The low-power and general-purpose NPN silicon BJTs like; BC109, BC107, and BC108 are frequently found in most electronic devices and equipment. These transistors were produced by Philips & Mullard Ltd in the year 1963 & launched in April 1966. At first, the range of these transistors is expanded ultimately in TO-18 metal packages to include other types of packages, high voltage ratings, better gain groupings selection & complementary PNP types. Some electronics manufacturers have indicated their parts through a high power dissipation rating as compared to others. This article provides brief information on the BC108 transistor, pin configuration, specifications, and its applications.
What is BC108 Transistor?
BC108 transistor is a NPN, low-power semiconductor and three-terminal device, used for switching or amplifying power or signals. This transistor’s TO-18 package is made up of metal covering cans where this package’s heat resistance is higher & the external covering acts as the heat sink. BC108 is an NPN Transistor, thus we need to give a small amount of +ve voltage to the base terminal so that the necessary amount of current will be supplied throughout the base terminal of the transistor. So this transistor is suitable for fuzz pedals & other effects like Big Muff clones and vintage silicon Fuzz Face builds.
Working
Once the BC108 transistor is biased, it allows 200mA of a maximum current across the CE junction, which is known as the saturation state. We know that a transistor is a current-controlled device thus whenever the current at the base terminal is detached, then the transistor will become completely off, so the transistor within this stage works in Cut-off Region & the BE voltage could be approximately 660mV.
When voltage or current is provided to one pair of these transistor terminals then it controls the flow of current through other pair of terminals, Because the output power is higher as compared to input power, the transistor can amplify a signal.
This BC108 transistor is switched ON by providing the necessary current to its base terminal until the voltage supply at the base terminal reaches zero. The base terminal of this transistor cannot be left floating due to false triggering and it can cause troubles within the circuit. To overcome this trouble, we have to use pull-down resistors.
Pin Configuration:
The pin configuration of the BC108 transistor with its symbol is shown below. This transistor includes three terminals and each pin’s functionality is discussed below.
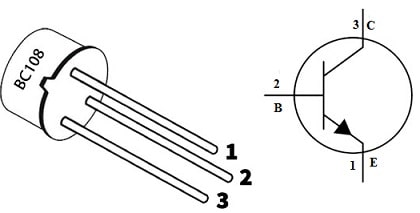
BC108 Transistor PinOut
Pin1 (Emitter): Current supplies through this terminal to the collector terminal.
Pin2 (Base): This base terminal is used to control the transistor so it helps in triggering the device.
Pin3 (Collector): The collector terminal is the larger part of the transistor which has a larger current. So electrons that are emitted from the emitter terminal are simply collected through the collector terminal.
Features & Specifications:
The features and specifications of the BC108 Transistor are discussed below.
- BC108 is an NPN bipolar junction transistor.
- It is a three-terminal and low-power semiconductor device.
- This transistor is available in the TO-18 package.
- TO-18 package of this transistor is designed with metal covering cans outside & the external covering will perform as the heat sink.
- The TO-18 package of this transistor has a small metal marking portion which begins from the emitter terminal, base, & collector.
- The collector-to-emitter voltage or VCE is 25V.
- The collector-to-base voltage or VCB is 30V.
- The emitter to base voltage or VEB is 5V.
- The saturation voltage from collector to emitter ranges from 0.25V to 0.60V, indicating the device’s region switching.
- The collector current of this transistor is 0.2A.
- This transistor’s power dissipation is 0.6W/℃.
- The DC current gain value for this transistor ranges from 110 to 800Hfe.
- The value of the BW transition frequency of this transistor is 150MHz.
- This transistor’s temperature ranges from -65 to 200℃.
- The thermal resistance of this transistor is 175℃/W.
- The noise figure of this transistor is 10dB.
- The output capacitance of this transistor is 4.5Pf.
Equivalent & Complementary Transistors
The equivalent BC108 NPN transistors are; BC548, BC547, 2N3904, BC549, BC107 & 2N3053. The complementary pair of BC108 NPN transistors is PNP BC178. The SMD version of the BC108 transistor is MMBTH10 (SOT-23). Replacement of a transistor is possible with its equivalent in a suitable circuit based on requirement is necessary. To know how to replace it, please refer to this; Replacing Transistors in Electronic Circuits: Factors and Considerations.
How to use BC108 NPN Transistor for Long Term in a Circuit?
To use the BC108 NPN transistor for a long time in a circuit, the user should follow the secure operating guidelines. Do not utilize the transistor on its absolute maximum ratings & stay always below 20%. This transistor’s maximum collector current is 100mA thus it does not drive load above 80mAmps. The maximum voltage from collector to emitter is 20V so do not drive any load above 16V. This transistor must be used at above -65 °C & below 150°C temperature. The base resistance of the transistor also plays a important role in the longevity of the transistor. Hence choosing the right base resistance for a transistor is important. Read more on it in How to select a base resistance of a transistor ?
Police Siren Circuit using BC108 Transistor
A simple police siren circuit using the BC108 transistor is shown below. This circuit generates an alarm sound similar to the police siren. The required components to make this police siren circuit mainly include; switches S1 and S2, resistors 9V battery, R1- 100K, R2- 47K, R3-22K, R4- 100 Ohms and R5- 56 Ohms, Capacitors C1-10uF, C2-22nF and C3-2.2uF, transistor Q1- BC108, Q2-2N3702 and an 8 Ohms K1 speaker. Connect the circuit as per the diagram shown below.
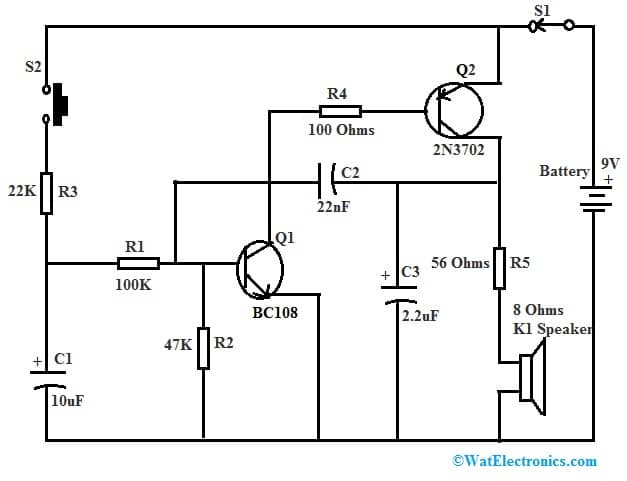
Police Siren Circuit using BC108 Transistor
Working
The working of this police siren circuit follows as follows; once the S2 push button switch is pressed the C1 capacitor charges and makes the Q1 transistor ON gradually. Similarly, when the S1 push button switch is released the C1 capacitor discharges & makes the Q1 transistor OFF gradually so that frequency reduces and gives a siren sound.
Whenever the Q1 transistor is turned ON, its collector voltage will drop to make the Q2 transistor turn ON. Here the C2 capacitor will be charged nearly to full voltage supply and increases the CE voltage of the Q2 transistor. This change in voltage is connected to the base of the Q1 transistor using the C2 capacitor. Thus the Q1 transistor comes a little out of saturation. Thus, the voltage at the collector terminal of the Q1 transistor falls & makes the Q2 transistor more OFF. So this action will continue until both Q1 & Q2 transistors turn OFF. After that, the C2 capacitor discharges, and again Q1 transistor will be turned ON to begin a new cycle. Once the C1 capacitor is charged the tone will increase & when the C1 capacitor is discharged the tone will drop.
Applications
The applications of a BC108 NPN transistor include the following.
- BC108 NPN Transistor is an extremely versatile device, used in different applications; flashers/ LED dimmers, high-frequency switching, preamps for power amplifiers, modulators & demodulators for RF.
- These transistors are used in input stages to make low-noise-based circuits, low-noise signal processing, etc.
- These are used in different circuits; RF circuits, Low noise circuits, Switching circuits, modulators, and demodulators mainly for RF circuits.
- These are used in Darlington pairs, LED dimmers, etc.
- This transistor can be used to switch, amplify (or) power signals.
- These transistors are frequently found in electronics & equipment.
- These are used in the applications of low-power amplifying (or) High-speed switching.
- These are used in LED dimmers, power amplifiers, and flashers.
- This transistor is used in audio applications.
Before selecting any transistor within a suitable application, we need to consider different factors. Know more about it in How to Select a Transistor article.
The transistors can also be interface with a microcontroller. Check on these links on how to interface and the precaution need to be taken before interfacing it to a microcontroller.
Precautions to be taken before connecting a transistor to the microcontroller.
Please refer to this link for the BC108 Transistor Datasheet.
Thus, this is an overview of the BC108 transistor, pin configuration, specifications, circuit, working, and its applications. The BC108 transistor is an NPN, low-power, through-hole-silicon planar epitaxial transistor available in the TO-18 metal package. This transistor is mainly used for switching as well as amplification purposes in different applications. Here is a question for you, what is a BC548 transistor?