The transistor is a semiconductor device that includes three terminals like emitter, base, and collector. The main function of the transistor is for switching and amplifying the base signal. But at present, these are frequently used within embedding integrated circuits. These transistors are available in two types PNP and NPN. In PNP transistors, the majority of charge carriers are holes whereas in NPN-type transistors, the majority of charge carriers are electrons. In transistors, the most common category is BJT or Bipolar Junction Transistor. This article provides brief information about BC547 Transistor, pin configuration, specifications & its applications.
What is BC547 Transistor?
BC547 is an NPN type of bipolar junction transistor that includes three terminals like Emitter, Base & Collector. This transistor is forward-biased whenever the current supplies from the collector terminal to the emitter. This transistor works as a closed switch when a high voltage signal (5V) is applied to the base terminal, known as forward biasing. Similarly, this transistor works as reverse biased if the transistor’s base terminal is connected to GND where the emitter and collector terminals will work as an open switch. So there is no flow of current throughout the transistor.
This transistor controls a large amount of current at the emitter & collector terminals when a small amount of current is supplied to the transistor’s base terminal. This NPN transistor is generally used for switching & amplification purposes.
Working
BC547 is an NPN transistor where a P-region is sandwiched between two N-type regions. A depletion region is created at the border of the P & N, a, which blocks the flow of charge carriers from one region to another.
Whenever the input voltage is applied at its Base terminal, some amount of current will start flowing from the base terminal to the emitter & controls the flow of current at the collector terminal. The voltage supply between the base & the emitter is, at the emitter terminal, it is negative at the base terminal & is positive at the base terminal.
The voltage supply between the collector & the base is negative (-Ve) at the base terminal & positive (+ve) at the collector terminal. The voltage supply between the collector & the emitter is, it is negative (-Ve) at the emitter terminal & positive (+ve) at the collector terminal.
Pin Configuration:
The pin configuration of the BC547 transistor is discussed below.
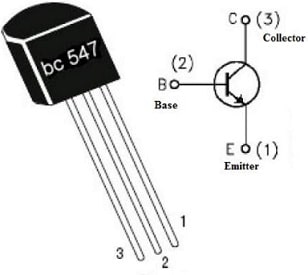
BC547 Transistor Pin Configuration
- Pin1(Collector): This pin allows the flow of current. This terminal collects the majority of charge carriers from the emitter terminal.
- Pin 2 (Base): This pin controls the transistor biasing.
- Pin3(Emitter): Current drains out from this pin. This pin provides charge carriers to the collector terminal through the base pin.
Features & Specifications:
The features and specifications of the BC547 transistor include the following.
- BC547 is a bipolar junction transistor.
- It is an NPN-type transistor.
- The highest current gain of this transistor is 800Amps.
- The collector-emitter voltage is 65 volts.
- This transistor includes three terminals.
- The collector-base voltage of this transistor (VCB) is 80 volts.
- The emitter-base voltage (VEB) is 8V.
- The continuous collector current is 100mAmps.
- The base current at the emitter terminal is limited to a maximum of 5mAmps at 6Volts.
- It is available in the To-92 package.
- The polarity of this transistor is NPN.
- The semiconductor package with the transition frequency 300MHz is 92.
- The power dissipation is 625mW.
- Continuous collector current (Ic) is 100mAmps.
- The emitter to base voltage or VBE is 6V
- The base current or IB max is 5mA
- Maximum operating temperature ranges from -65 to +150 C.
The equivalent BC547 transistors are; BC549, 2N2222, BC548, 2N3904, 2N3055, 2N3906 BC636, BC639, 2N2222 TO-18, TO-92, 2N2369, 2SC5200 & 2N3055.
Temperature Alarm Circuit with BC547 Transistor
The temperature alarm circuit using BC547 Transistor is shown below. This circuit is used to detect the temperature and activates a buzzer once the temperature is detected. The required components of this circuit include a 9V battery, thermistor, BC547 transistor, and Variable resistor. Connect the circuit as per the diagram shown below.
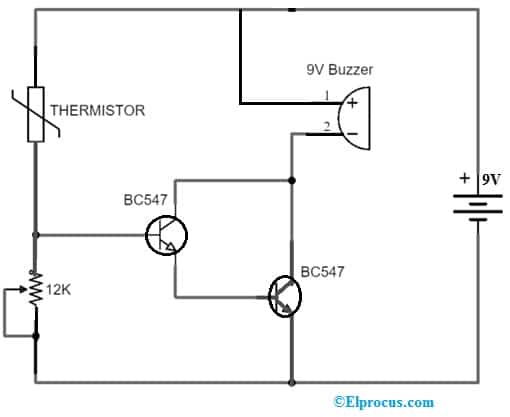
Temperature Alarm Circuit with BC547 Transistor
Working
The temperature alarm circuit is a very simple & inexpensive circuit. This temperature circuit operates with a 9V battery or adaptor. This circuit uses a thermistor for detecting heat. A thermistor is a device that has the maximum resistance whenever the heat is low & its resistance reduces when the heat increases.
This circuit uses two BC547 NPN transistors to form a Darlington pair. A buzzer in this circuit acts as an alarm and the voltage of the buzzer must be the same as the input voltage. A variable resistor in this circuit is to adjust the heat level at which point you want your alarm to trigger.
At first, the temperature alarm circuit remains off in the absence of heat. Once the thermistor gets heat then its resistance can be reduced & it allows the flow of current throughout it.
Now the two transistors in the circuit receive their necessary voltage to activate the buzzer. In this manner, you will be informed once the heat is there. This temperature circuit is compact & easily fitted anyplace. This circuit is used in those equipment or devices that you don’t want to get overheated.
Please refer to this link for Choosing Base Resistance for Transistors in Electronic Circuits.
Applications
The applications of BC547 transistors include the following.
- This transistor is used for amplification of current, fast switching, pulse width modulation, used in audio amplifiers, transistor Darlington pairs, and drivers like a relay driver, an LED driver, etc.
- This transistor is used in low-power applications like LEDs illuminating, sensor signal amplifying, etc.
- This transistor is used for switching & amplification purposes.
- These transistors are used in different electronic circuits like amplifiers, preamps, drivers, sensors, touch switches, switching, water level indicator, and volume level changing circuits.
Please refer to this link for Choosing Base Resistance for Transistors in Electronic Circuits.
Please refer to this link for Replacing Transistors in Electronic Circuits.
Please refer to this link for How to Select a Transistor.
Please refer to this link for BC547 Transistor Datasheet.
Thus, this is an overview of the BC547 Transistor, its circuit, working, and its applications. BC547 is a semiconductor device used to switch or amplify electronic signals & electrical power. This transistor includes three terminals that are used for connecting an external circuit. Whenever a voltage (or) current is given to single pair of the terminals of a transistor simply controls the flow of current by the other pair of transistor terminals. Here is a question for you, what is a PNP transistor?