The BC548 is an NPN epitaxial silicon transistor that was created with the metal-cased BC108 family transistors. This transistor is a successor to the BC238 transistor & different from the BC108 transistor in the package shape. The specifications of the BC548 transistor are the same or exceed the BC148, BC238 & BC108. So this transistor is a suitable alternative within any circuit that is designed for the older BC148 or BC108. The BC548 transistor is generally used in American & European electronic equipment. It is the first type of BJT, so used in hobby electronics designs wherever a general-purpose transistor is necessary. This article provides brief information on the BC548 transistor, pin configuration, specifications, and its applications.
What is a BC548 Transistor?
The BC548 is an NPN type of bipolar junction transistor that is used in many electronic circuits for switching & amplifying purposes. This transistor can be used as a switch to drive load below 500mA. This transistor is available in special module numbers like; BC548A, BC548B & BC548C but the main difference among them is their DC current gain value only. The gain value of BC548A transistor ranges from 110-220, BC548C gain ranges from 420 – 800 and BC548B ranges from 200 – 450. So this gain value will decide transistor’s the amplification capacity.
Working
The working of the BC548 transistor is; this transistor is biased by supplying current to the base terminal which must be restricted to 5mA. Whenever the base pin of this transistor is held at the ground terminal the emitter & collector terminals will stay open. Similarly, whenever a signal is given to a base terminal then it will be closed. Once this BC548 transistor is completely biased it allows a 500mA of maximum current to supply across the emitter & collector terminals, this stage is known as the saturation region. Once the base current is detached this transistor will become completely off, known as the Cut-off region. The maximum current amount that could be supplied throughout the Collector terminal is 500mA, so we cannot connect any load that uses above 500mA.
The input voltage which is applied at the base terminal is increased slightly then it generates a large change within output voltage across both emitter & collector terminals. As compared to both base and collector terminals, the emitter terminal is doped highly. So the voltage at the collector terminal is larger as compared to the base voltage.
Pin Configuration:
The pin configuration of the BC548 transistor with its symbol is shown below. This transistor includes three terminals and each terminal and its functionality is discussed below. These three transistor terminals are dissimilar in terms of doping concentration & operation.
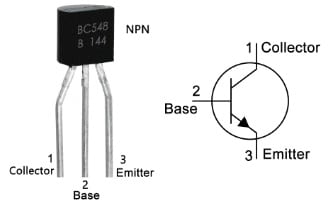
BC548 Transistor Pin Configuration
- Pin-1 (Collector): Current flows in throughout this terminal.
- Pin-2 (Base): This pin controls transistor biasing.
- Pin-3 (Emitter): The flow of current Drains out throughout this terminal.
Features & Specifications:
The features and specifications of the BC548 Transistor are discussed below.
- It is a Bi-Polar and NPN-type transistor.
- This transistor includes three pins.
- This transistor is available in the TO-92 package.
- Its collector current (maximum) is 500mA.
- Its collector-to-emitter voltage (max) is 30V.
- Its collector to base voltage (max) is 30V.
- Its emitter to base voltage (max) is 5V.
- Its transition frequency is 150 MHz.
- Its collector dissipation (max) is 625MW.
- Its DC current gain ranges from 110 to 800.
- Its storage and operating temperature must range from -55 to +150C.
- The type of mount is a through-hole.
- Its moisture sensitivity level or MSL is 1 (Unlimited).
- Its maximum power is 500mW.
Equivalent & Complementary Transistors
Equivalent BC548 transistors are; BC547, BC549, BC550, 2N2222, 2N3904 and 2N3906 and PNP complementary BC548 transistor is BC557, BC558 & BC556.
How to use BC548 Transistor safely in a Circuit for a Long Time?
To increase the BC548 transistor’s performance, you have to follow the specifications given above. Do not drive any load above 30V and use the transistor pins with exact direction because a wrong connection can lead to transistor damage. A suitable resistor needs to be used always at the transistor base terminal to provide it necessary current. Always need to maintain the temperature from -55 to +150C.
Crystal Tester Circuit with BC548 Transistor
The crystal tester circuit using the BC548 transistor is shown below. Generally, in making different electrical and electronic projects, you need to choose the right frequency crystals. For that, you require a crystal tester circuit which is also called an xtal tester circuit. This circuit is very helpful in checking whether a crystal element is functioning fine or not. Crystals are very significant elements within many circuits as well as projects. This tester circuit simply forms an oscillator circuit. If the crystal works properly then the LED will blink.
The required components to make this crystal tester circuit using the BC548 transistor are shown below. This circuit can be build with different electronic components like; 6V DC supply, BC548 transistors-2, 1N914 diodes-2, LED, Resistors like; 2.2KΩ, 47KΩ, 1KΩ and 10KΩ and capacitors like; 0.1µF, 1nF & 100pF. Connect the circuit as per the circuit diagram shown below.
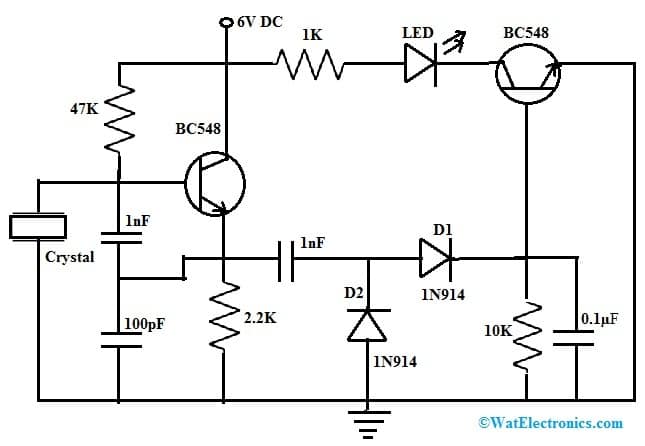
Crystal Tester Circuit using BC548 Transistor
Working
This circuit uses two BC548 transistors which are connected simultaneously. This circuit works with 6 volts and the resistors in the circuit are connected before every component to restrict the flow of current. In this circuit, the crystal is connected directly to the T1 transistor’s base terminals. Whenever the crystal generates oscillator signals it will trigger the T1 transistor where this transistor’s output can be rectified through 1N914 diodes.
After that, this output is filtered through capacitors before achieving a T2 transistor. Once this transistor gets this signal it will activate which drives the LED. If the LED glows then the crystal will work properly. If the LED in the circuit does not glow then we can conclude that it shows the crystal under test is faulty or damaged.
There are many electronic projects which work with high-frequency equipment. These projects use normal crystals to produce the oscillator circuit’s frequencies. By using this crystal tester circuit, you can simply test & verify any crystal operation.
Advantages
The advantages of a BC548 transistor are discussed below.
- This transistor uses superior process technology.
- This transistor’s error voltage is low.
- Its switching speed is very fast.
- It has full voltage operation.
- It has high current & power handling ability.
- This transistor’s DC current gain is very good.
- It provides less noise as compared to other transistors like; BC549 & BC550.
- This transistor handles with 500mA of maximum current so it drives many other components like integrated circuits, other kinds of transistors, part of circuits, LEDs, relays, etc.
BC548 Transistor Applications
The applications of a BC548 transistor are discussed below.
- BC548 transistor is used to amplify weak signals within Darlington pairs.
- This transistor is used in sensor circuits.
- This transistor is used to drive loads below 500mA.
- It is used for audio amplification and also different driver modules like; LED driver, switching, and relay driver.
- These are used in amplifier modules such as; signal amplifiers, push-pull amplifiers, audio amplifiers, etc.
- These are used in amplifiers, audio preamps, touch switches, LED flash, RF, Heat sensors, and PWM circuits.
- These transistors are used in quick-switching devices and alarm devices.
- This transistor is used in various general-purpose applications.
- These transistors replace other types of general-purpose transistors such as; BC547, 2N3904, etc.
- The collector current of this transistor is 500mA which is a very good feature of this kind of transistor so you can drive a broad range of loads simultaneously within an electronic circuit.
- This transistor has extremely good collector dissipation & DC current gain characteristics so it is perfect to utilize it in amplification as well as pre-amplification phases of a circuit.
Please refer to this link for How to Select a Transistor.
Please refer to this link for the BC548 Transistor Datasheet.
Thus, this is an overview of the BC548 transistor, pin configuration, specifications, circuit, working, and its applications. The BC548 transistor is broadly used and can be obtained easily from different electronic components stores. This transistor is used to drive different loads maximum of 500mA of current like LEDs, relays, and many more. The maximum collector dissipation of this transistor is 625 milliwatts, so it is a good feature to utilize it as a small amplifier. Here is a question for you, what is a BC547 transistor?