There are different types of Power Transistors from TIP series like; TIP41 (NPN), TIP31(NPN), TIP42 (PNP), TIP2955 (PNP). TIP122 (NPN), TIP127 (PNP). The term TIP stands for “Texas Instruments Power” and is a series of BJTs manufactured by Texas Instruments. This series was launched in the 1960s and is still used today because of its durability, simplicity & simple use. This article provides brief information on one of the TIP series transistors namely; the TIP127 Darlington transistor, pin configuration, specifications & its applications.
What is TIP127 Darlington Transistor?
The TIP127 is a PNP-type Darlington transistor with a monolithic Darlington configuration and base island layout. This transistor is manufactured by using planar technology. This PNP transistor shows exceptional high gain performance connected with extremely low saturation voltage. This transistor is available in the TO220AB Plastic case package and is mainly designed for low-speed switching & general purpose amplifier applications. TIP127 transistor can switch up to 60V loads with 8A of peak current and 5A of continuous current.
Pin Configuration:
The pin configuration of this TIP127 Darlington transistor with its symbol is shown below. This transistor includes three terminals which are discussed below.
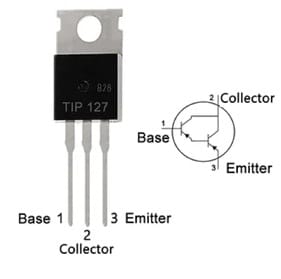
TIP127 Darlington Transistor Pin Configuration
- Pin-1 (Base): This pin is used for transistor biasing by turning it ON/OFF.
- Pin-2 (Collector): This pin allows the flow of current and is connected normally to load.
- Pin-3 (Emitter): The current flow Drains out throughout this terminal.
Features & Specifications:
The features and specifications of the TIP127 Darlington transistor include the following.
- This is a PNP Darlington transistor.
- Its package type is TO-220.
- The material of this transistor is Si.
- This transistor’s maximum DC current gain is high – 1000.
- Its continuous collector current is 5A.
- Its collector-emitter voltage is 100V.
- The base current of the transistor is 120mA.
- Its emitter to base voltage is 5V.
- Its collector-to-emitter voltage is 100 V.
- Its collector-to-base voltage is 100 V.
- Its emitter to base voltage is 50 V.
- Its peak collector current is 8 A.
- Its Junction and storage temperature ranges from – 65 to + 150°C.
- Its maximum collector dissipation is 65 watts.
Complementary & Equivalent Transistors
The complementary TIP127 PNP transistor is TIP122. The equivalent TIP127 PNP transistors are; TIP107, BD650, BD268A, BD652, MJE6042, BDT62B, MJE6041, MJF127, MJF6668, MJE6042, TIP137, BD802, BD902.
How to use a TIP127 PNP Transistor safely in a Circuit?
To use the TIP127 PNP transistor very safely in a circuit for a long time, it is suggested not to operate any load > 5A using this transistor. Do not drive any load > -100V with this PNP transistor. An appropriate base resistor must be used with this transistor to protect from overcurrent flow. Always verify the pin configuration of this transistor before connecting within any application circuit. This transistor should not be used or stored below a temperature of -65 centigrade & above +150 centigrade.
100 Watts High Power Amplifier Circuit with Transistors
A 100 Watts high-power amplifier circuit is used to amplify a small signal to a required range. In modern electronics, amplifiers play a key role and these are available in different forms like; integrated amplifiers, preamplifiers, and power amplifiers. So here we are going to design a 100Watts high-power amplifier with transistors.
The required components to make this high-power amplifier circuit mainly include; a TIP222 NPN Transistor, condensor mic, TIP127 PNP transistor, 3.5mm female audio jack port, 1K potentiometer, 3.5mm male Audio Jack, 470uF capacitor, 12V DC Supply, 150k resistor, breadboard and connecting wires. Connect this circuit as per the circuit diagram shown below.
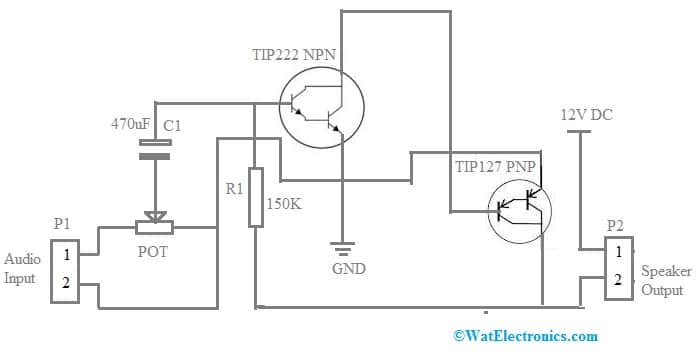
100 Watts High Power Amplifier Circuit with Transistors
Working
This high-power amplifier circuit uses TIP122 & TIP127 Darlington pair PNP & NPN transistors which work like normal PNP or NPN transistors. These transistors have a 5A of good collector current rating & about 1000 gain. They can withstand about 100V across their CE terminal thus they can be used for driving heavy loads.
This high-power amplifier circuit works the same to a simple amplifier circuit. This simple circuit works with a 12V DC power supply.
In this circuit, an audio input is taken from an audio transducer like a mic. This transducer works as the DC control signal mainly for the Q1 transistor. Here, the 47uF capacitor simply blocks the DC component by allowing the signal of the AC component only to supply through. Here Q1 Transistor amplifies the signal and transmits it to the Q2 transistor’s base terminal. Further, the TIP127 transistor changes the input signal and supplies it to an audio o/p device like a loudspeaker.
This transistor can also be interfaced with microcontroller similar to a normal transistor. Check on this link to know more about it. Interfacing transistor to a microcontroller
and before connecting it few precaution need to be taken. check on Precaution to be taken while connection a transistor to microcontroller. Please refer to this link for the TIP127 Darlington Transistor Datasheet.
Advantages
The advantages of the TIP127 PNP transistor include the following.
- This transistor has a high voltage and current rating.
- It has less saturation voltage.
- These are reliable and durable.
- It provides a very high current gain as compared to a single transistor.
- It provides high input impedance.
- This transistor is extremely responsive to the current.
- Darlington pair transistor provides low response time.
- It provides less noise.
- Darlington pair transistor configuration generates less heat.
The disadvantages of the TIP127 PNP transistor include the following.
- The voltage drop will be there across base & emitter terminals when this transistor is in the saturation region.
- It has a low switching speed.
- It has limited bandwidth.
- This transistor provides high power dissipation because of high saturation voltage
- The overall leakage current of this transistor is higher.
- This transistor configuration can cause a phase shift at certain frequencies within the negative feedback circuit.
TIP127 Darlington Transistor Applications
The applications of the TIP127 PNP transistor include the following.
- A TIP127 transistor is used in different applications.
- This transistor is used as an amplifier or a switch and it provides more sensitivity to a tiny signal.
- This transistor is used as a different audio amplifier for directly amplifying & operating a speaker for small audio coming from any device.
- This transistor can be used as an audio preamplifier (or) any signal amplification.
- This transistor is used in different general-purpose applications wherever you need high gain.
- These are used in switching & power linear applications.
- These transistors are suitable for high-power & medium power electronics such as; motors controlling, high-power LEDs, or solenoids.
- These transistors can be used at the microcontroller’s output.
- These transistors drive different loads <5A.
- This transistor is used in electronics laboratories.
- These are used in DIY projects, Electronic/ Electrical major projects, or mini projects.
- The TIP127 transistor’s main purpose is to amplify current.
- This transistor is frequently used in applications where a small i/p current controls a larger o/p current.
Thus, this is an overview of a TIP127 Darlington Transistor, pin configuration, features, specifications, circuit, working, and its applications. This is a PNP-type bipolar junction transistor and is composed of three semiconductor material layers; two P-type and one N-type. This transistor is commonly used wherever amplification or high-current switching is necessary. This transistor can also be used where a low-current signal source or microcontroller is required to control high-power devices like LED control, relay driving, and motor control. During this transistor operation, it generates heat, particularly when handling high currents. So it is significant to utilize a suitable heat sink to prevent this from overheating. Here is a question for you, what is a TIP122 transistor?