A PNP transistor is a semiconductor device, made with N-type doped material arranged between two P-type materials. The majority-charge carriers of this transistor are holes emitted by the emitter and collected by the collector. The flow of electrons in this transistor will be from the emitter terminal to the collector. Thus, this transistor will be turned ON whenever there is a zero voltage on the base terminal. This article provides brief information on one of the PNP-type transistors namely; BC556 transistor, pinout, specifications, and applications.
What is a BC556 Transistor?
BC556 is a PNP transistor, used to switch or amplify electronic signals & electrical power. This transistor includes three terminals, used for connecting to an external circuit. This is a PNP Transistor, so needs to provide 0V to the transistor’s base terminal to turn it on. The current or voltage is applied to one pair of transistor terminals, which then controls the flow of current through another pair of terminals. This is because the output power exceeds the input power, resulting in signal amplification by the transistor.
The BE voltage of this transistor is approximately 660 mV. The gain of the BC556 transistor ranges from 125 to 450 which decides the transistor’s amplification capacity. The peak current supplied throughout this transistor is around 200mA which merges with the gain value to make this transistor an ideal choice mainly for an audio amplifier.
Working
Whenever the BC556 transistor is biased, then it allows 100mA of the maximum current across the collector to the emitter junction, known as the saturation state. In this state, driving a load that utilizes > 100mA current may harm the device. We know already that a transistor is a current-controlled device. Thus, whenever the base current is detached, the transistor will be turned off completely, known as the Cut-off Region.
A transistor needs a little current to turn it on. The current required to turn ON this transistor is < 2mA because BC556 is a PNP transistor, so it turns on whenever the base terminal is connected to the GND & it will be turned off whenever a positive voltage is provided to the base terminal of the transistor.
This transistor is turned ON whenever the base terminal is connected to the ground. This transistor will stay ON unless the voltage supply at the base terminal of the transistor achieves the above turn-off voltage of the base which ranges from 0.7V to 0.9Volts.
Pin Configuration:
The pin configuration of the BC556 transistor is shown below. This transistor includes three terminals like emitter, a base, and a collector which are discussed below.
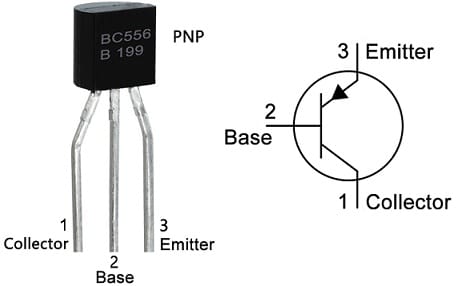
BC556 Transistor pin Configuration
- Pin-1 (Collector): This terminal collects the electrons emitted from the emitter.
- Pin-2 (Base): This terminal helps in controlling the transistor biasing.
- Pin-3 (Emitter): Emitted electrons from the emitter move into the primary PN junction.
Features & Specifications:
The features and specifications of the BC556 transistor include the following.
- BC556 is a three-terminal PNP transistor.
- It is available in a TO-92 and SOT54 plastic package.
- Collector to emitter voltage of this transistor or VCEO is -65V.
- It has low noise.
- This is a Pb−Free transistor.
- Its maximum current is 100 mA.
- This transistor uses advanced process technology.
- It has low error voltage and fast switching speed.
- It has high power & current handling capacity.
- Its collector power dissipation maximum is 0.5W.
- Collector to base voltage maximum is -80V.
- The emitter to base voltage is -5V.
- Its maximum collector current is 0.1 A.
- Its collector capacitance is 8 pF.
- The transition frequency is 150 MHz.
- Its operating junction temperature maximum is 150 °C.
Equivalent & Complementary Transistors
Equivalent BC556 transistors are; BC558, A1015, S8550, BC557, 2N4403, 2N3906, BC857, 2N5401 & 2N2907. Complementary BC556 transistors are; BC546, BC548, BC547 & BC549. To know how to replace a transistor, you need to refer to this link; Replacing Transistors in Electronic Circuits: Factors and Considerations.
How to use BC556 Transistor Safely in a Circuit?
To use the BC556 Transistor securely in a circuit, we suggest using this transistor below its maximum ratings. Do not drive > 100mA load. The highest collector-to-emitter voltage is -65V thus do not drive >-36V load. This transistor’s maximum operating junction temperature must be 150 °C.
Connecting a resistor to the transistor’s base terminal in any circuit is compulsory to keep away from it being damaged. To know more about that, please refer to this link; Choosing Base Resistance for Transistors in Electronic Circuits.
Lamp Flasher Circuit using Transistors
The simple electronic circuit known as a Lamp Flasher is commonly used to produce a visual signal in the form of a flashing LED or Lamp. It can flash incandescent lamps with a 6-Volt rating. This circuit is often employed for creating flashing beacons on vehicles and can also be seen in use for warning and construction signposts.
The required components to make this circuit mainly include; two transistors like; a breadboard, BC556 & BC549, resistors like; 1K, 15K & 100K, a 6V Battery, a Lamp, a 10uF electrolytic capacitor & connecting wires. Connect the circuit as per the below circuit shown.
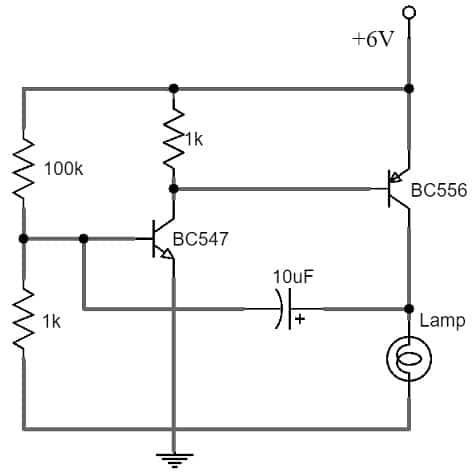
Lamp Flasher Circuit using Transistors
Working
This simple lamp flasher circuit works on the regenerative feedback principle. Once the power supply is provided to this circuit, the 6V DC works as a control signal to the Q1 BC549 transistor base terminal. After that, this transistor output works as the input signal to the Q2 BC556 transistor. From the collector terminal of Q1, the output DC signal works as a control signal mainly for the Q2 transistor. This activates the collector o/p of the Q2 transistor & the 6Volts lamp will start flashing. This circuit is very handy & can be fit easily within a small box.
This lamp flasher circuit is used in different circuits like; a micro-power-based low battery indicator, an off-line switching power supply & a lightning detector. This circuit can also serve as windshield wiper controllers, micropower high voltage supply, police sirens, and lamp dimmers in various devices. It can also be used in hazard flashers, turn indicators of different vehicles, etc.
BC556 Transistor Applications
The applications of the BC556 transistor include the following.
- BC556 transistor is used to design simple audio circuits.
- It can serve as a general-purpose amplifier.
- Users employ this transistor in driver modules, which incorporate LED driver, Relay Driver, etc.
- They utilize it in amplifier modules like signal amplifiers, audio amplifiers, etc.
- The transistor is integral to the Darlington pair.
- Designers use it to drive loads <100mAmps.
- They incorporate it into circuits such as Preamplifier circuits, H-Bridge circuits, oscillator circuits, current mirror circuits, comparator circuits, etc.
- It plays a crucial role in impedance buffering, linear amplifiers, astable multivibrators, bistable multivibrators, and switching applications.
Please refer to this link for the BC556 Transistor Datasheet.
Thus, this is an overview of the BC556 Transistor, pinout, specifications, circuit, working, and its applications. The BC556 PNP transistor is used in AF amplifier and switching, signal amplification, and audio pre-amplification applications. It is available in three special part numbers; BC556A, BC556B, and BC556C. But the main difference between these three part numbers is mainly their hFE values. So, the BC556 transistor current gain value ranges from 110 to 800, the BC556A current gain value ranges from 110 to 220 and BC556B transistor current gain value ranges from 200 – 450 & BC556C has 420 – 800 current gain value. Here is a question for you, what is a BC880 transistor?