In our day-to-day life, we all utilize different types of sensors. From that, the temperature sensor is one kind of sensor that is used most frequently in different forms like microwaves, water heaters, refrigerators, thermometers, etc. Generally, these types of sensors are used in a wide range of applications to measure the amount of coolness or hotness of the device and change it into a readable unit.
Do you know how the temperature of the buildings, dams, boreholes, soil are measured:? Well, this can be done through a special kind of temperature sensor to calculate the readings of temperature through electrical signals. This article discusses an overview of temperature sensors and their working with types and applications.
What is a Temperature Sensor?
A sensor that is used to measure or maintain a fixed temperature in any device is known as a temperature sensor. This kind of sensor plays a key role in different applications. Physical measurement like temperature is the most common one in industrial-based applications. A temperature sensor provides temperature measurement within a clear form using an electrical signal.

Temperature Sensor
These kinds of sensors are available in various forms, which are utilized for various temperature management techniques. The temperature sensor working mainly depends on the voltage across the terminals of the diode. So, the temperature change is directly proportional to the resistance of the diode.
The measurement of resistance across the terminals of the diode can be done and to change the readable temperature units like Celsius, Fahrenheit, Centigrade & exhibited in the form of numeric over readout units. In the field of geotechnical monitoring, temperature sensors are utilized to calculate the inner temperature of different structures such as buildings, dams, bridges, power plants, etc.
Temperature Sensor Circuit
The circuit diagram of the relay switch using the temperature sensor is shown below. Once the circuit gets the heat then the relay will trigger the load. Any voltage can be applied to this relay like 110V AC or 220V AC or DC appliance so that we can control it routinely on the preferred temperature. This circuit is simple and cheap to build. For electronics beginners, it is a perfect circuit.
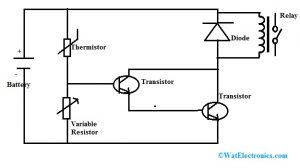
Temperature Sensor Circuit with Relay Switch
The required components to make this temperature sensor circuit are 9V input DC supply DC, 10KΩ thermistor, transistor BC547B, 6V relay, 1N4007 diode & 20KΩ variable resistor. The operating of this circuit can be done with a 9V battery, an adapter, or a transformer. This circuit includes 2- BC547B transistors like a Darlington pair. So the circuit sensitivity, as well as gain, can be increased through these transistors.
The required range of heat can be adjusted using a variable resistor at which you desire to activate your relay. In this circuit, a thermistor plays a key role because it detects heat. This circuit working is quite simple. Once the thermistor gets heat then its resistance will be reduced and it allows the flow of current to activate the transistors.
Once both the transistors are triggered then they allow the voltage toward the relay to activate. So now, the load which is connected to this relay will be activated. This circuit is very useful like operating the fan at the preferred temperature. It activates an alarm in emergencies where you don’t want to overheat.
Types of Temperature Sensor
The temperature sensor is categorized into two types like contact & non-contact where the contact type sensors are mainly used in dangerous areas. Further, these types of sensors are classified into different types which are discussed below.
Contact Type Temperature Sensor
Contact type temperature sensor is used to notice the amount of temperature within a target through direct physical contact with it. These sensors can be used to detect solids, liquids, otherwise gases in broad temperature ranges. The contact type temperature sensors are available in different types like RTD, thermocouple, thermometer, thermistor, etc.
Among them, thermocouples are usually less costly because of the simple material & model is used. The other type of sensor is a thermistor where resistance will be reduced when the temperature enhances.
Thermocouple
The most popular and frequently used temperature sensor is thermocouple due to its sensitivity, accuracy, broad temperature range, simplicity & reliability. Generally, this kind of sensor includes two different metal sections like copper & constantan which are jointed through the welding process.

Thermocouple
The design of this sensor can be done with two different metals which are connected through two wires at two points. The voltage among these wires replicates the change within the temperature. Even though, as compared to RTD, the accuracy will be less slightly. The temperature range of this sensor ranges from -200 °C to -1750 °C but these are expensive.
Once the two metal junction is cooled or heated, then a voltage can be formed that can be connected back toward the temperature. SO this is called as thermoelectric effect. Generally, these are not expensive when their materials and design are simple.
The thermocouple output mainly depends on its type where the normal thermocouple is categorized into different types like K, J, T, N & E which are called base metal thermocouples. The S, B & R type thermocouples are called Noble Metal thermocouples and the C & D types are called Refractory Metal type thermocouples.
The temperature range of thermocouples ranges based on its types like the following.
- The temperature range of ‘J’ type thermocouple ranges from 0° – 750°C
- The temperature range of ‘K’ type thermocouple ranges from -200° – 1250°C
- The temperature range of ‘E’ type thermocouple ranges from -200° – 900°C
- The temperature range of ‘T’ type thermocouple ranges from -250° – 350°C
- The temperature range of ‘N’ type thermocouple ranges from 0° – 1250°C
Thermistors
Thermistors are also known as thermally sensitive resistors are made with ceramic materials such as particular metal oxides which are coated with glass. The working principle of the thermistor is, once temperature increases then its resistance will be increased.

Thermistor Sensor
According to the principle, it is categorized into two types like Positive Temperature coefficient (PTC) & Negative Temperature coefficient (NTC). In a positive temperature coefficient, when the temperature of material increases, then resistance will be increased whereas in NTC, the temperature decreases then the resistance will be decreased. The thermistor’s resistance will be increased when the temperature increases.
This kind of temperature sensor exhibits a predictable, precise & huge change within the change of a variety of temperatures. The huge change is nothing but the temperature will be reflected quickly with accurately. Thermistors are more accurate as compared with thermocouples. These sensors are made with polymers or ceramics.
Thermostats
This kind of sensor includes a bi-metallic segment that is designed by using two dissimilar metals like nickel, aluminum, copper, or tungsten. These metals can be bonded jointly to make a Bi-metallic strip. The thermostat’s main working principle depends on the dissimilarity within the coefficient of linear expansion of the metals. So, it pushes them to produce a mechanical movement because of the increase in heat.

Thermostat
The bimetallic strip is used as an electrical switch within thermostatic controls. The wide use of this is to control heating elements of hot water within boilers, hot water storage tanks, furnaces; radiator cooling systems in vehicles, etc.
RTD or Resistive Temperature Detector
The designing of a resistive temperature detector can be done from accurate conducting metals like platinum enclosed in a coil. The electrical resistance of an RTD changes when the temperature changes. The RTD is also called a resistance thermometer & calculates the temperature through the resistance of the element of RTD using the temperature.

RTD
RTD or Resistance Temperature Detectors are the metal foil of thermistors & these are the most exact &expensive type of temperature sensors. RTDs have PTC (positive temperature coefficients) however different from the thermistor. The output of this is very linear generating very precise temperature measurements.
The common types of resistive temperature detectors are designed from platinum known as PRT or Platinum Resistance Thermometer. The most frequently available type sensor is Pt100, which includes a typical resistance value like 100Ω at 0oC.
Semiconductor based ICS
These kinds of temperature sensor-based integrated circuits are available in two different types like local temperature & remote digital type. Local temperature IC type is used to calculate their temperature through the transistor’s physical properties. Remote digital type is used to calculate the exterior transistor temperature.
Local temperature sensors use the outputs of either analog otherwise digital. The outputs of analog are either current or voltage whereas digital outputs can be observed in different formats like SMBus, I²C, SPI & 1-Wire. These sensors detect the temperature on PCBs. A small temperature sensor like MAX31875 can be used in different battery-powered based applications.
The working of Remote digital temperature sensors is similar to local temperature sensors which use the transistor’s physical properties. The main difference is that the transistor is placed away from the sensor IC. Some FPGS & microprocessors comprise a bipolar sensing transistor to calculate the IC’s die temperature.
Thermometers
A device like a thermometer is used to calculate the temperature of, liquids, solids otherwise gases. As the name suggests, it is the combination of two terms like thermos and meter where thermo is nothing but heat.
The thermometer includes a fluid such as mercury otherwise alcohol within the glass cylinder. The quantity of the thermometer is proportional linearly toward the temperature. Once the temperature enhances, then the quantity of the thermometer also enhances.
Thermometer
When the fluid of the thermometer is heated then it increases in the thin tube. This thermometer includes a calibrated scale that specifies the temperature. The thermometer includes marked numbers beside the glass tube that specifies the temperature once the mercury line reaches that point. This temperature can be saved within these scales like Kelvin, Celsius, or Fahrenheit. So, it is always smart to note down for which scale the meter is adjusted.
Contact Less Temperature Sensor
Noncontact or contactless type temperature sensors do not get in touch with the target. So, they calculate the temperature by using the heat source’s radiation. The common type of contactless sensor is the IR (infrared) sensor and the main function of this is to detect the object’s energy remotely & generate a sign to a circuit that detects the temperature of an object through an exact calibration plan.
These kinds of meters are not in contact with the target directly, and they calculate the amount of coolness or hotness throughout the emitted radiation through the heat source. The non-contact type temperature sensors are used in a wide range. In the Co-vid 19 pandemic, it is used to test the temperature of the people.
Some More Temperature Sensors are discussed below.
LM35 Temperature Sensor
LM35 IC is one kind of temperature sensor that generates an analog signal like an output signal. The output of this IC changes depending on the temperature around it. This kind of IC is very small in size as well as cheap also. The main function of this IC is to calculate temperature anyplace among -55°C -150°C.
The interfacing of this IC can be done using any microcontroller that contains the ADC function.
This IC can be powered by providing a +5V regulated voltage to the i/p pin & the GND pin can be connected to the GND of the circuit.
Infrared Temperature Sensor
IR temperature sensor detects electromagnetic signals which range from 700 nm – 14,000 nm. Once the IR spectrum expands up to 1,000,000 nm, then these sensors do not calculate over 14,000 nm. The working of IR sensors can be done by focusing the IR energy generated from an object on photodetectors.
These photosensors change the energy into an electrical signal that is comparable to the infrared energy generated through the object. Because the IR energy generated from any object can be proportional to its temperature. The electrical signal provides a precise temperature reading of the object. The IR signals are supplied to the IR sensor through a plastic window.
Generally, plastic does not permit IR frequencies to flow throughout it; the sensors utilize a transparent form to specific frequencies. This plastic material filters out unnecessary frequencies to protect the electronics within the IR sensor from dirt, dust, etc.
Water Temperature Sensor
This kind of sensor allows the control unit to recognize the engine from overheating or an abnormal increase in temperature. The connection of this sensor can be done in the cars next to the thermostat based on the manufacturers.
In some vehicles, there are two kinds of temperature sensors; one sensor is used to transmit data from the car engine system toward the control unit & another one is used from the control unit to the control panel. When the temperature of the car engine alters, the device’s potential dissimilarity output can also be changed & this can be calculated through the control unit of the engine.
Coolant Temperature Sensor
A coolant temperature sensor or an ECTS (engine coolant temperature sensor) or an ECT sensor is mainly used to gauge the temperature of the coolant within the cooling system that gives a sign for how much temperature the engine in the car is giving off. The coolant temperature sensor works through the ECU of the vehicle by monitoring continually to confirm the car engine is working at the optimal temperature or not.
To obtain a precise temperature reading of the car, the ECU transmits a regulated voltage toward the CTS. The resistance of the coolant temperature sensor changes throughout temperature; so this is how the ECU monitors the temperature change.
The ECU utilizes this reading to calculate the coolant temperature & from there regulates the fuel mix, fuel injection, timing of ignition & controls once the electric cooling fan is turned ON/OFF. This data can also be used to transmit a precise temperature reading of the engine on the control panel.
Human Body Temperature Sensor
The human body temperature like MAX30205 is used to calculate the temperature of the human body. This sensor is precise to 0.1°C over the measurement range of 37°C to 39°C & 16 bits resolution. This human body temperature sensor features an over-temperature alarm for making a fan switch ON through OS output hysteresis.
This sensor changes the measurements of temperature to digital form through an ADC and sigma-delta. The MAX30205 temperature sensor features three address select lines using 32 obtainable addresses. The supply voltage of this sensor ranges from 2.7V – 3.3V and the supply current is 600µA & an I2C-compatible lockup-protected interface to utilize in various applications. This IC can be used in a TDFN package with 8-pin & works over the temperature range from 0 NC-to-+50NC.
Please refer to this link to know more about Temperature Sensor MCQs
Advantages
The advantages of temperature sensors include the following.
- Temperature range is extremely wide that ranges from -200oC – +2500oC
- The bridge circuit is not required
- Response time is very fast
- It quickly responds once temperature changes
- These are simple to design
- The initial cost is less
- Strong
- Thermocouple measures temperature in the range of -200oC to +2500oC
- RTD measures the temperature in the range of -200oC to +850oC
- Thermistor measures the temperature in the range of -100oC to +260oC
- The IC sensors measure the temperature in the range of -45oC – 150oC
- Thermocouple doesn’t use any additional power and they are very simple to design and strong, less cost, etc.
- RTDs have high accuracy, more stable, more linear as compared to the thermocouple
- Thermistor operation is very fast and they provide higher output.
- IC sensors are not expensive, maximum output &more linear as compared to other types.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of the temperature sensor include the following.
- The drawbacks of thermocouples are; least stability, nonlinearity, low voltage, required reference, sensitivity, etc.
- The drawbacks of RTD are; expensive, absolute resistance is loess, required current source not strong as compared to the thermocouple.
- The drawbacks of the thermistor are; required current source, self-heating, fragile, non-linearity, support is limited, etc.
- The drawbacks of IC sensor are; operation is slow, required power supply, self-heating, configurations are limited, the temperature is upto150oC, etc.
Applications
The applications of temperature sensors include the following.
- These are used in electric motors, surface plates, home appliances, computers, equipment in industries, warming electrical radiators, production of food, alcohol breathalyzer, etc.
- Some more applications of temperature sensors include transit, power & utilities, HVAC, heat exchangers, calibration &Instrumentation, industrial process, drilling, heating systems, energy, laboratory, etc.
- These sensors are used to control the temperature of a motor & control the motor operation.
- The temperature of drilling can be controlled by the drilling operator within the applications of geothermal.
- These sensors are uses to save the electric cables from burnings from overheat
- The temperature of the water can be checked by the user so that the water heater can be controlled to conserver the energy.
- The operator can control the temperature of the bearing and engine oil
- The room temperature can be controlled through this sensor by operating the cooling system.
Please refer to this link to know more about Types of Resistors.
Please refer to this link to know more about Touch Screen Technology MCQ’s, Resistance Temperature Detector MCQs..
Please refer to this link to know more about Temperature Measurement MCQs
Thus, this is all about an overview of the temperature sensor and its working. Temperature sensors are mainly applied in medical devices, cooking appliances, automobiles, computers & other kinds of machinery. Here is a question for you, how do you check a temperature sensor?