We know that resistor is the passive electrical component and at present, there are different types of resistors used in different applications based on the requirement like industrial, commercial, military, and automotive. This article discusses one kind of resistor namely wire wound resistor and its types. These types of resistors are used in industrial and commercial applications for a long time. In electric & hybrid electric vehicles, these resistors are used like pre-charge as well as discharge resistors. This article discusses an overview of wire wound resistors, types, and their applications.
What is Wire Wound Resistor?
A wire-wound resistor is one kind of passive component where a metal wire with a high resistivity is used by wounding around an insulating core for providing the resistance. The main function of the wire-wound resistor is to restrict, reduce the current flow to a certain level. The wire-wound resistor symbol is shown below.

Wire Wound Resistors
Generally, a metal wire is made of an alloy like Nichrome (Nickel-chromium) otherwise a Manganin (copper-nickel-manganese alloy) as they operate at high temperature and they provide high resistance for the flow of current. These resistors are very old type but they are still manufactured as they include excellent low resistance values properties and generate extremely accurate & high power ratings.
Wire Wound Resistor Construction
The construction of the wire-wound resistor changes widely. The materials used in the resistor and its manufacturing mainly depend on the way this component is used within a circuit.
The wire-wound resistor construction can be done by winding the metal wire in the region of a metal core. In this kind of resistor, a metal wire can be used as the resistance element whereas a metal core can be used as the non-conductive material. Therefore, even the heat at a high temperature does not go into the resistor. So, this resistor works at high temperatures.
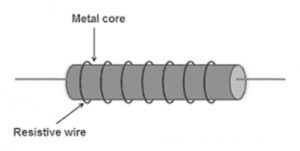
Construction of Wire Wound Resistor
These resistors are available in different ranges from a small surface mount to a huge tubular power resistor which is applicable in electronic equipment & instruments where more power dissipation & high accuracy are necessary. As compared to metal oxide resistor, this resistor is mostly used due to small size and stability is high at high temperature.
These resistors are many produced through alloys because pure metals include a high TCR (temperature coefficient of resistance). But, pure metals are used for high temperatures like Tungsten. The TCR is an indication of how much the resistance will vary when the temperature varies and this is measured in ppm/˚C units. For resistor wire, the typical alloys used mainly include
- Copper
- Silver
- Nickel Chromium
- Iron Chromium Aluminum
- Iron Chromium
Types of Wire Wound Resistors
Wire wound resistors are classified into two types namely precision wire wounds and power wire wounds. These resistors can be changed to utilize within different sensors like potentiometers, temperature & current. These resistors are adaptable, so they can be utilized in a broad range of applications.
Precision Wire Wound
Precision wire wound resistor is generally used to measure bridges, calibration equipment and also used in precision AF attenuators. The tolerance typical values of the resistance value are 0.1% otherwise better. The resistor’s temperature coefficient value mainly lies approximately 5 ppm/°C, which is significantly better as compared to the metal film resistors like 25 ppm/°C.
The stability of this resistor is quite good like 35 ppm at full power rating operation. Generally, the rise of temperature for this resistor is under 30°C. So they can be covered through epoxy resin materials.
Power Wire Wound
This resistor is the non-inductive type that functions at high temperatures. These types of resistors are most frequently used in high-power applications. These are different types which can be categorized through their construction & package like Silicone resin encapsulation, Vitreous enamel coating & Aluminium case.
Different Factors
The resistance of this resistor mainly depends on the following three main factors of metal wire which are discussed below.
- Resistivity
- Length
- Cross-Sectional Area
Resistivity
The metal wire’s resistivity and resistance of this resistor are directly proportional. A high resistance metal wire opposes a huge current. So, the resistor provides huge resistance toward the current. Conversely, a low resistance metal wire opposes a small amount of current. Thus, this resistor gives less resistance toward the current.
Length
The length of the wire and resistance of the resistor is directly proportional. The length of metal wire is high then it provides high resistance due to the flow of electrons at a large distance. Thus, the electron collision possibility through the atoms is high. So, several electrons will crash throughout the atoms and there will be a loss of energy in the heat form & the remaining small free electrons flow freely by holding electric current. Consequently, a small number of free electrons will flow throughout the resistor.
When the metal wire length is short then it offers less resistance due to the flow of electrons at a small distance. Therefore, the electrons crash possibility through the atoms is less. Thus, a small number of free electrons will crash through the atoms. So there will be a loss of energy in the heat form and the remaining electrons will move freely by holding current. So, a huge amount of current will supply throughout the resistor.
Cross-Sectional Area
The resistance of a resistor & the cross-sectional area of the wire are inversely proportional. The metal wire including less cross-sectional area can provide less space for the flow of electrons. Therefore, the chance of electrons crash through the atoms is high. So, a small amount of current will flow throughout the resistor.
The metal wires including a high cross-sectional area can offer sufficient space for the flow of electrons. Thus, the chance of electrons crash through the atoms is less. Thus, a huge current will flow throughout the resistor.
High-Frequency Effects
Wire wound resistor includes some capacitance & inductance, due to this reason they control the flow of current within an AC circuit and this effect is generally not required. Because of the resistor design principle, these resistors include the worst high-frequency properties for all kinds of the resistor.
To apply the winding to the resistor, there are many ways based on the application. As compared to AC, DC has some issues through the winding arise due to the self-induction and parasitic capacity. These effects can be reduced through different types of winding like Bifilar winding, Ayrton-Perry winding & Winding on a flat former.
The above-mentioned windings can be applied for decade banks as well as measurement devices. The disadvantage of these techniques is the complexity of the manufacturing procedure.
Advantages
The advantages of wire wound resistor include the following,
- Not expensive
- Both the accuracy & stability are high
- Wide range of resistance
- As compared to other resistors like carbon, these resistors are used within high-power circuits.
- It is constant thermally.
- It is not sensitive to noise
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of wire wound resistor include the following,
- These resistors are applicable for low- frequencies but not for high frequencies, and it functions as an inductor. So, non-inductive wire wound resistors are used for high frequencies.
- As compared to carbon size, it is expensive
- Its size is large
Applications
The applications of wound resistor include the following,
- These resistors are applicable where the stability of high temperature & very close tolerance is required.
- Telecommunication
- Computers
- Audio & Video Devices
- Electronic Equipment in Medical Field
- Space & Defense
- Current Sensing
- Telephone Switching Systems
- Current and Voltage Balancing
- Transducers Instrumentation
- Equipment for Battery Testing
- X-ray Equipment
- Lighting Controls
- Machine Tools
- Motor Controls
- Metering Systems
- Power Drives in Industries
- Control Systems in Industries
- Monitoring Systems for Gas & Engine
- Telephone Switching Systems
Thus, this is all about the need for the wire-wound resistor. These resistors have some desirable characteristics like better surge handling capability. As compared to other technology, these resistors provide high precision & temperature coefficients with tightly controlled & more stable. The values of these resistors are 0.005 ohms within power ratings from 0.25-2 watts. Here is a question for you, what are the different types of resistors?