An Op-amp (operational amplifier) is a device that possesses linear characteristics. It is good at the conditioning of the signals as well as is utilized for the amplification of the voltage signals. This is a basic differential amplifier that consists of three terminals. Among these three terminals, two are used for the input and one is utilized for the output. The first terminal at the input is known as the inverting one it is represented by the minus sign. The second terminal at the input represents the non-inverting and it is represented as a plus sign.
These are abbreviated as Op-Amps. It is capable of performing basic mathematical operations that is addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The single output terminal is capable of sinking and sourcing both the current and the voltage signals. This type of amplifier can also be used as a good option for the filtering of signals.
What is an Operational Amplifier (Op-amp)?
A basic device that consists of three terminals from which two terminals represent the input and the one is for output is defined as a basic Operational Amplifier. The signal generated at the output is the result of the multiplication of the two factors one is the input signal that is applied and the other is the gain of the amplifier. These amplifiers are coupled with the components like resistors and capacitors so that the efficiency of the amplification can be improved. These op-amps are also designed with different features and to operate with various characteristics.
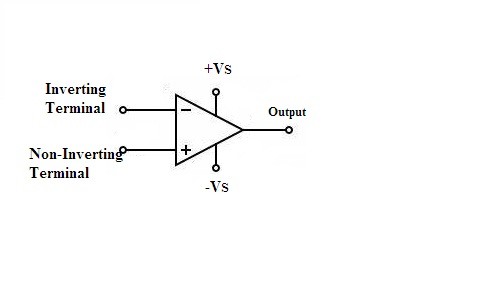
Symbol of Op-amp
Block Diagram and the Working of Operational Amplifier
A basic operational amplifier can be divided into four main blocks. They are
- Input Stage
- Gain Stage
- The Phase Level Shift
- Output Stage
The initial input stage consists of a basic differential amplifier where it can operate in the differential mode. As there are inverting and the non-inverting terminals present at the input side. When the Ac signal applied at the non-inverting terminal the signal generated at the output of this stage will be of the same polarity. But the signal applied at the inverting terminal produces the output with the phase shift of about 180 degrees.
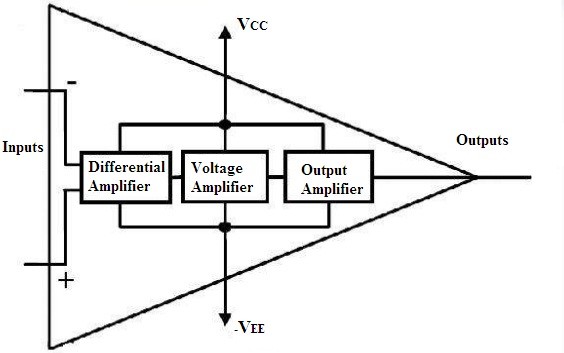
Block Diagram of Op-amp
Hence this makes the op-amp dual input and the single output amplifier. Then the outcome of the first stage is forwarded to the intermediate stage. The required gain of the voltage is introduced at this stage of the amplifier.
As well as at this stage the direct coupling is present. It means that the output of the intermediate stage has the value of the voltage that must be above the ground potential. Hence this paves the way to make the voltage that is DC to shift down it to zero. For this reason, the third stage with a level shifter is introduced.
In this stage, the circuit of emitter follower transistor is present along with the source of current that is maintained at constant. Further, the output of the level shifting stage is given to the final stage in which there exists the amplifier of the type push-pull which increments the swing in the voltage that is generated at the output.
In this way, the four stages describe the basic structure of an operational amplifier.
Characteristics of Operational Amplifier (Op-amp)
Some of the characteristics of an operational amplifier are as follows:
- The value of the input impedance is high.
- The value of the impedance at the output is low.
- The frequency range of the amplifying signals is from zero Hz to 1 Mega Hz.
- The value of the offset voltages and the currents are low.
- The gain of the voltage is high.
Ideal Operational Amplifier
An ideal operational is not possible practically. The characteristics of the ideal operational amplifier are:
- There is no basic offset voltage is present in the ideal op-amp.
- The gain of the open-loop in this ideal case is infinite.
- The impedance at the input is infinite. Therefore it acts as the voltmeter in the ideal condition.
- The impedance at the output is zero. This type of ideal op-amp possesses the characteristics of voltage source at the ideal stage.
- There is zero noise level in the ideal op-amp.
- The value of the bandwidth is of infinite range.
That’s how the characteristics of the ideal op-amp differ from the practical op-amp.
Operational Amplifier Types
The op-amps are classified based on the gains. They are
1). Low Gain Amplifiers
The amplifiers with the low gain value are known as low gain amplifiers. These are used as the buffers and for the matching of the impedance.
2). Medium Gain Amplifiers
If the intensity of the gain of the amplifiers is of medium value then these amplifiers are defined as the medium gain amplifiers. It has tremendous applications in the field of medicine. These are used in recording the waveforms of ECG and to require the value of the muscle potentials.
3). High Gain Amplifiers
As the gain of the amplifiers is high these are utilized to record the sensitive data for example while recording the information of the signals from the brain these amplifiers are used.
Operational Amplifier Uses
There are various uses of operational amplifiers.
- It can be used for the amplification of voltage signals.
- It can be used as the inverting amplifier by connecting the terminal of the non-inverting at the input to the ground.
- It can also be used as a non-inverting amplifier by making necessary circuit modifications.
- The changes made in the input voltage can affect the output voltages. This makes the op-amp to use it as a voltage follower.
- The most important and frequently used Operational Amplifier is the comparator. It has the capability of comparing the signals.
- These comparators are used in performing various digital logic operations. Because the voltage in this case produced at the output is limited.
Please refer to this link to know more about How to select an op-amp?
Please refer to this link to know more about Op Amp Integrator & Inverting Amplifier Circuit.
Please refer to this link to know more about Operational Amplifier MCQs
The above are some of the uses of the operational amplifiers. The signal given at the input goes through the various stages in between before it reaches the output. Every stage has its own level of specification. Finally, the output obtained is a well defined amplified signal. Now can you describe if these op-amps are suitable for the amplification of the power signals?