
GSM and CDMA
The cellular mobile service is being used everywhere in the world today. GSM and CDMA are two dominant technologies in the world of mobile communication. These two technologies differ in the way in which the calls and data transfer takes place over a network and mobile. This article discusses an overview of the difference between GSM and CDMA.
What is GSM?
GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communication. It is a digital mobile telephony system used for trans-receiving of the data and voice signals and is a second-generation standard for mobile networks.
The GSM standard operates on three different carrier frequencies 900MHz, 1800MHz, and 1900MHz. 900MHz band is used for the original GSM system and the 1800MHz band is added to support the increasing number of customers. The 1900 MHz frequency band is used mainly in the United States.
A GSM phone is a digital cellular technology used for transmitting mobile voice and data services. GSM makes use of the narrowband Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) technique for transmitting signals.
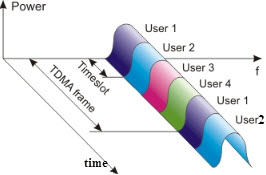
Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA)
The GSM standard has led to the evolution of wireless services like GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) UMTS (Universal Mobile Radio System) and EDGE (Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution). Its users were the first to take the advantage of Short Message System (SMS).
A GSM system makes use of cells to provide wireless communication to the subscribers. The GSM mobiles are identified by using Subscriber Identity Module (SIM). This is a removable smart card that contains the information of the subscriber. This SIM card allows the customer to switch from one mobile to another.
Please refer to this link to know more about GSM Questions & Answers
Advantages of GSM
- GSM provides improved spectrum efficiency
- Low-cost mobile set and base stations
- High-quality speech
- International roaming
- Compatibility with Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN)
What is CDMA?
CDMA stands for Code Division Multiple Access. It is used in cellular communication similar to GSM and is a second-generation and third-generation standard for mobile networks. It is the most secure mode of communication because of its spread spectrum property.
CDMA is a form of multiplexing where a number of signals occupy a single transmission channel and optimizing the use of available bandwidth. This technology is used in the ultra-high frequency (UHF) cellular systems having a band ranging from 800MHz to 1.9GHz.
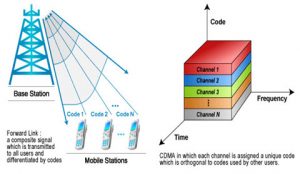
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
CDMA uses analog to digital conversion in combination with spread spectrum technology. First, the audio signal is digitized to binary elements.
The frequency of the transmitted signal is then made to change according to the code. Thus, it can be intercepted only by a receiver whose frequency is programmed with the same code.
The original CDMA standard called CDMA One offers a transmission speed of up to 14.4 kbps in its single channel form and up to 115kbps in an eight-channel form. CDMA2000 and wideband CDMA deliver the data many times faster.
Please refer to this link for Code Division Multiple Access MCQs
Advantages
- Efficient utilization of fixed frequency spectrum.
- Flexible allocation of resources
- Multipath fading may be substantially reduced due to large signal bandwidth.
- No limit on the number of users.
- Impossible to decipher the code sent and better signal quality.
- No sense of hand-off when changing cells.
- The CDMA channel is nominally 1.23MHz wide.
- Soft hand-off minimizes signal breakup as the handset passes from one cell to another.
- CDMA is compatible with other cellular technologies, thus allowing a national wide roaming.
Differences between GSM and CDMA
|
S.no |
GSM | CDMA |
| 1 | The GSM is based on a wedge spectrum called a carrier.
|
The CDMA is based on spread spectrum technology.
|
| 2 | This carrier is divided into time slots, and each user is assigned a different time slot. Thus, until the ongoing call is finished, no other user can access the same slot. | This technology allows each user to transmit over the entire frequency spectrum all the time. |
| 3 | Less security compared to CDMA technology.
|
More security is provided in CDMA technology.
|
| 4 | No built-in encryption. | It has built-in encryption |
| 5 | Signals can be detected as the GSM signals are concentrated in the narrow bandwidth. | The signals cannot be detected easily in CDMA.
|
| 6 | The GSM network operates in the frequency spectrum of 850MHz and 1900MHz.
|
The CDMA network operates in the frequency spectrum of 850MHz and 1900MHz.
|
| 7 | GSM is used over 80% of the world’s mobile network.
|
CDMA is exclusively used in the United States, Canada and Japan.
|
| 8 | GSM uses EDGE data transfer technology.
|
CDMA has faster data transfer as EVDO ready data transfer technology is used
|
| 9 | It offers a maximum download speed of 384 Kbps.
|
It offers a maximum download speed of 2 Mbps.
|
| 10 | A SIM card is required for the working of the GSM device.
|
CDMA phones do not have these pulses.
|
| 11 | A GSM is more flexible than CDMA as the SIM can be replaced with other GSM devices. | A CDMA is not flexible. |
| 12 | GSM phones emit continuous wave pulse. Thus, there is a need to reduce exposure to electromagnetic fields.
|
CDMA phones do not have these pulses.
|
| 13 | GSM phone emits about 28 times more radiation on average as compared to CDMA.
|
Very less radiation |
This article is all about the difference between GSM and CDMA technology. Furthermore, for any help on GSM and CDMA technology or doubts regarding this article, you can contact us by commenting on the comment section given below.