Generally, form factors are related to different electronic devices like motherboards, cell phones, etc. For motherboard, it can be referred to as one kind of hardware peripherals & its structure. So motherboard form factors are micro-ATX & ATX. Similarly, for mobile phones, it is referred to as the complete shape, design of the phone like the traditional candy bar shape, which changes from the slide & flip form factors.
At present, most of the phones are available with touch screens, so the form factor for the touch-based phone is the slate. So it is essential to understand the standards. It’s important to understand that the standards are optional and may not be stick to by manufacturers. There are some cases wherever these are very essential while upgrading a motherboard because the motherboard follows fixed standards otherwise form factor. This article discusses an overview of a form factor.
What is a Form Factor?
The form factor is the ratio of the RMS value which is known as the root mean square toward the average value of voltage or current. The average of all the instant values of voltage & current over one entire cycle is called the alternating quantities of average value.

Form Factor
Mathematically, it can be expressed like the following
Form Factor = Irms/Iav = Erms/Eav
Here in the above equation, the values of Irms & Erms are the RMS values of the voltage & current correspondingly. Eav & Iav are the standard values of the alternating voltage & current correspondingly.
The value of this when current altering sinusoidally, it can be given as
Form Factor = Irms/Iav = Im/√2/2Im/π = π Im/2√2 Im = 1.11
The Form Factor value is 1.11
There is the main relationship between the values of average, peak & the RMS for an alternating quantity. Thus, to convey the relationship among all these quantities, form factor and peak factor are used.
For different sinusoidal waveforms, the form factors include the following.
- For a sine wave is π/2√2 or 1.11072073
- For a sawtooth waveform is 2/√3 of 1.15470054
- For a half-wave rectifier is π/2 or 1.11072073
- For a triangle waveform is, 2/√3 or 1.15470054
- For a half-wave rectified sine wave is π/2 or 1.5707963
- For a square wave is 1
- For a full-wave rectified sine wave is π/2√2 or 1.11072073
- For pulse wave is 1/√D
- For triangle wave is 2/√3 = 1.1547
- For Gaussian white noise is 2/√3
What is the Importance?
The computer form factor example is the disparity between a laptop computer & a desktop. Even though the similar parts are attached & shaped differently. For instance, from a desktop, the keyboard cannot place into the keyboard space of a laptop.
For hardware, it is dependent & the design of the components that go into the big hardware unit. The component’s shape & size are affected by the power specifications as well as the connections. Most of the manufacturers have some fixed rules, so these components work together electronically & electrically by being physically placed into the existing space.
The component form factors standardization mainly includes the incapability of unsuited components to place physically into space. For instance, the form factors of mini-USB receivers prevent the connectors of micro-USB from being connected. The two connector’s specifications are dissimilar so it could cause harm to the remaining data or components if the incorrect one were connected.
Importance of Form Factor
Computer Form Factor
The computer form factor like RAM will change by preventing mismatched components from being connected. Every computer memory generation can be made so it cannot be placed into a slot on a motherboard because that was designed for a different memory generation.
As the specifications of every memory generation change then placing unsuited memory will not work & causes electrical harm to the processor or motherboard. If you desire to include memory to improve your computer, then utilize a tool like Crucial® Advisor™ otherwise System Scanner to get compatible parts
In addition to the various generations, there are various shapes & sizes of memory for different types of hardware. So, desktop computers, servers, notebook computers, mobile telephones & laptop computers all utilize different memory form factors which include physically different numbers, configurations & sizes of connection pins.
SSD
Using an HDD (hard disk drive) to an SSD (solid-state drive) is very confusing. Once you recognized what kind of performance & how much space for storage is required, then this is well-matched through your system.
SSDs can be defined through three main factors like the drive size, the physical space & the connection interface type then the drive will live in the computer. The three different SSD factors are discussed below.
2.5-Inch
The typical SSD form factor is 2.5-inch that is arranged in the drive bay of desktop computers or most laptops. As many operators change their hard drives through solid-state drives, then this type has become a standard for all SSDS & HDDs. These are mainly designed to reduce the requirement of changing the connecting interface cables.
mSATA
mSATA is a smaller form factor and the size of this is one-eighth of a 2.5-inch drive. These are mainly designed for inserting into an mSATA socket on a motherboard of a system. These are utilized in very thin & mini devices otherwise like a minor drive within desktops.
M.2
This is the smallest form factor and the size of this is a stick of gum. The connection of these can be done through an M.2 socket by connecting to the motherboard. These are mainly designed for ultrabooks & space-constrained tablets.
Motherboard Form Factors
The motherboard is an essential component in all computers and the main function of this is to interact with all the computer elements like the RAM, CPU, graphics card, storage, I/O, etc. It is essential to recognize all its limitations, capabilities, etc. Similarly, the form factor is a key element to consider for the computer.
The classification of the motherboard can be done based on the processor type, form factor, chipset, etc. The essential components of the motherboard include RAM, CPU, DRAM, IDE connectors, AGP Slot, ATX power supply, PCI Slots, Bridges, etc
Motherboard form factors will change based on the physical size & electrical and electronic connections. These are slower to modify, however when important connections are invented, then new technology can be reflected within motherboards.
These are mainly designed for the hardware unit size, the number of cards, processors, memory, drives to connect to a motherboard. As compared to the motherboards of desktop computers, the motherboards of laptop computers are approximately different.
The list of motherboard form factors includes the following.
- Micro ATX
- Mini ATX
- Nano
- BTX
- Advanced Technology Extended (ATX )
- Advanced Technology (AT)
- Baby AT
- Flex ATX
- Low Profile Extension (LPX) & Mini LPX
- New Low Profile Extended (NLX)
A computer without a motherboard is of no use and in the same way, a motherboard with no computer is also of no use. So, a motherboard with a computer needs to have one person to manage. The primary functionality of the motherboard is to handle the microprocessor chip and from here all the other devices are connected.
The design, power supply, board types, ports, dimensions, and the arrangement of a motherboard is termed as form factor. This term impacts where all the individual elements come and arrange the computer’s covering. There exist various form factors that many of the computer motherboards make use of so that they function well in all the standard situations.
For instance, a completely functioned motherboard consists of many PCIe connections when compared with a mini-ATX board. The form factor type for a motherboard is based on the enhancement of technology. As there is a continuous enhancement in the technology, the standard level of the motherboard has to be altered correspondingly. The level of standard decides the arrangement and design of the board. From the above list, a few of the prominent motherboard form factors are discussed below.
Micro ATX
The measurements are 9.6 × 9.6 inches. This type supports nearly four expansion sections where this allows for a free combination of PCI, ISA shared, AGP and PCI. When compared with a standard type of ATX, the mounting holes are varied because the dimensions are different. Whereas this also allows compatibility with many of the ATX slots. The micro ATX supports both AMD and Intel types of processors and is mainly implemented on minimal form factor desktops.
Mini ITX
This type of form factor consumes minimal power, and it is of size 6.7 × 6.7 inches. The dimensions in this type of motherboard hold crucial responsibility. Even the device was manufactured with the thought of using less amount of power, currently, there exist no restrictions, and these gain huge benefits and developed in many phases.
The application of the Mini ITX motherboard was in many domains and this was mainly because of the open standard factor. This is the general format for many kinds of devices like industrial purposes, vehicle embedded systems, and the Internet of Technology. This device was the initial system with the minimal format and got popularization by reaching all kinds of projects.
Nano ITX
For this, the measurements are 4.7 × 4.7 inches. These are completely integrated boards that are manufactured to consume a minimal amount of power. It can be used in most applications but was exclusively designed for entertainment purposes such as smart TVs, PVRs, infotainment devices, and many others.
BTX
The BTX motherboard form factor is even termed as balanced technology extended motherboards. When compared with ATX boards, the BTX boards are entirely different. Because of the PCI and USB 2.0 technologies, BTX boards gained the main prominence. These are minimal in size than that of micro ATX boards and have good component arrangement mainly with back panel input and output controllers.
With the advancement of BTX boards, the electronic industry turned in the direction of tower-sized systems that provide many system compartments. The main benefit of the BTX system is that it makes use of airflow to provide cooling to the system. Here, the expansion components and memory placements are swapped so that other major components such as chipset, processor receive a good amount of air. The lessens the fans requirement so that it further reduces the risk of nose those generate with many fans.
Whereas the drawback of BTX boards is developers cannot get used to implementing these boards in their implementation quickly.
ATX
The development of ATX boards took place in the year mid of the 1990s. This board was considered as innovative as it brought up various changes. Before the invention of ATX, expansion sections were received along with riser cards and those have to be fitted into the board. Whereas using ATX boards there was no requirement of riser cards and it lessened the space needs.
This motherboard form factor proposed new power pins such as a 20-pin connector and various headers used for aeration. The board consists of only a few overlaps having connectors, I/O connections, driver bays, and predecessors.
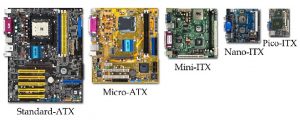
The comparisons of motherboard form factors include the following.
- Standard-ATX type is manufactured by Intel in 1995. The dimension of this is 12 × 13 inches & it is used on desktop or workstation.
- Micro-ATX type is manufactured by Intel in 1997. The dimension of this is 9.6 × 9.6 inches & it is used in Small Form Factor
- Mini-ITX type is manufactured by VIA in 2001. The dimension of this is 6.7 × 6.7 inches & it is used as Small Form Factor
- Nano-ITX type is manufactured by VIA in 2003. The dimension of this is 4.7 × 4.7 inches & it is used in Embedded Systems
- Pico-ITX type is manufactured by VIA in 2007. The dimension of this is 3.9 × 2.8 inches & it is used in Embedded Systems
- Mobile-ITX type is manufactured by VIA in 2009. The dimension of this is2.4 × 2.4 inches & it is used in Embedded Systems
Know more about Computer Port Question & Answers.
Thus, this is all about an overview of form factor definition & its importance. The common features of Mini ITX, ATX & MicroATX motherboards are; they give support to similar CPUs, run similar graphic cards & back panel ports are the same. Here is a question for you, what is the peak factor?