In networking cables, when the loss of signal strength occurs then it is known as attenuation. So, when a signal passes through a channel, then the signal intensity will be reduced with distance. In idealize materials; the signal amplitude can be reduced through the wave dispersion whereas, in natural materials, they generate an effect to weaken the signal. Further, this weakening signal will result in absorption & scattering.
The conversion of signal energy from one form to another by taking up from the channel is called absorption. Scattering is the signal reflection within directions except for its unique way of propagation. So combined effect of scattering & absorption is known as attenuation. This article discusses an overview of attenuation & its types.
What is Attenuation?
Attenuation is a reduction of signal strength that occurs through any type of signal like analog or digital. Sometimes it is also called loss & it is a normal signal transmission effect over long distances. In fiber optic & conventional cables, it can be specified in terms of the number of decibels for each foot, mile, kilometer, 1,000 feet. The attenuation is low for each unit distance, and then the cable efficiency is more.
Once it is required to transmit signals over long distances through a cable, one or more repeaters can be placed with the cable length. Here repeaters play a key role in enhancing the signal strength to defeat attenuation. This increases the highest attainable communication range.
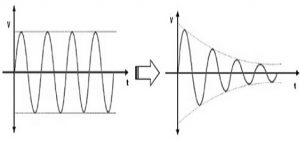
Attenuation
The unit of attenuation is Decibels or dB and is 1/10th of a Bel that was developed by engineers at Bell Telephone Laboratories. A Decibel is a logarithmic unit that explains a relation of two measurements. The fundamental equation that explains the disparity in dB in between two measurements can be expressed as
ΔX (dB) = 10log (X2/X1)
In the above equation, ΔX is the disparity in some measure denoted in dB
X1 & X2 are two dissimilar measured values of ‘X’
The logarithm is to base 10.
The main purpose of dB units is to allow the ratios of different sizes to be explained to work easily through numbers.
Different Types
The different types of attenuation are deliberate, automatic, and environmental.
- Deliberate type mainly occurs where the volume control is required to reduce the level of sound on electronic devices.
- Automatic type is a common feature of TVs as well as other audio devices to avoid the distortion of sound through automatic sensing level that activates circuits.
- Environmental type is associated with a power loss of signal because of the transmission channel; whether that is copper wired, fiber optic, or wireless.
Significance
Attenuation is significant in ultrasound & telecommunication applications because it is critical to conclude the strength of the signal as a function of distance. Attenuation meaning is the signal power loss otherwise amplitude caused throughout its transmission using a particular channel.
Reducing the attenuation loss is very significant in the applications of wireless, cellular & microwave as to function properly. An optical data link mainly depends on modulated light getting the receiver through sufficient power to be properly demodulated. This power can be decreased during attenuation that consequences in a loss of the light signal that’s being broadcasted.
Attenuation Measurement in an Electrical System
The attenuation measurement can be done in dB for each unit length of channel like dB/cm, dB/km, & it can be denoted through the attenuation coefficient of the channel. In an electrical system, attenuation is the reduction or loss within the amplitude otherwise signal strength because it transmits through its length.
Once the signal transmits throughout the copper wire conductor some of the signals will be absorbed. Attenuation is a consequence of resistance within the conductor & associated dielectric losses which are amplified through longer run lengths & high-frequency signals.
By enhancing the insulation dielectric properties & enhancing the size of the conductor, will decrease the attenuation and it can be expressed in dB (decibels). If it is associated with signal power then the formula can be expressed as
AP = 10 log10 ( Ps/Pd )
Here, ‘Ps’ is the power at the source & ‘Pd’ is the power at the destination. If it is expressed as Voltage, the attenuation the formula becomes:
Av = 20 log10 ( Vs/Vd )
Here, ‘Vs’ is the voltage at the source whereas ‘Vd’ is the voltage at the destination.
How to Enhance Signal Strength to Avoid Attenuation?
A technique like amplification is used to enhance the strength of a signal for preventing attenuation. So, amplification of signal electrically enhances the line signal’s strength using one of several technical methods. Usually, in computer networks, amplification comprises logic for the reduction of noise to stop the fundamental data message from becoming corrupted within the procedure.
A network device like a repeater incorporates a signal amplifier into its circuitry, so it works like a mediator between two endpoints of the message. The repeater device gets the information from the original sender & processes it using the amplifier after that transmits the stronger signal ahead to its final destination. In addition to repeaters, the signals can be amplified using directional antennas as well as other antenna upgrades.
Attenuation in Networking
In computer networking, it is the loss of communication signal force that is calculated in decibels. When the attenuation rate increases, then transmission through an e-mail when a user tries to transmit then it will become more distorted. Attenuation in computer networks mainly occurs due to the following reasons.
Range: Both the wired as well as wireless transmission slowly disperse within strength over longer distances
Interference: Interferences like radio otherwise physical obstructions on wireless networks
Wire Size: As compared to thicker wires, thinner wires experience more attenuation on wired networks
Line attenuation on a DSL (digital subscriber line) network computes loss of signal in between an access point & a home of a DSL provider. On DSL networks, it is dangerous due to the values of line attenuation which are very large that ranges from 5 dB to 50 dB. Based on the quality of line transmission, dynamic rate scaling will change the highest data rate of connection to up or down in fixed increments.
Attenuation in Optical Fiber
The optical power loss occurs when the light transmits through the fiber called attenuation in an optical fiber that can be caused through absorption, scattering & bending losses. The signal attenuation can be defined as the ratio of Pi (optical input power) to the Po (optical output power). The signal attenuation can be expressed as
α = (10/L) log10 (Pi/ Po)
Attenuation in optical fiber can be caused due to the following factors.
- Absorption Loss
- Scattering Loss
- Micro bend Loss
- Mode Coupling Loss
Absorption Loss
Absorption loss is associated with the composition of the material as well as the optical fiber fabrication method. This kind of loss can cause the optical power dissipation of the fiber cable. Even though glass fibers are very pure, some contaminations still stay as deposits after cleansing. The quantity of absorption through this contamination mainly depends on their absorption as well as the wavelength of light.
Scattering Loss
Scattering losses can be caused through the light interaction by fluctuations in density in an optical fiber cable.
Micro bend Loss
These types of losses are tiny microscopic twists of the fiber axis that happen mostly once the fiber is cabled. These twists happen because of outside forces, not level coating & procedures of improper cabling. Macrobid loss includes a large curve radius that is similar to the diameter of the fiber.
Mode Coupling Loss
In fiber optics, coupling loss is nothing but the power loss that happens once coupling light from one channel to other
Attenuation Coefficient
The attenuation coefficient characterizes how simply a material can go through a light beam. A huge coefficient is nothing but that the light beam is rapidly attenuated when it transmits throughout the channel whereas a small coefficient is nothing but the channel is fairly transparent to the light beam.
The attenuation coefficient SI unit is the reciprocal meter (m−1).
The word “attenuation” is also used in contexts other than computer networking. For instance, sound mixers and audiophiles may use attenuation techniques to manage sound levels when they blend different audio recordings.
Please refer to this link to know more about Antenna MCQs& Modulation Question and Answers.
Thus, this is all about an overview of attenuation in optical fiber, electrical systems, etc. Generally, it is used in the field of radiology to converse the features of an anatomical arrangement signified in an X-ray. In beer production, this process is used to change the sugar alcohol & carbon dioxide through fermentation. When the attenuation is high, the sugar is changed into alcohol. Here is a question for you, what is fiber optic cable?