require any additional power source, then you can utilize the alternate post. Once the posts are connected to the breadboard, then you can use several methods to fix the power supply toward the posts as well as toward the breadboard.
Benchtop Power Supplies
Benchtop power supplies mainly used in electronics labs which provide an extensive range of current & voltage to your circuit. A banana connector is used to give a power supply toward the binding posts. The power supply to a breadboard can be supplied with binding posts using banana cables.
On the other hand, you can use IC hooks, alligator clips otherwise any other cables through a banana connection to hook your board up to various supplies. Another advanced technique of utilizing the binding posts is to connect a barrel jack with wires & attach them to the posts but it needs some middle soldering skills.
Connection of ICs on Breadboard (DIP Support)
Generally, connecting electronic components on a breadboard like resistors, capacitors, diodes, etc is quite easy but connecting integrated circuits (ICs) is quite different. When we notice the board, there is a gap line within the two vertical columns. This gap is very helpful in connecting ICs on a breadboard.
We can place any size of integrated circuits onto the breadboard through break rail without shorting its terminals. You can notice the connection of IC in the following image, which includes five holes within a single column. Once an IC is placed then we can have four available holes for each pin of an IC to make interconnection. We can place a wire at any place from these 4 points to acquire a connection through that specific IC pin.
Breadboard Wires
There are different types of wires are used for breadboards based on the requirement. So selection of wires is essential for breadboards to build the projects, so instead of standard wires, different types of wires are used which include the following.
Jumper Wires
Jumper wires are used in making small circuits as they are slightly longer. These wires are harder to track the errors. Jumper wires metal pins connected to the end and are flexible, so it will be simple to insert into the board. In electronics stores, these wires are easily available but at little cost.
Jumper Wire Kit
The jumper wire kit is one kind of plastic box including wires in different sizes, lengths, and colors. Both the ends of these wires are twisted at 90 degrees so that it will be very easy to insert into the breadboard. As compared to lengthy wires, these wires are very perfect & neater Jumper wires are available with two or more links in several colors, make it difficult to arrange the circuit with standard color code.
Hookup Wires
These wires are also called lead wires which are available in rolls and insulated with single-core. The length and the insulation of this wire can be removed through some tools namely wire strippers to use as a jumper wire. These kinds of wires are available in various colors and at less cost. So we can easily color-code the circuit.
Before choosing these wires, one thing we have to keep in mind that is, you have to purchase solid single core type wire instead of standard wire. Because solid core type wires are designed with a single solid metal part because these are very rigid. So inserting it into the breadboard is very simple. Whereas, standard wires are designed with several separate wires but these wires are very solid to insert into the breadboard
Alternatives
The alternatives of breadboards which need soldering are veroboards & protoboards. The most similar type of board is the Veroboard which includes holes that are connected through a single axis. Another alternative is protoboards which include similar kinds of holes but none of the holes on the board are connected.
Advantages
The advantages of breadboard include the following.
- It is used to make a temporary prototype for the electronics projects
- This is reusable because it doesn’t need any soldering.
- These boards are less weight because the material used to make this board is a lightweight plastic material.
- Testing can be done very easily
- The arrangement of these components can be done very simply into the holes on the board to make the design of a circuit.
- It is economical and simple to use
- It does not use any difficult parts.
- Drilling is not necessary to connect the components because the holes on the board are embedded already
- Modifying can be done very quickly
- We can add or remove the components on the breadboard
- These boards are available in different sizes and shapes
- These boards can be adjusted very easily
Disadvantages
The limitations or disadvantages of breadboards include the following.
- These boards are not used for high current applications
- For low-frequency applications, low-frequency boards are not used
- For making simple circuits, it needs more physical space.
- The number of connections on the breadboard can make the circuit messy because of several wires.
- The connections on the board can be disturbed once the components are connected or removed.
- Reliable connections are less
- Signaling is limited.
Uses/Applications
The applications or uses of a breadboard include the following.
- The main application of a breadboard is to form simple electrical connections among different components so that you can check your circuit before soldering it to the board.
- These boards allow different components to be simply placed or removed or the term prototyping instantly comes to mind permanently.
- If a designer designs a simple circuit or module then they need to check, so this board offers a fast & cheap solution
Different Ways to Power a Breadboard
There are different methods to providing power supply to a breadboard like using Arduino Board, Battery & a Dedicated Power Supply.
Using Arduino Board
If you are an Arduino user, then this technique is very simple for you because, the Arduino board gets its power supply from an exterior power supply or a computer, so you can just give power to a board by borrowing its power supply. To protect the board from the Arduino, you need to follow these steps
- First, connect the GND pin of an Arduino using female headers to the power rails of the board
- From the header, the red wire can be connected to the +ve power rail of the board
- Black wire can be connected to the –Ve power rail of breadboard from the GND terminal of Arduino.
Using a Battery
- The second method to power a breadboard is using a battery like the following.
- Connect the red wire of a battery to a positive bus
- Connect the black wire of the battery to the negative bus
How to Use a Breadboard?
Here is a simple example circuit to know how to use a breadboard. First, we need to connect a simple circuit to the breadboard. Previously, we have discussed the board, connections, and it’s working but now we have to start connecting a circuit on a breadboard. Here, a simple LED circuit is taken to give connections on the board. This circuit can be built with a resistor, LED, and power supply. To make a circuit with an LED, the following steps we have to know.
- A breadboard
- Connecting wires
- 9V battery
- Battery
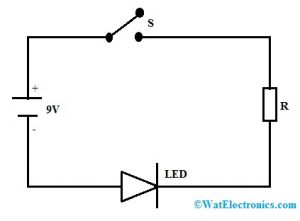
Basic LED Circuit Diagram
Step-1
Place the LED into the Breadboard by bending the long terminal of the LED. Plug the anode terminal of the LED into the top rail on the breadboard whereas the short terminal is inserted into the main part
Step-2
Place the resistor on the breadboard & bend the resistor terminals to plug one of the terminals of a resistor into a hole under the cathode terminal of the diode.
Step-3
Place the connecting wire into the Breadboard under the resistor terminal & the bottom rail.
Step-4
Connect the two terminals of the battery to the Breadboard. In this board, the battery’s red wire can be connected to the top rail whereas the black wire can be connected to the bottom rail. Switch on the battery to provide the power supply to the circuit so that the LED will turn ON.
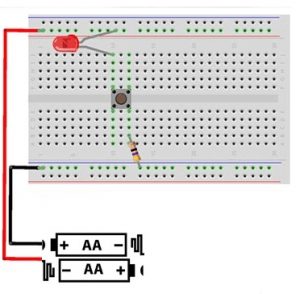
Circuit Connection on Breadboard
Common Mistakes
A common mistake while connecting a circuit on a breadboard is not very important because connections of the board are temporary. So, you can simply reconnect the circuit by changing the components. However, you have to pay attention to some common faults & keep away from them to complete your project easily. The common mistakes are
- Touching terminals
- Forgetting to connect both faces of the board using jumper wires
- Leads connection to incorrect row
- Mixing positive & negative wires
- Reversely connected polarities
- Inadequate contact among leads & clips
- Connecting one component leads within the similar row
Safety Tips for Breadboard
It is very important to connect a circuit systematically & neatly on a breadboard so that one can correct it & get it running simply & rapidly. It also assists once someone else requires knowing and inspecting the circuit. The following tips are very useful for breadboard.
- Use the top & bottom bus rails always for connecting power supply instead of using a direct power supply
- When the jumper wires are coded with color then it will help in reducing the confusion while designing a circuit. For instance, green color wires are used for GND connections, red color wire for +Ve power whereas black color one is for -Ve power connections.
- Jumper wires should be connected lay flat on the board so that the board does not turn cluttered.
- Connect the jumper wires in the region of the ICs but not on the packages so that IC can be changed easily when required.
- Cutting the components leads can lead to insert very closely to the board.
- Be careful when connecting components
- It is significant to be particularly careful while placing ICs into the holes of the board.
- Power supply terminals should not connect otherwise it may cause a short circuit.
- Once the board is connected to the power supply, do not leave it alone
- Do not stroke the IC elements with uncovered hands once the circuit supplies through it because they are sensitive components, so there is a chance to get damage.
- Once the power supply is given to the board, do not connect or remove components
- It is necessary to monitor exact polarity once certain components are connected to the circuit, otherwise, that may break down the dielectric within the component
- If water or liquid dropped onto the board, then right away remove it from the power supply.
- Maintain your surroundings clean and in sequence
Breadboard Sizes
There are different sizes of breadboards are available in the market which is used based on the application.
- Half Size
- Tiny Breadboard
- Little Breadboard Bits
- Large Breadboard
Half Size
The half-size breadboard is applicable for mini-projects. The length and width of this board is 5.5 cm x 8.5 cm including a standard dual strip within the middle & two power rails on two faces. In this breadboard, power rails can be removed simply to make the board thin.
Tiny Breadboard
These breadboards are very small in size. This kind of breadboard does not include power rails however it includes 17 rows. These boards are applicable when you have fewer components to connect.
Little Breadboard Bits
These breadboards are available in different sizes like 4X4, 2X8, and 2X4. The 4×4 type includes hour strips with four-pin terminal strips. The 2×8 type includes 8 strips with two-pin terminal strips. The 2×4 boards include 4 strips with two-pin terminal strips.
Large Breadboards
Large breadboards are big in size, very useful for major projects which are located onto a metal plate. These boards are available with four colored posts which can be used through a bench-top supply. These boards include bumpers to maintain the board from slipping in the region of your desk.
How to Choose a Breadboard?
There are several factor need to consider while choosing a breadboard. The following factors need to consider once purchasing a breadboard.
- Spring Contacts
- Construction of Power Rail
- Plastic Housing
- Several Breadboards Mechanical Mating
- Backing of Breadboard
- Metal Plate based Assemblies of Breadboard
- Breadboards Size & Quantity
- Power Supplying to the Breadboard
Thus, this is all about an overview of a breadboard, connections, how to use, different wires used, types of boards, advantages, disadvantages, and its uses. From the above information, finally, we can conclude that it is used to connect and test the circuits. Breadboards are essential to building different circuits as well as electronics projects. A breadboard allows you to test your own mini-project circuits, however, it also includes the correct category to assist you to follow a board diagram.
The connection of a circuit can be done by inserting different components through holes on the breadboard. The main benefits of using a breadboard are that the electronic components are not soldered. If the components are placed incorrectly then they can be moved simply to the latest location on the board. Here is a question for you, what is a Printed Circuit Board or PCB?