A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor device like; an anode and cathode where the anode is the positive end and the cathode is the negative end. The main function of a diode is to allow the flow of current only in a single direction from the anode terminal to the cathode. To remember in which way current supplies throughout a diode, you have to remember the mnemonic ACID which stands for “anode current in diode” or anode-cathode is a diode. These components are the most significant electronic components used in modern electronic circuits for protection, rectification, switching, etc. Diodes are available in different types and shapes which are used based on the requirement in applications. Among them, a fast recovery diode or FRD is one of the main diodes used mainly for its fast reverse recovery time. This article discusses an overview of fast recovery diode, working, and its applications.
What is a Fast Recovery Diode?
A PN junction diode that has a fast reverse recovery time is known as a fast recovery diode, fast switching diode, or fast diode. Generally, the current in the diode flows in forward bias only and it blocks in reverse bias. However, because of the stored charge in its junction, it will not block current immediately once the voltage applied changes from forward bias to reverse bias. So it conducts in reverse direction because of the stored charge carriers for a short period of time so this time is known as reverse recovery time.
Thus, this diode is used for high-frequency signal rectification up to 100 kHz. This diode’s reverse recovery time (Trr) ranges from 10 to 100 ns. The fast recovery diode symbol is shown below which is the same as a conventional diode due to their same operations apart from their switching speed.
FRD Symbol
These diodes can be categorized into two types based on their design. One diode is formed through a diffused PN junction whereas the other type is a metal semiconductor diode. These metal-semiconductor diodes possess very high switching speeds as they use majority charge carriers only & the storage of minority charge carriers is negligible.
Construction
The construction of a fast recovery diode is the same as a conventional diode because it is a PN junction diode, so p-type & n-type semiconductors are joined to form a PN junction. The semiconductor material of this diode has recombination centers which help in recombining the charge carriers stored & decreasing their lifetime. So the junction is drained rapidly for the stored charge & the recovery reverse time is decreased. In this diode, Gold can be added as recombination centers within the semiconductor material like GaAs (gallium arsenide).
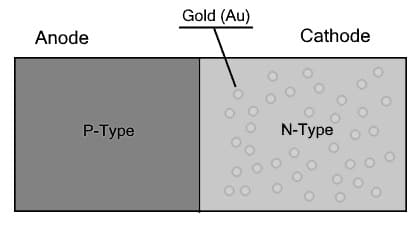
Construction of Fast Recovery Diode
As compared to a conventional diode, this diode greatly decreases the reverse recovery time. But, there is a limitation because when the number of recombination centers increases, the reverse current will be increased. So the gold quantity being included in semiconductor material can be taken into consideration.
Working
The working of a fast recovery diode is the same as a conventional diode because both diodes are used mainly for rectification. Once an AC signal supplies throughout a diode, then the positive half cycle will flow throughout it whereas the negative half cycle will be blocked but not immediately. It needs some amount of time to move from the conduction to the blocking state.
We know that a time period can be defined as the time necessary to complete a single cycle. So, a signal’s time period is inversely proportional to its frequency (T = 1/f). The signal with low frequency has a large time period so they are slow and the time period of high frequency signals is very short & a negative half cycle’s duration is extremely small.
A conventional diode with a large recovery time conducts the fast negative half cycle. So they need a diode that has an extremely small recovery time for blocking the negative half cycle. This small recovery time can be achieved by a fast recovery diode by including gold as recombination centers within its semiconductor. The charge carriers throughout the conduction state flow to the reverse face of the PN junction. Once the voltage applied reverses, the charge carriers will start to shift to their sides.
The charge carriers like Electrons are very fast & quickly recover although the holes take much time due to being heavier. Both the charge carriers can recombine with each other & form the depletion region to block the flow of current. In the semiconductor, the recombination centers are located at a small distance to help in the hole recombination to provide a very fast recovery time.
Fast Recovery Diode Circuit
The fast-recovery diode implementation for the power MOSFET circuit is shown below. In this circuit, the body diode anode terminal is connected to the source terminal of MOSFET, cathode terminal is connected to the MOSFET’s drain terminal. Thus if we provide the ‘VDD’ negative voltage across the source & drain terminals, then it will connected forward-biased. So the MOSFETs reverse-blocking capacity breaks. Therefore, this can be utilized in inverter circuits mainly for reactive loads without the requirement of an excessive diode across a switch.
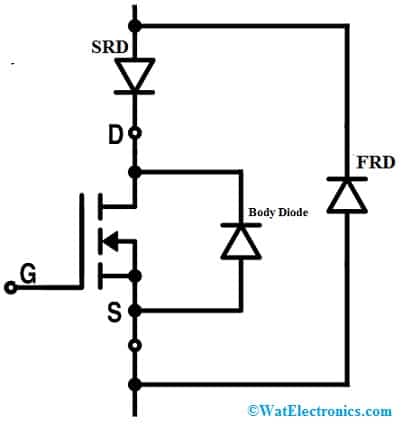
Fast Recovery Diode Implementation for MOSFET
Although in the above circuit, the internal body diode of the MOSFET has enough current & also switching speed for most applications where ultrafast diodes are necessary. So in those situations, a fast-recovery diode or FRD is connected externally in an anti-parallel way. However, a slow-recovery diode or SRD can also be necessary in the circuit to block the action of the body diode.
Electrical Characteristics
The fast recovery diode’s electrical characteristics are discussed below.
- The max peak reverse voltage this diode can withstand ranges from 600V to 1000V.
- The reverse recovery time can be defined as the time it takes for a recovering state from forward conduction to reverse blocking. The reverse recovery time of this diode ranges from 10ns to 200ns.
- The highest leakage current of this diode within reverse bias conditions ranges from a μA to tens of μA.
- The forward voltage drop of this diode across its PN junction is approximately 1.3 – 3.6 volts
Schottky Diode and Fast Recovery Diode
The difference between Schottky and fast recovery diode includes the following.
|
Schottky Diode |
Fast Recovery Diode |
| Schottky diode is a solid-state diode with a metal-semiconductor junction. | Fast recovery diode is a PN junction diode with gold doping to reduce reverse recovery time. |
| This diode is also called a low-voltage diode, Schottky barrier diode, or hot-carrier diode. | This diode is also called a fast-switching diode or fast diode. |
| This diode uses majority charge carriers only for current flow. | This diode uses both holes & electrons in the flow of current. |
| This diode’s anode terminal is metal and the negative terminal is an N-type semiconductor. | This diode’s anode terminal is a P-type semiconductor whereas the cathode terminal is an N-type semiconductor. |
| The MS junction of this diode has a very thin depletion region. | The PN junction of this diode has a wider depletion region. |
| The junction capacitance of this diode is lower. | The junction capacitance of this diode is higher. |
| The switching speed of this diode is very high for up to 100 GHz signals. | The switching speed of this diode is high for signal rectification up to 100 GHz. |
| This diode efficiency is higher. | This diode efficiency is lower. |
| The reverse recovery time of this diode ranges from a few ns – 10 ns. | The reverse recovery time of this diode ranges from 10 to 200 ns. |
| The forward voltage of this diode is low approximately 0.4 – 0.6 V. | The forward voltage of this diode is high approximately 1.3 – 3.6V. |
| The max reverse voltage this diode can withstand is up to 150 volts. | This diode withstands large reverse voltages approximately 1200 volts. |
| This diode is mainly used for high-frequency signal rectification. | This diode is mainly used for RF-based applications. |
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of a FRD or fast recovery diode include the following.
- This diode has a high switching speed.
- This diode’s reverse recovery time is very low.
- As compared to conventional type diodes, these diodes have low losses & improved efficiency.
- These diodes have high-speed operation and reliable performance.
- These diodes significantly improve switching power supply efficiency & decrease switching loss.
- These diodes have high efficiency when compared with a conventional diode.
- As compared to Schottky diodes, these diodes have low reverse leakage current and this diode can resist high reverse voltage.
- These diodes exhibit quicker switching times.
- These diodes ensure the efficient & smooth working of your electronic circuits.
- These diodes provide fast recovery time & low forward voltage drop by reducing power losses & increasing the efficiency of the circuit.
The disadvantages of a FRD or fast recovery diode include the following.
- The reverse leakage current within this diode will increase by adding gold-like recombination centers.
- The power consumption of this diode is high.
- The forward voltage drop of this diode is higher.
Applications
The uses or applications of a fast recovery diode include the following.
- The FRDs are used mainly in rectifiers, particularly for high-frequency rectification.
- These diodes are used in various electronic circuits in different automobile and industrial sectors.
- These diodes help in detecting high-frequency-based RF waves within radio signal detectors.
- These types of diodes are widely used for modulation & rectification purposes.
- These are used analog & digital communication circuits.
- They are used for RF signals within envelope detectors and also high-speed-based DC-DC converters.
- Fast recovery diodes are applicable in AC to DC adaptors or chargers, inverters, DC-DC converters, power converters for wind turbines, motor control, and drives, CAV (construction & agricultural vehicles), commercial, PFC & UPS.
- Fast recovery diodes are used in high-frequency rectifiers, power factor controllers, Power factor correction, inverters, Switching power supplies & DC-DC converters.
- These diodes are very significant components in electronic circuits that need very rapid & efficient switching like power supplies, motor control circuits, inverters, etc.
- These types of diodes provide zero reverse recovery time so used frequently in high-frequency applications like RF technology.
Thus, this is an overview of a fast recovery diode that provides a short reverse recovery time making them superior in terms of switching loss & switching speed. These diodes are called fast recovery diodes due to their extremely low reverse recovery time. So, it switches very quickly from reversed to forward mode. These diodes are used for high-speed rectification due to short reverse recovery time, used in AC to DC converters & inverters through under several hundreds of hertz switching frequency due to high withstand voltage. Here is a question for you, what is a standard recovery diode?