Inverting Amplifier Theory
Inverting amplifier is one of a simple circuit in which the output is in phase shift with respect to the input. It consists of two input terminals named as inverting and the non-inverting input terminals. As the inverting terminal of it is provided with the input supply it is referred to as inverting amplifier. The output generated after the operation performed this signal is again fed back to the input terminal. In this way, the feedback is provided so that the noise levels and distortions can be minimized in the circuit.
Negative feedback is preferred in this case of amplifiers. The design criterion of the amplifier is simple. The gain of the inverting amplifiers is high. The other terminal that is non-inverting is connected to the ground. As the gain is high for these kinds of amplifiers small values of the input voltage or signal is enough to generate the maximum value at the output.
What is Inverting Amplifier?
The value of the input applied at inverting terminal where the non-inverting terminal is connected to the ground or the zero potential. The output generated is again feedback to the inverting terminal. This type of amplifier is defined as the inverting amplifier. This feedback condition of the amplifiers makes the gain factor high.
Inverting Amplifier Op-Amp
Generally, a basic operational amplifier consists of two input terminals in which one acts as an inverting terminal and the other is a non-inverting one. Only one terminal is present at the output side. In case of the inverting amplifiers, the non-inverting terminal is connected to the ground. But the potential maintained is the same at both the terminals. The output signal generated requires a minimum value of the input to be applied.
This type of amplifier possesses the maximum gain value because the output that is generated is again applied to the inverting terminal through a feedback resistor. It is only because of the feedback resistor we get an amplified signal. If there is no feedback resistor then op-amp would try to maintain the voltage level at the inverting input terminal same as the non-inverting terminal which is ground . In that scenario the output voltage would be same as the input as there is no difference between the input voltages. The feedback resistor plays a important role for an operational amplifier to function as an inverting amplifier or an non-inverting amplifier.
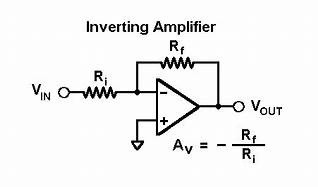
Inverting Amplifier as Op-Amp
Circuit Diagram:
This can be designed with the basic operational amplifier. At the input inverting terminal is supplied with the voltage signal through the input resistor connected to it. The non-inverting terminal concerning the circuit is connected to the ground. The output terminal is again connected to the input inverting terminal through the feedback resistor. If the op-amp is considered to be ideal in such cases the gain of the circuit will be at its peak. However, the negative feedback is followed by the amplifier makes the gain factor high.
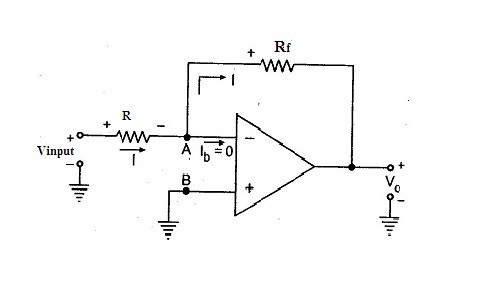
Inverting Amplifier Circuit Diagram
The output signal that is generated due to this amplifier is that will be of angle 180 degrees out-of-phase in comparison to the applied input signal. The voltage that is applied at the inverting terminal its potential value will be the same as that of the potential at the non-inverting terminal. The behavior of this amplifier resembles the differential amplifier.
Inverting Amplifier Gain
The gain of the inverting amplifier can be given as the ratio of the output voltage to the applied input voltage.
Gain of the Voltage= output voltage/ input voltage
The gain can also be obtained with the help of the resistors. That is the ratio of the feedback resistor to the resistor present at the input terminal determines the gain value. As it is an inverting amplifier the gain is represented by the negative sign. The voltage gain can be denoted by ‘A’.
A= -Rf / R in
Waveform :
The waveform of the inverting amplifier clearly states that to the applied input voltage the output generated is the out of phase. That means if the applied input voltage is positive the generated output will be negative and vice-versa.
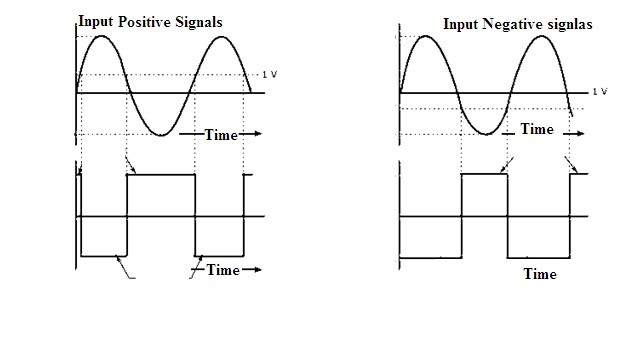
Inverting Amplifier Wave forms
Advantages and Disadvantages of Inverting Amplifier
The advantages of the inverting amplifier are as follows
- It follows the negative feedback.
- The gain factor of these amplifiers is very high.
- The output generated will be out of phase with the applied input signal.
- The potential values at both the inverting and the non-inverting terminals maintained at zero.
The disadvantages of the inverting amplifier are as follows
- The gain is high but the feedback that is followed must be maintained to be distortion less.
- The applied input signal should not contain the noise because small value applied will be multiplied and obtained at the output.
Applications :
This amplifier is advantageous because it follows the feedback called negative. Because of these reasons among the other operational amplifiers, it possesses the high gain value. Even it maintains the same potential of voltage at both the terminals. This makes the this amplifier to be utilized in many fields. Some of the applications of the inverting amplifier are as follows
- As the output generated is of the 180-degree phase shift. It can be used as a phase shifter.
- It can be practically used in the applications of the integration.
- At the applications where the signal must be balanced inverting amplifiers are utilized.
- In the concept of mixers when the radio frequency signals are present these amplifiers are used.
- Any applications or the system prototype that is designed with the sensors prefer inverting amplifiers at the output stage.
Please refer to this link to know more about Inverting Amplifier MCQs
It is utilized in various fields where the gain and the minimum noise is the major concern. But mainly where the analog signals are considered these amplifiers are widely used. Hence it is a good phase shifter with the maximum gain. This makes the amplifier very worthful because of negative feedback. However, it is among the very widely used amplifiers. Finally, it is a best-suited amplifier for both the analog and the digital signals. Can you describe the practical implementation of the inverting amplifier?