Conveying of our messages to someone happens through voice, few gestures, expressions. This is the human way of communication. Whereas in the technological context, there are multiple ways of transmitting messages either in the form of audio, digital bits and baseband signal transmissions. The fundamental method of transmission is telecommunication and modulation is the core system for any of the telecommunication devices. These days, the standard forms of communication devices are co-axial cables, microwaves, copper wires, and even wireless communication. The transmission happens either in the form of analog or digital and these signals have to be modulated to remove noise effects, to travel over long distances and remove attenuation effects. And the one kind of modulation we are going to discuss today is “Analog Modulation”.
What is Analog Modulation?
An analog signal is a continuous wave where the time differing variable of the wave is represented in the relation of other time differing quality which is analogous to other time changing signals. And analog modulation is the procedure of transmitting low-frequency signals such as TV signals or audio signals with that of high-frequency carrier signals like that of radio frequency signals. In this type of modulation, a bandpass channel is required where it corresponds to the specified range of frequencies. These frequencies are transmitted over a bandpass filter which allows certain frequencies to pass preventing signals at undesirable frequencies.
When the carrier signal is represented by the equation
Accos (2∏fct + Ф)
Here Ac term represents amplitude, fc term represents frequency and Ф term represents a phase of the carrier signal.
Types of AM
The type of analog modulation is based on the type of carrier signal property and so there are mainly three kinds of analog modulations and are
- Amplitude Modulation
- Frequency Modulation
- Phase Modulation
Amplitude Modulation
In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the carrier signal is varied in correspondence with the amplitude of the modulating signal by maintaining frequency and phase at constant. Here, is the pictorial representation of amplitude modulation.
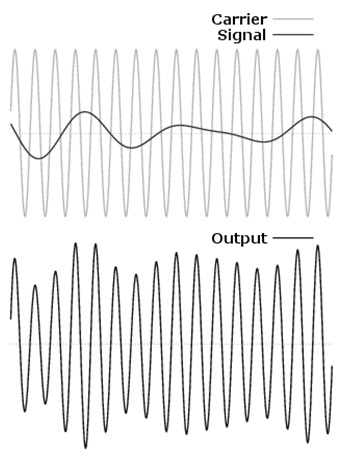
Amplitude Modulation
When the modulating (input signal) is represented as
i(t) = Aicos(2∏fit)
and the carrier signal is represented as
c(t) = Accos(2∏fct)
And in the expressions, Ai and Ac represent the amplitudes of two waves while fi and fc are the frequencies of the two waves correspondingly.
Solving the two expressions, a modulated wave is represented as
M(t) = [Ai + Ac cos (2∏ (fi + fc)t )]
The modulating signal has a bandwidth which is twice the bandwidth of the message signal i.e. 2fi
Frequency Modulation
In frequency modulation, the frequency of the carrier signal is varied in correspondence with the amplitude of the modulating signal by maintaining amplitude and phase at constant. Here, is the pictorial representation of frequency modulation.
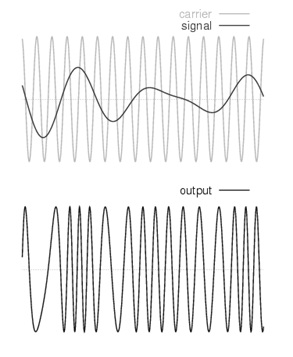
Frequency Modulation
When the modulating (input signal) is represented as i(t)
and the carrier signal is represented as
c(t) = Accos(2∏fct)
then the frequency-modulated wave is
M(t) = A cos (2∏fc + ks(t)t + Ф)
The bandwidth of the FM modulated wave has to be considered in two cases
- In narrowband FM, the bandwidth is two times the maximum frequency of the FM.
- In wideband FM, the bandwidth is very large of the FM spectrum.
Phase Modulation
In phase modulation, the phase of the carrier signal is varied in correspondence with the amplitude of the modulating signal by maintaining amplitude and frequency at constant. Here, is the pictorial representation of phase modulation.
P(t) = Accos[Wct + kpm(t)]
Here Ac represents the amplitude of the carrier signal
Wc represents the carrier signal’s angular frequency = 2∏fc
And m(t) represents the modulating signal
The bandwidth of the PM modulated wave has to be considered in two cases
- For minimum amplitude signals, the bandwidth is
- In wideband FM, the bandwidth is very large in the FM spectrum.
Differences between Analog and Digital Modulation Techniques
Both analog and digital modulation techniques are mostly implemented and the main difference that lies between these is the type of data they used to transmit the message. In analog modulation, the inputs have to be analog format and in digital modulation, the input has to be in digital format. Based on the type of applied input, the output is also quite separate.
| Analog Modulation |
Digital Modulation |
| Any values that lie in between the minimum and maximum ranges of the transmitted signal are considered as valid. | In digital modulation, only two values are considered and are “1” (HIGH) and “0” (LOW). All other values are considered as noise signals and rejected.
|
| Analog signals are continuous waves and are sine waves | Digital signals are discrete in nature and represented as square waves.
|
| Transmission of signals can be easy in analog type because the most used signals for transmission are in analog type like voice | In digital modulation, the signals have to be passed through converters (ADC and DAC) to recover the originally transmitted signal. Transmission of digital signals might require other additional equipment, and this enhances the complexity to implement and cost to spend |
| Any kind of noise or interference that lies in the frequency bandwidth might mix up with the original signals and this causes degradation. | In digital modulation, noise signals are completely eliminated |
| The output of analog modulation is less accurate. | The output of digital modulation is accurate.
|
| AM generates signals to carry out frequently varying information | Digital modulation generates signals whose rate varies at specific time intervals. |
| The human voice is the best example of analog modulation | The signals transmitted through the computer are examples of digital modulation |
Advantages and Disadvantages of AM Transmission
Both the modulation types are with certain limitations, advantages, and disadvantages. Few of to be discussed are as below:
Advantages
- Supports flexible bandwidth ranges
- Resolve fault components in a streamlined manner
- Enhanced lifespan
- Simple to manage using mathematical calculations and functions
- Easily managed over sensitive routing
- Diffusive weather dependencies are less.
Disadvantages
- Complicate to implement
- Accurate transmission need perfect transmitters and receivers
- No protection for transmitting information
- There exists no option for data saving
Applications of Analog Modulation
As analog modulation consists of various types (amplitude, frequency, and phase), there is a wide range of applications using these techniques. Some of the applications are:
- AM techniques are used in aircraft to establish communication between the pilot and the station and the other way too.
- Implemented in satellite communications.
- Telemetry, seismic processing, and radar implement the methods of frequency modulation.
- Used in music creation and also for video transmissions and magnetic-tape recording scenarios
- FM radio broadcastings
- Monitoring of EEG signals also utilize analog modulation types
- Used in VCR tape recordings
FAQs
1). Is digital better than analog?
Both signals have their own pros, cons, and applications. Apart from those, digital signals are far better than analog signals because digital information is easily represented, reproduced, and generated too.
2). What is analog communication?
This kind of communication represents the transmission of continuous time modifying signals that propagate in the form of Electromagnetic waves.
3). What is modulation in simple words?
It is the procedure of varying the characteristics of the carrier signal with the input signal where the data is to be transmitted.
4). Which type of modulation is used in TV transmission?
As TV transmissions require both audio and video signals, FM is necessary for audio signals and AM for video signals.
5). What is analog to analog conversion?
Analog-to-analog also called modulation is the interpretation of analog data through analog signals. It is the procedure where the properties of the carrier wave are modified as per the amplitude of the message signal.
Please refer to this link to know more about Phase Modulation MCQs, Analog Electronics MCQs & Sampling Theory and Pulse Modulation MCQ’s.
As because of the wide range of applications, more benefits, and implementations, analog modulation types gained more prominence to transmit signals. Know more about the concepts of what are the derivatives and other waveforms related to analog modulation?