The development of computer networking was in most prominence and the progression of networking started by Arpanet development in the late period of the 1970s. Before this, the usage was with computer vendor networks where those are designed mainly to connect the mainframe with terminals and entry stations. Whereas the thought behind networking is to establish communication between computer devices where both are considered as peers to accomplish resource sharing.
Computer networks are extensively categorized based on the criteria consisting of the transmission media, which is utilized for signal transmission, bandwidth, traffic control, and many. Computer networks are also constructed from fundamental building blocks like network interfaces, hubs, switches, and many others along with the physical transmission media. Today, this article mainly explains the concept of Network Interface, its porting, network interface devices, and hardware/software.
What is Network Interface?
A network interface is defined as the computer hardware which is used for connecting the network media to a computer and it has the capacity to deal with the lower range of network data. For instance, a network interface card might consist of a connector to accept the cable or has either aerial for wireless reception and transmission and the corresponding circuitry.
In the case of Ethernet networks, every network interface is included with a distinctive MAC address generally accumulated in the NIC’s permanent memory location. To eliminate any kind of addressing conflicts that arise between network devices, there will be the maintenance of MAC addresses individually. The Ethernet MAC address size is nearly 6 octets. The main three octets are used for distinguishing types of controller manufacturers.
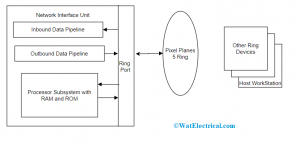
Network Interface Unit
This is the basic information of a network interface.
Network Device
A network interface device is also termed a network interface unit (NIU) acts as the interface between client and network provider local system. These NIUs are represented in grey-colored boxes external to the client’s locations where here the network provider’s data comes to an end and the client’s wiring starts.
The characteristics of the network device are:
- Network device differentiates connection in between provider and client.
- The protection of local loop wiring till the network device is the accountability of the phone supplier whereas the protection of wiring from the network device to the client location is the customer’s accountability.
- The network device also safeguards the customer wirings and device from the transient energy present in the local loop such as lightning where the circuit protector here performs this functionality.
- The main utilization of NID is to check the proper functionality of the connection. It consists of a test jack and when it is not functioning properly, it signifies that there is damage in the line which was to be fixed by the service supplier. Or else when the test jack is functioning properly, this implies that there is damage to the device of client wiring.
- Usually, NID is considered the basic connecting device that does not involve creativity or logic.
- Few of the network devices consist of logic and capabilities which are termed as Intelligent NIDs or smart jacks. Those consist of a PCB and they provide few features such as code and signal conversions, redevelopment of degraded signals, and others.
This is the crucial information about the network device.
Network Device Types
Here we discuss the few TCP/IP supporting network interface types which are explained below:
IEEE 802
The IEEE 802 comes under the family of IEEE standards where manages both metropolitan and local area networks. The entire IEEE 802 suite offers an extended array of networking abilities. These protocols consist of flat addressing systems where those have functioned at level-1 and 2 in the OSI approach.
Wireless LAN
This is even extensively recognized as WiFi or WLAN where this is the most known category in the IEEE 802 family which is mainly utilized for home and office applications. This is the standardized version of IEEE 802.11 and it has many shared properties as with the wired Ethernet connection.
SONET
SONET is called synchronous optical networking. The other name of SONET is SDH where the expanded form of this is a synchronous digital hierarchy and this is the standardized kind of multiplexing protocol where it can transfer many digital bits through optical fiber using layers.
The initial intention behind the construction of SONET devices is to transport circuit way of communications from different types of sources mainly to assist real-time, circuit-switched voice in PCM way. Even though, because of the neutrality performance of the protocol and transport adapted characteristics, this SONET device was the main selection for the transportation of ATM bit frames.
Internet Protocol Suite
This is also called TCP/IP, the prominent network interface and stands as the base for current generation computer networking. This provides both connection-adapted and connection-less services through an intrinsically unpredictable network that is navigated by the datagram transmission at the IP level.
This suite even characterizes routing parameters, addressing for IPv6 and IPv4 having extended addressing ability. This is the most defined array of protocols for the Internet.
Network Interface Porting
A network interface port is the physical docking spot where any external appliance can have a connection to the computer. Along with the physical port, this might be a programmatic docking spot where the data passage happens from program to computer across the Internet.
To know what type of protocol receiving traffic it must be directed to, various port numbers are utilized. They permit only a single host over one IP address to operated a networking service. Every port number provides different services and for every host, there are 65535 ports every. This porting is all regulated by IANA.
VLANs and interfacing groups include virtual ports. The interfacing groups consider various physical ports as one port, whereas VLANs divide physical ports into many logical types of ports.
VLAN is the logical type of port that accepts and transmits VLAN tagged traffic. The features consist of a VLAN ID for the port. The fundamental interface grouping port is termed as VLAN trunk port and the associated switch ports need to be configured to trunk VLAN IDs.
So, computer networking interfaces support a wide range of applications and services like WWW, digital type of audio and video, printers, email and direct messaging, fax equipment, application shared use and accumulation servers, and in many.
Please refer to this link to know more about Network Layer MCQs, Computer Port Question & Answers, Network Interface Card MCQs.
This is the concept of the network interface. This article has provided clear and detailed information on network interface porting, types, and devices. To have a clearer understanding of this concept, get to know what is network interface hardware/software?