BC177 is a widely used PNP transistor from the BC17x series. The other PNP transistors from this series are BC178 & BC179 which are very popular & utilized in different applications. The BC10x series is an NPN complementary transistor series that includes three NPN transistors; BC107, BC109 & BC108. This PNP transistor is accessible within three different versions based on the values of DC gain which can be decided by the final alphabet of its part number. If the alphabet is ‘A’ then its gain value ranges from 125 to 260 & if its alphabet is ‘B’ then the gain value ranges from 240 to 500. This article discusses about BC177 transistor, pin configuration, specifications, and its applications.
What is BC177 Transistor?
BC177 is a PNP transistor available in the TO-18 metal case used to switch or amplify electronic signals & also electrical power. This transistor is composed of semiconductor material with three terminals that help connect an external circuit. Whenever a voltage supply or current supply is provided to one pair of terminals of a transistor then it controls the flow of current throughout other pair terminals because the output power is higher than the input power, so that it can amplify a signal. This is a versatile transistor, used in various applications where a simple switching device is required for low power loads and also in high-frequency RF applications.

BC177 Transistor
While searching for an appropriate transistor for your application depending on a few features, it is very significant to refer to this – How to Select a Transistor.
Working
Whenever this BC177 transistor is biased, it allows a -200mA of maximum current across CE Junction, known as saturation state. If a load is driving that utilizes > 200mA current that may harm the circuit permanently. When the current supply at the base terminal is detached the transistor will become completely off, this state is called as Cut-off Region, thus there is no flow of current throughout the CE junction.
The gain of the BC177 Transistor ranges from 125 to 500 which decides the amplification ability of this transistor. The peak current supplied throughout this transistor is 200mA and is merged with the gain value to make this transistor a perfect choice to use in RF applications.
The behavior of this transistor when it is connected to GND and 5V power supply follows as;
To turn ON BC177 Transistor in any circuit, it requires a little current. The base current for this transistor is <10mA, it will be turned on whenever the base terminal is connected to the GND & it will be turned off whenever a positive voltage is provided to the base terminal of the transistor.
Whenever we switch ON the BC177 Transistor by simply connecting the base terminal to the GND, then this transistor will stay on except the base voltage reaches above the base turn-off voltage which ranges from 0.7 to 0.9V. This transistor’s base terminal cannot be left floating or else there could be fake triggering, that may cause some problems within the circuit. To resolve this problem, we have to connect pullup resistors to pull up the transistor’s base to VCC.
BC177 Transistor Pin Configuration:
The pin configuration of the BC177 transistor is shown below. This transistor includes three terminals which are discussed below.
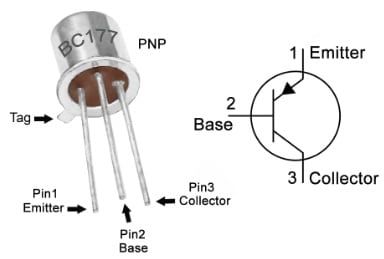
BC177 Transistor Pin Configuration
- Pin-1 (Base): This terminal helps in controlling the transistor biasing.
- Pin-2 (Collector): The collector terminal collects the emitted electrons from the emitter.
- Pin-3 (Emitter): This terminal emits the electrons and moves into the primary PN junction.
Features & Specifications:
The features and specifications of the BC177 transistor include the following.
- BC177 is a Bipolar transistor.
- Transistor polarity is PNP.
- It is available within the To-18 metal can package.
- This transistor uses advanced process technology.
- It has low error voltage, full voltage operation & quick switching speed.
- It has high current & power handling capacity.
- Maximum DC gain or hFE is 500.
- This transistor’s continuous collector current or IC is -100mA to -200mA.
- Its emitter to base voltage or VBE is -5V.
- The collector dissipation current is 0.3W.
- Its transition frequency is 200 MHz.
- The noise figure ranges from 2 to 10 dB.
- Its maximum operating junction temperature (Tj) is 175 °Centigrade.
- Collector capacitance is 5pF.
- Its voltage from collector to base terminal orVCBO is 50V.
- Collector to emitter voltage or VCEO is 45V.
- Its emitter to base voltage or VEBO is 5V.
- Continuous collector current or IC is 0.2Amps.
- The transition frequency or fT is 200MHz.
- Output capacitance is 4pF.
- Its power dissipation or PD is 1W.
- Its DC gain or hFE ranges from 120 to 460.
- Its operating temperature ranges from -65 to – 200°C.
Equivalent & Alternative Transistors
The equivalent BC177 transistors are; BC108, BC107, NTE159M & MMBT3904. Alternative BC177 transistors are; BC178 & BC179. The complementary BC177 NPN transistor is the BC107 transistor.
Replacing an appropriate transistor within any application based on necessity is very significant. To know how to replace a transistor, you need to refer to this link; Replacing Transistors in Electronic Circuits: Factors and Considerations.
How to use BC177 Transistor Safely in a Circuit?
To use the BC177 Transistor in a circuit securely, we suggest utilizing this transistor below 20% of its complete maximum ratings. Its max collector current is 100mA so do not drive > 80mA load. The highest collector-to-emitter voltage is -45V thus do not drive >-36V load. This transistor should be stored and operated always at >-65 °C &< 150°C temperature.
Connecting a resistor to the transistor’s base terminal in any circuit is compulsory to keep away from it being damaged. To know more about that, please refer to this link; Choosing Base Resistance for Transistors in Electronic Circuits.
Remote Tester Circuit using BC177 Transistor & TSOP1738
A remote tester circuit using BC177 Transistor & TSOP1738 is shown below. Generally, IR remotes are used to control music systems, DVD players, TVs, etc. But based on device type, there are different kinds of remote controls accessible that work on an approximately 38KHz frequency signal.
Generally, we check our remotes multiple times if they are properly working or not. To check the remote working, this simple remote tester circuit is designed using a TSOP1738 IR receiver sensor & BC177 transistor. This IR sensor is enclosed with a FET signal amplifier & a PIN photodiode within an Epoxy case. This sensor works with 5V by providing an active low output, & provides active high output without input signal.
The required components to make this circuit mainly include; a BC177 transistor, TSOP1738 IR sensor, 1N4001 diode, 6V DC battery, resistors – 47Ω, 10K and 1K – 2, 5mm LED, Breadboard, and connecting wires. Connect the circuit as per the remote tester circuit shown below.
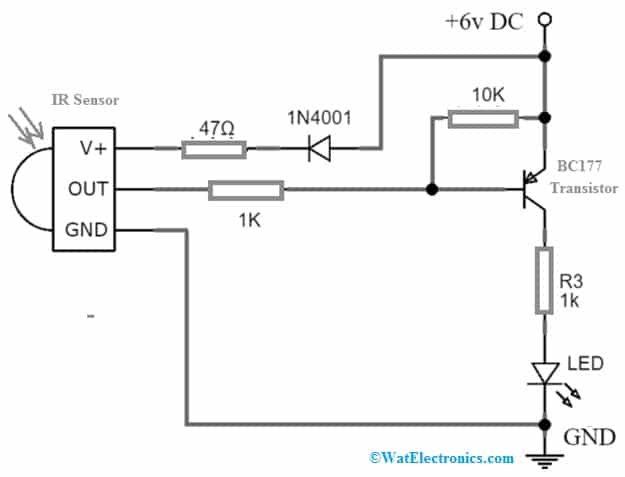
Remote Tester Circuit using BC177 Transistor & TSOP1738
Working
This remote tester circuit uses a BC177 transistor, but you can also replace it with another transistor like; BC158, BC558, BC177 (or) 2N905. This circuit operates with 6 volts operating voltage. Once an IR sensor receives an infrared signal then its VO pin will drop & its output will change from higher to lower. So this will supply the current to the transistor’s base terminal. Once it receives current, then it will start conducting to turn ON LED. At every trigger signal of the infrared sensor, the BC177 transistor will make the LED glow. So this provides a sign of whether the remote is functioning properly or not.
The 1N4001 diode in this circuit is used to drop 0.7V and provides the necessary 5V to the sensor from the 6Volts supply. Here, a 47Ω resistor is used to restrict the current supply into the sensor. Further, this remote tester circuit can be enhanced for indication of sound with a piezo speaker in between the collector terminal of the transistor & the negative terminal. The applications of remote tester circuits involve different devices like; ACs, TVs, DVD players, or media players.
Applications
The applications of the BC177 transistor include the following.
- BC177 transistor is used as an essential power amplifier, used for amplifying low-power signals.
- This is suitable in low noise input stages, driver stages, & signal processing circuits of TV receivers.
- This is a general-purpose PNP transistor, used for different switching & amplification purposes.
- It can be used as a switch to drive up to 100mA of load & it can be used as an amplifier in different low-power audio amplifiers, preamplifiers & audio amplifier stages.
- This transistor can be used for amplifying different small signals by noise reduction because it has good noise figures & DC gain.
- It can be used within RF-based applications up to 100MHz.
- This transistor can be used in different circuits like; audio amplifiers, small signal amplification, audio preamplifiers, Darlington pairs, and for switching loads below 100mAmps.
- These are used in preamplifiers of microphones, simple switching applications, relay drivers, lighting systems, signal amplifiers, and audio amplifiers.
Please refer to this link for the BC177 Transistor Datasheet.
Thus, this is an overview of the BC177 transistor, pinout, specifications, circuit, working, and its applications. This is a PNP transistor and is available in a TO-18 metal package, mainly designed to be used in general-purpose switching & amplification tasks in its limits. Here is a question for you, what is a BC558 transistor?