An electronic instrument that can display the changes in signal voltages graphically is known as an Oscilloscope. It is utilized to process, capture, display, analyze, store the waveform and bandwidth of the signals. The oscilloscopes are of two types based on the type of signal. These are classified into two types namely analog oscilloscope and digital oscilloscope.
An Analog oscilloscope uses an electron beam to map and display the continuous variable input voltages of the signal, and a digital oscilloscope samples a given input signal by using a converter like ADC and displays the digital output on the CRT screen. The digital oscilloscopes are further classified into Digital Storage Oscilloscope (DSO), Digital Phosphor Oscilloscope (DPO), and Digital Sampling Oscilloscope. Now, this article gives a brief explanation about the theory, working principle, and function of Digital Storage Oscilloscope.
What is Digital Storage Oscilloscope?
Digital storage oscilloscope definition is an electronic device that stores and analyses the signal in the digital format is known as Digital Storage Oscilloscope (DSO). When the input signal is given to the DSO, then it is processed, stored in the memory, and displayed on the screen. It stores the signal in the form of digital data as either 1 Or 0.

Digital Storage Oscilloscope
The advanced features of the DSO are triggering, storage and measurement. It can display the waveform or signal both numerically and visually. It is often referred to as the Digital Sampling Oscilloscope. Rather than using analog techniques, it used Digital Processing Techniques to capture, analyze, process, store, and display the signal on the screen.
Block Diagram
The block diagram of the Digital Storage Oscilloscope is shown below.
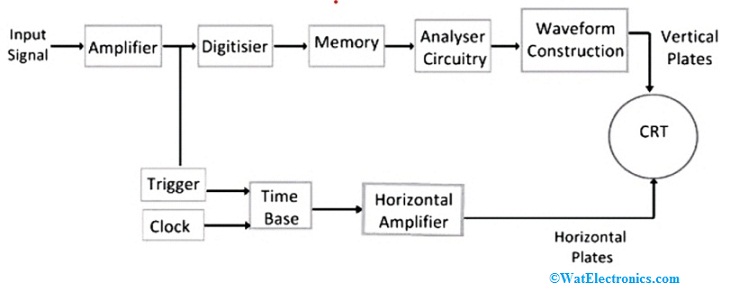
Digital Oscilloscope Block Diagram
The analog input signal is digitized by the digital storage oscilloscope and is stored in the digital memory. The Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) is employed to display the stored signal or data in the memory. As the stored data in the memory is in digital format, the signal is reconstructed into analog form and displayed on the CRT.
The analog input signal is amplified by the amplifier and its output is digitized by the digitizer and stored in the memory. The analyzer circuit analyses the digital output and it can be reconstructed to visualize the final waveform using the Interpolation technique. The output is displayed on the CRT screen.
Please refer to this link to know more about Oscilloscope MCQs
Digital Storage Oscilloscope Theory
The digital storage oscilloscope theory states that various hardware and software modules are used together to process, analyze, display and store the data of the applied input signal by the user. It consists of elements such as an amplifier, analog to digital converter, analyzer circuit, digital memory, time base with clock and trigger, circuit for waveform reconstruction and display, LCD or LED display, and the power supply.
The sampling of time-varying analog signals is done periodically by the DSO and stores the waveform in memory. The internal clock is used to divide the input signals into separate time slots to digitize the instantaneous amplitudes of the signal by the DSO and then the digital data is stored in the memory. The waveform is regenerated by the display at a predetermined clock rate, is viewed in series of dots, and can be reconstructed using the interpolation technique.
The triggering allows the DSO to stabilize the signal and display the waveform repeatedly. Before starting the trace of signal, the oscilloscope must be triggered first.
Working Principle
The working principle of a Digital Storage Oscilloscope (DSO) is based on digitizing and storing the input signals with the help of CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) and digital memory. The process of digitization is the sampling of input signals at different periodic signals. Here, the signal’s maximum frequency measured by the DSO depends on 2 factors, which are sampling rate and the converter nature. And also the function of the digital storage oscilloscope depends on the sampling and the converter.
Sampling Rate
In this factor, the sampling theory is used for the safe analysis of input signals. The statement of sampling theory is, the sampling rate of the signals should be twice as fast as per the received input signal’s highest frequency. That means, sampling rate refers to the fast and high conversion rate of an analog to a digital converter.
Converter
It uses high-priced flash, whose resolution decreases with an increase in sampling rate. So, the limited resolution and bandwidth of the DSO are obtained due to the sampling rate.
The shift registers are used to overcome the requirement of ADC (Analog to digital converters). The applied input signal is sampled and stored in the shift register. Then, the signal in the shift register is read out slowly and stored in the form of digital data. The use of a shift register reduces the converter cost and can operate up to 100 Mega samples/second.
The Function of Digital Storage Oscilloscope
- The function of a digital storage oscilloscope is to process, capture, analyze and display the applied analog input signal in digital format and also store the data in the digital memory. The signals are received, stored, and displayed by the DSO to calculate the frequency, amplitude, time period of a signal. It operates in 3 modes such as roll mode, store mode, and save Or hold mode.
- In roll mode, the DSO displays the fast fluctuating input signals very clearly on the screen without triggering. It is one of the basic modes in the working of DSO and similar to the operation of CRO. It monitors the characteristics of the given input signal to process and displays its trace on the screen.
- In-store mode, the signals are stored in the memory.
- In hold mode or save mode, the data is saved Or held for a while until it gets stored in the digital memory.
- The other modes used in the working of digital storage oscilloscopes are refresh mode, single-shot mode, and equivalent time mode.
Waveform Reconstruction
According to the sampling theory, the given input signal is sampled to avoid the aliasing effect. But the aliasing effect can still occur in the signal because the output signal is obtained in the series of dots in response to the sample value.
A technique called Interpolation is used by the Digital Storage Oscilloscope (DSO) for final wave visualization. The technique that generates new data points by using a set of known discrete data points is known as Interpolation. Generally, it is classified into two types, illustrated in the figure shown below.
Linear Interpolation
In this type, the data points, which are in the form of dots are connected with a straight line as shown in the figure above. It is used in the generation of pulse waves or square waves.
Sinusoidal Interpolation
In this type, the dots are connected to generate a sinusoidal waveform as shown in the figure above. It is used in oscilloscopes.
Advantages
The advantages of Digital Storage Oscilloscope include,
- Easy to operate, efficient data display, and high quality
- It allows the property of flexible display with infinite storage time
- Analyzes and stores the data in the digital format (0 or 1) and prevents signal degradation
- It provides triggering, storage, measurement functions to display the signals digitally or in virtual format.
- Cost-Effective when compared to analog oscilloscopes.
- It can trace and record temperature changes.
- It can analyze high-frequency transient responses.
- It can collect large samples of input data with the help of storage memory.
- It can reconstruct the waveform.
Please refer to this link for Sampling Oscilloscope MCQs, Digital Storage Oscilloscope MCQs
Applications
The applications of Digital storage oscilloscope include,
- It is used in circuit debugging to test the voltage of the signal
- Used in testing during manufacturing
- Used in Radio Broadcasting to test the signals
- Used in Research and medical field
- Used in video and audio recording equipment
- Used to measure time period, frequency, voltages, currents, inductance, capacitance, and time intervals between the signals in both AC and DC circuits.
- Used in the representation of radar’s target like airplane, ship, etc visually.
- Used to analyze the TV signals
- Used to compute the V-I characteristics of transistors and diodes.
Please refer to this link to know more about Digital Image Processing MCQs, Cathode Ray Oscilloscope MCQs & Measurement & Instrumentation MCQs
Thus, this is all about an overview of Digital Storage Oscilloscope – Definition, Block Diagram, Working Principle, Function, Waveform reconstruction, advantages, and applications. Modern Digital Storage Oscilloscopes are operated with highly advanced signal analysis, which makes them more accurate and powerful. Here is a question for you, “What are the disadvantages of Digital Storage Oscilloscopes? “