MJE13007 is an NPN transistor and is made with silicon (Si) material. This transistor is mainly designed to be used wherever fall time is critical like; high−voltage and high-speed-based power switching inductive circuits. This transistor is mainly applicable for 115V & 220V switch−mode applications like; inverters, switching regulators, solenoid or relay drivers, deflection circuits & motor controls. This article provides brief information on an MJE13007 transistor like; pinout, specifications, circuit, and its applications.
What is MJE13007 Transistor?
MJE13007 is an NPN type of bipolar junction transistor that includes layers where one layer is p-doped and the remaining two layers are n-doped. Here, the p-doped layer is sandwiched between two n-type layers. This transistor includes three terminals like a BJT. The small i/p current at the base terminal is utilized to produce a large o/p current across both the emitter & collector terminals. The emitter to base voltage of this transistor is 9V which means this transistor needs 9Volts to initiate the action of the transistor.
This MJE13007 transistor comes under the NPN category where the major charge carriers are electrons while holes are the minor charge carriers. It is very significant to note that in BJT, both charge carriers are involved in the transistor’s conductivity. The mobility of electrons is more efficient than holes. Furthermore, the flow of current from the emitter terminal to the collector terminal in PNP whereas in NPN, it flows from the collector terminal to the emitter.
The MJE13007 transistor working is; the base terminal of this transistor is responsible for the transistor’s overall action. Once the voltage is given at the base terminal, it will get biased & current starts flowing from the collector terminal to the emitter.
Pin Configuration:
The pin configuration of the MJE13007 transistor is shown below. This transistor includes three terminals which are discussed below.
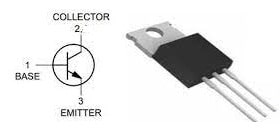
MJE13007 Pin Configuration
- Pin1 (Base): This terminal is used to control the transistor biasing by turning ON/OFF the transistor.
- Pin2 (Collector): The current flows throughout this terminal and is connected normally to load.
- Pin3 (Emitter): The current drains out throughout this terminal and is connected normally to GND.
Features & Specifications:
The features and specifications of the MJE13007 transistor are discussed below.
- It is a three-terminal NPN BJT.
- It is available within the To-220 package.
- Its collector-to-emitter voltage or VCE is 400 Volts.
- Its DC current gain or hFE ranges from 8 to 40.
- Its collector-to-base voltage or VCB is 700V.
- Its continuous collector current or IC is 4A.
- Its maximum base current is 2A.
- Its emitter to base voltage or VBE is 9V.
- Its power dissipation is 80W.
- These transistors are RoHS-compliant & Pb−free.
- Its operating & storage junction temperature ranges from -55 degrees centigrade to 150 degrees centigrade.
Equivalent & Complementary Transistors
Equivalent of MJE13007 transistors are; MJE13005, 2SC3795 and KSE13007. Complementary Transistors are; FJP13007, KSE13007F, KSE13007, MJE13007A, STD13007For MJE13007G and other NPN type power transistors are; 2SC5200, BD139, 2N3055, MJE13001 & TIP31C. Transistor replacement in any application is possible with its equivalent based on the requirement. To know how to replace it, please refer to this; Replacing Transistors in Electronic Circuits: Factors and Considerations.
How to use MJE13007 in a Circuit to get Long-Term Performance?
To use a MJE13007 transistor in a circuit to get long-term performance, it is suggested not to drive any load above 8 A. Use a base resistor to this transistor always and this transistor should not be operated below temperature -65 to +150 °C. Always ensure the pinout of the transistor before placing it within the electronic circuit. Connecting a base resistor to the base terminal of the transistor is advisable to avoid it being damaged. Please refer to this link for; Choosing Base Resistance for Transistors in Electronic Circuits.
While looking for a suitable transistor for your application based on a few factors, it is very important to look into a few points on How to Select a Transistor.
Inverter Circuit using MJE13007 Transistor
The simple inverter circuit using the MJE13007 transistor is shown below. This simple inverter circuit is used for small loads such as; Mobile Phone chargers, 15w LED bulbs & electrical accessories. This circuit uses a 15W LED bulb like a load although you can also use any relative AC load.
The required components to make this inverter circuit mainly include; two MJE13007 transistors, a 12-t0-12V center tapped transformer, a 15w LED bulb, 330 Ohm resistors two, and a 12V battery.
The connections of this circuit follow as;
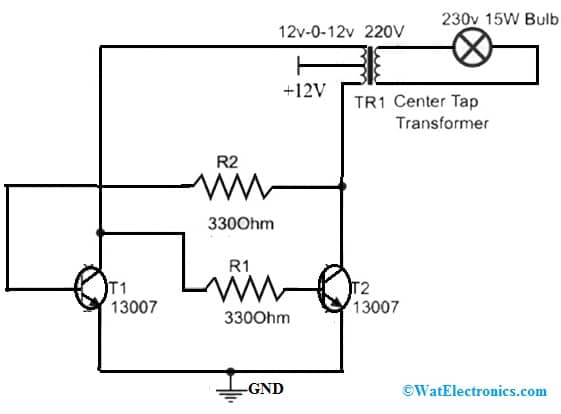
Inverter Circuit using MJE13007 Transistor
- The transistor emitter terminals are connected together for the GND terminal.
- Connect the base terminal of one transistor to the collector terminal of the other transistor through a 330-ohm resistor.
- Connect collector terminals of both the transistors with the center tap Transformer.
- Here, the corner points of the transformer are used but the middle pin is not connected in this inverter circuit.
- For input power, a 12V lead acid battery is used. Here, the transformer’s center tap point will be mainly utilized for the +12v supply.
- An external load like a 15W LED bulb is connected to the transformer’s secondary winding.
Working
The working of this circuit is; that whenever we provide 12V to this circuit one of the transistors will go into the conductive stage. So, one-half of the transformer’s coil will conduct. So the T1 transistor will stay conductive until the breakdown happens. After that, the T2 transistor will conduct. So this entire Push-Pull configuration process repeats repeatedly. Thus, from the transformer’s coil, we can obtain the 220V o/p.
When a 12v battery DC input voltage source is connected to the circuit, the LED will glow. So the circuit works perfectly. This simple inverter circuit is suitable for small loads such as; 15w LED bulbs, electrical accessories, and mobile phone chargers. This inverter circuit is used to control AC devices, AC lights (or) bulbs. It can be utilized in UPS and power supplies with small modifications.
Transistors can be interfaced with a microcontroller. To know how to interface click on Transistor Interface with microcontroller. Few precautions need to be taken while interfacing a transistor with a microcontroller. Read on Precautions to be taken while interfacing a transistor to a microcontroller.
Applications
The applications of the MJE13007 transistor include the following.
- It is used in current electronic circuits.
- It is used in SMPS (switched-mode power supply).
- It is used to support loads below 8A.
- It is used in voltage regulators, motor control & -bridge circuits.
- It is used for amplification & switching purposes.
- It is used in astable and bistable multivibrator circuits.
- It is used in high-current switching loads upto 4A.
- It is used in inverters and DC-to-DC converters.
- It is used in motor speed control.
- These transistors are used in solenoid drivers or relay drivers.
- These transistors help in operating AC devices.
- It is used in UPS circuits and power supplies with some small modifications.
- These are used commonly in SMPS designs with a switching transformer for switching 115V/220V of AC voltage at high frequencies.
Please refer to this link for the MJE13007 Transistor Datasheet.
Thus, this is an overview of the MJE13007 transistor, working, pin configuration, specifications, circuit, working, and its applications. This is an NPN, high voltage BJT including 400V of collector to emitter voltage, 4A of collector current, and 0.9uS of high switching speed. So it is the perfect choice to use within high-speed and high-voltage-based switching circuits for inverter & also converter applications. The collector dissipation power of this transistor is 75W, thus a heat sink is compulsory whenever operating at maximum voltages. This transistor can also be used in a straightforward relay driver (or) solenoid driver due to its capability to handle up to 8A of peak current. Here is a question for you, what is the MJE13005 transistor?