John Dalton in 1800 was the one who explained regarding the law on multiple proportions. Atom represents the fundamental units that can be divided into subatomic particles. This leads to the development of atomic models. In 1898 Thomson proposed a model by stating that mass of the atom is equally distributed or spread over it but Rutherford’s scattering experiment demolishes the statement in 1909.
Hence the existence of the nucleus with some electric charge at the center has been estimated along with the revolving of electrons around it. Further Bohr’s model unable to explain the structure of atom that consists of multiple electrons and it disobeys Heisenberg uncertainty principle. Later in 1926 Schrodinger’s equation has been proposed. As per the model based on quantum, it’s clear that numbers of electrons are arranged in the respective shells. Atom size measured in terms of angstrom that is 10-10 meter.
What Structure Does Atom Consists?
Each atom has its nucleus and the electrons bound to it. Protons and neutrons present inside the nucleus are known as nucleons. Mostly the nucleus is responsible as the major constituent for the mass of the atom. The structure of the atom mainly surrounds around electron, proton, and neutron. Atom’s behavior is relevant to the orbital in which electrons are revolving and the chemical properties are determined by the shells.
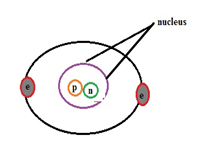
The General Structure of Atom
The General Structure of Atom
An electron is negatively charged, a proton is positive in charge whereas a neutron is neutral. If the atom has equally balanced electrons and protons in that case atom become neutral otherwise it leads to the formation of an ion. Based on the highest content of electrons and protons one can describe either the charge of the atom is positive or negative.
Electromagnetic force binds electrons and nucleus. Protons and neutrons consist of nuclear force to attract each other inside the nucleus. The presence of a number of protons indicates the atomic number. Similarly, a number of neutrons describe the isotopes. Magnetic properties of the element can relate to the presence of the number of electrons in it. Atoms interaction and distraction towards each other leads to the physical changes in the environment. This can be done by chemical bonding between them.
There exists a quantum state in which proton must be present in the nucleus but it should differ for every proton that is it follows Pauli’s exclusion principle. Therefore protons, neutrons , and electrons are categorized under fermions. As the charge has been classified neutrons compared to protons are heavier in terms of mass. Electrons have a mass of 9.109382911*10-28 gram. Proton or neutron comparison with the electron is 1,836 times heavier.
As the electron tends to rotate in order to obtain stability it jumps from one orbital to another one this makes the behavior of the atomic spectra so unpredictable. This technique is known as a quantum leap. When it occurs from a higher level to the next lower level there is an emission of radiation in terms of photons.
Properties of Atom:
Based on the number of protons, electrons and neutrons atom properties can be described:
(1) Atomic number:
Presence of the number of protons in the nucleus derives the atomic number it relates to the chemical properties of an atom. The symbol used for the representation of an atomic number is Z. it is clearly stated that atomic number is influenced by the positively charged particles. If the elements consist of the equal number of protons and electrons results in a neutral atom. Carbon is one of the neutral atoms.
Example: Z = 6, represents carbon.
(2) Atomic mass:
Mostly the weight or mass of the atom is dependent on its nucleus. Nucleus weight is dependent on the sum of the masses of proton and neutrons. This type of mass is known as atomic mass. The symbol A denotes atomic mass. If the neutrons and protons are different in number then it is termed as Isotopes.
Example:
Hydrogen is the best suitable example that can relate to this condition. Based on neutrons it is classified as
(a) Protium: It consists of 99.985% of the hydrogen atom with only one proton in it.
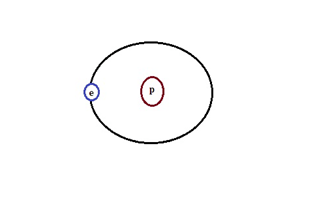
Hydrogen Isotope-Protium
(b) Deuterium: It has one proton and one neutron.
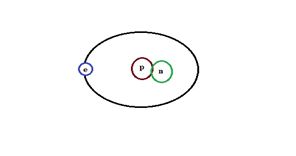
Hydrogen Isotope-Deuterium
(c) Tritium: It possesses two neutrons and a proton it. Naturally, this condition is not possible one has to make it based on requirement.
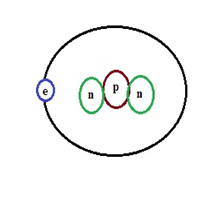
Hydrogen Isotope-Tritium
(3) Radioactive:
The variations in the number of protons and neutrons lead to the changing in a nucleus. Then the respective atom is known as radioactive. This condition is nothing but an unstable nucleus. At this stage, the atoms will be in the same state until it becomes stable. The elements that have an atomic number more than the limit of 82 are said to be radioactive.
Example: Lead
(4) The spin of electrons:
There is a property regarding spinning of electrons as it comes under fermions it takes only half of the integer spin. Example helium is a chemical element based on its number of protons its atomic number is two. In order to occupy in the same orbit, it should be spin in different directions. This results in the movement of electric charge so that they are considered as a magnet in tiny shape. Electrons do have a magnetic moment and it is almost 9.28*10-24 joule per tesla.
(5) Electric charge:
Atoms that involved in the movement of electron and in the formation of bonds in order to achieve stability results in the formation of an ion. In this process the atom that is a giver becomes positive and the one who takes it becomes negative.
(6) Relative atomic mass:
As the numbers of protons are equivalent to the numbers of neutrons in the carbon making it a neutral atom the relativity in atomic mass is comparatively average per mass of the one carbon atom.
Summary:
This article explains the basics of atoms and the way its structure has been classified based on the concept of orbital, basing on subatomic particles chemical properties of atoms can be explained. Mainly its objective is to give the basic structure details and deal with the basic properties. The way electron, proton, neutron lies in the atom and in the way its masses are related and the charges of the fermions have been discussed. There is a strong influence of charge particles in the atom. Based on the charges the classification of ions and the effect of increase and decrease of subatomic particles results have been overviewed. The energies associated in between nucleus and electrons have been discussed.
Hence the atoms are the fundamental units of any basic structure its classification on subatomic particles has been helped in figuring out the presence of various chemical elements in the periodic table. Based on the classification we can deal with the properties of basic atoms. Generally we use lead pencils in our day to day activities have you ever get a thought of it how the leads are joined and made as a solid pencil?
Please refer to this link to know more about FPGA Architecture.