The 2N4402 is a general-purpose PNP-type transistor, where the N-doped semiconductor layer is sandwiched in between the two P-doped semiconductor layers. Generally, transistors are made up of germanium or silicon based on the chosen application. In the PNP 2N4402 transistor, two P-layers signify the emitter & collector terminals whereas N signifies the base terminal of the transistor correspondingly. This transistor works in such a way that the small current at the base terminal controls a large amount of current at the emitter & collector terminals. To conduct this PNP transistor, the emitter terminal will always be more positive than the base & collector terminals. This article discusses an overview of the 2N4402 transistor, pinout, specifications, and its applications.
What is a 2N4402 Transistor?
The 2N4402 is a silicon-based PNP transistor, used in general-purpose switches as well as amplifiers. This transistor is a better choice when you require a very simple switching device for low-power loads. This transistor’s gain ranges from 20 to 150 which determines the transistor’s amplification capacity. The highest current that can be supplied throughout it is 200mA, so when combined with this current value with the gain value, this transistor will be the best choice in an audio amplifier for a preamplifier. This transistor can also be used as a signal-switching transistor mainly for small signals.
Under normal conditions & exclusive of outside influence, there will be an appearing positive voltage at the base terminal of the transistor. So depending on the PNP transistor working principle; having a positive (+ve) voltage at the base terminal will this transistor in a maximum resistance condition. To turn on the device completely, a small amount of current needs to be supplied from the base terminal of the transistor.
While looking for a suitable transistor for your application based on a few factors, it is very important to look into a few points on How to Select a Transistor.
Working
Whenever this PNP transistor is biased, then it allows a maximum of 600mA of current across the CE Junction, which is known as the saturation state. In this condition, a load that uses >600mA current may harm the device. We know that a transistor is a current-controlled device thus whenever the current at the base terminal is removed the transistor will become off completely. This condition is known as Cut-off Region, so there is no current supply throughout the CE junction.
2N4402 Transistor Pin Configuration:
The pin configuration of the 2N4402 Transistor is shown below. This transistor includes three pins which are discussed below.
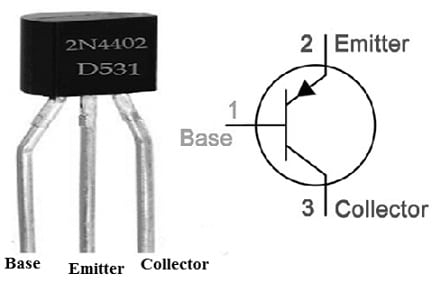
2N4402 Pin Configuration
- Pin1 (Base): The base pin of this transistor controls the transistor biasing.
- Pin2 (Emitter): This pin emits electrons into the initial PN junction.
- Pin3 (Collector): This pin collects the emitted electron from the emitter.
Features & Specifications:
The features and specifications of the 2N4402 transistor include the following.
- 2N4402 is an NPN Bi-Polar transistor.
- Its maximum DC gain or hFE is 150.
- Its maximum base current or IB is 50mAmps.
- It is available in the TO-92 Package.
- Its continuous collector current or IC is 600mA.
- Its maximum collector-to-base voltage |Vcb| is 45 volts.
- Its emitter to base voltage or VBE is 5V.
- Its collector dissipation is 0.3 watts.
- Its noise figure ranges from 2 to 10 dB.
- Its transition frequency is 100 MHz.
- Its maximum operating junction temperature or Tj is 175 °C.
- Its operating & storage junction temperature ranges from -55 to +150 °C.
- Its collector capacitance is 8.5 pF.
- Pb−free packages are accessible.
Equivalent & Alternative 2N4402 PNP Transistors
The equivalent 2N4402 PNP transistors are; BC559, NTE159, BC327, 2N4403, BC556,etc. Alternative 2N4402 PNP transistors are; 2SA708, BC528, BC527, KSA708, MPS4356, MPS4354, NTE159, ZTX552 or ZTX551. The 2N4402 complementary transistor is the 2N4400. The SMD 2N4402 transistor versions are; 2SA1519 (SOT-23), 2SA1518 (SOT-23), 2SA1521 (SOT-23) & 2SA1520 (SOT-23). Replacing a suitable transistor in any circuit based on requirement is very important. To know how to replace it, please refer to this; Replacing Transistors in Electronic Circuits: Factors and Considerations.
How to use 2N4402 PNP Transistor/Circuit Diagram
The transistor is a current-controlled device, thus to turn this transistor ON, a small amount of current is required. The base current of this transistor is < 50mA because 2N4402 is a PNP type transistor, so it will turn ON whenever the base terminal is connected to the GND & it will be turned off whenever a positive (+ve) voltage is provided to the base terminal of the transistor.
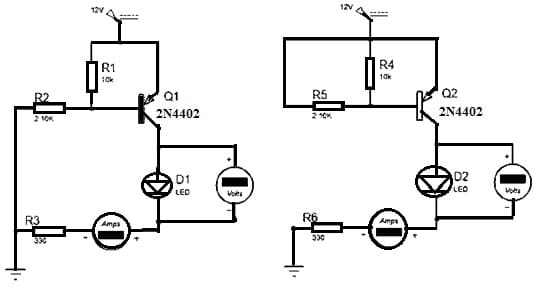
2N4402 Transistor Circuit
The following simulated 2N4402 PNP transistor circuit shows how this PNP transistor performs whenever the base of the basic circuit is connected to the GND & when it is connected to a 5V power supply.
This PNP transistor is turned ON by connecting the base terminal to the GND the transistor will stay on except the voltage on the base terminal is above the base turn-off voltage. The voltage of this transistor ranges between 0.7 to 0.9V. Here, the transistor base terminal cannot be left floating or else there could be artificial triggering, which may lead to problems within the circuit. For resolving the problem we need to connect pull-up resistors to pull up the transistor base to VCC.
Connecting a base resistor to the base terminal of the transistor is mandatory to avoid it being damaged. Please refer to this link for; Choosing Base Resistance for Transistors in Electronic Circuits.
Transistor can also be interfaced to a microcontroller. To know how please click on Interfacing a transistor to a microcontroller.
Please refer to this link for the 2N4402 PNP Transistor Datasheet.
Advantages & Disadvantages
The advantages of the 2N4402 PNP transistor include the following.
- This transistor can be used as a small signal-based switching transistor.
- This component is small, cheap, and easy to work
- These transistors are used for generating simultaneous & contentious power.
- PNP Transistor is used to source current.
- This type of transistor produces low noise.
The disadvantages of the 2N4402 PNP transistor include the following.
- They generate very little energy, so semiconductor fuses cannot guard transistors.
- The current capacity within reverse blocking mode is deficient.
- The output voltage of this cannot be changed very easily.
- It is very responsive to temperature.
Applications
The applications of the 2N4402 PNP transistor include the following.
- The 2N4402 transistor can be used to enhance low-power signals.
- Generally, this transistor is used when you require a simple switching device, especially for low-power loads.
- It can be used as a fundamental power amplifier for amplifying low-power-based signals.
- These transistors are used mainly for voltage & power amplification.
- This component is suitable when selecting a random switching device.
- This type of transistor is designed mainly for general-purpose switching & amplifier applications.
- It is used in lighting systems, audio amplifiers, microphone preamplifiers, relay drivers, signal amplifiers & lighting systems.
Thus, this is an overview of the 2N4402 PNP Transistor pin configuration, features, specifications, circuit, working, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. In the 2n4402 PNP transistor configuration, the emitter terminal is positive about the base and collector terminals. A small amount of current at the base of this transistor is used for controlling the large amount of current at the emitter & collector side. Here is a question for you, what is 2N4403 transistor?