A diode is a two-terminal component that allows the flow of current in only a single direction from the Anode (+) to the cathode (-). The terminals of the diode can be identified by a grey bar on the cathode terminal. Similarly, a rectifier diode is a type of diode mainly used for rectifying alternating current to direct current with the rectifier bridge application. This diode is made with germanium (Ge) or silicon (Si) materials. There are different rectifier diodes available like 1N4001, IN4002, IN4003, IN4004, IN4005, IN4006 & IN4007. This article discusses an overview of the 1N4004 diode, pin configuration, specifications, and its applications.
What is 1N4004 Diode?
1N4004 is a 1N400x series rectifier diode with two terminals known as anode & cathode where the current flows always from the anode to the cathode and it blocks the current flow in the reverse direction. This diode has 1A of maximum current carrying ability & its withstand peaks equal to 30Amps. These diodes are used in circuits that are designed mainly for below 1 amp. The reverse current of this diode is 5uA which is insignificant and its withstanding reverse voltage peak is equal to 400Volts.
Pin Configuration
The pin configuration of the 1N4004 Diode is shown below. This diode includes two terminals like anode and cathode where the function of these terminals are discussed below.
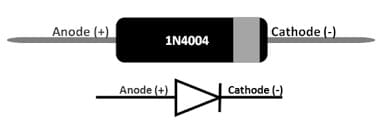
1N4004 Diode Pin Configuration
- Pin1 (Anode): This terminal allows the flow of current.
- Pin2 (Cathode): The flow of current exits always throughout this terminal.
1N4004 Diode Features & Specifications
The features and specifications of the 1N4004 diode include the following.
- It is a Silicon rectifier diode.
- It includes two pins.
- Its case o package is DO-204AL, Axial & DO-41.
- Its average forward current – 1Amps or 1000mA.
- Its non-repetitive peak current – 30Amps
- Its reverse current – 5uAmps.
- Its RMS reverse voltage – 280Volts.
- Its peak repetitive reverse voltage – 400Volts
- It is available in SMD & DO-41 Packages.
- Its maximum dissipation of power – 3W
- Its maximum operating & storage temperature ranges from -55 to +175 C.
- Its MSL or moisture sensitivity level is 1 (Unlimited)
- It has a single-element configuration.
- The type of diode is standard.
- Its height (H) is 5.2 mm.
- Its width (W) is 6.35mm.
- Its contact plating is Tin.
- Its weight is 245mg.
- Its capacitance is 15pF.
Equivalent & Replacements
Equivalent 1N4004 rectifier diodes are SF12, 1n4148, SF12, RL203, RL202 HER203, HER202, HER102, FR202, HER103, FR203, 1N4935 & 1N4934. 1N4004 diodes are replaced with 1N4004, 1N4006, 1N4005 & 1N4007.
How to use 1N4004 securely in a Circuit for a Long Time?
If you desire to enhance the life of this diode within a circuit, then it is suggested to not utilize this diode > 400V and >1A, do not drive any load. Need to verify pin-out connections frequently before utilizing this diode within any circuit. This diode needs to use or store within a temperature > -55 degrees C < +175 degrees C.
DC Voltage Doubler Circuit with 555 Timer IC
The circuit diagram of the DC voltage doubler with 555 Timer, capacitors & diodes is shown below. The following circuit uses a DC voltage that ranges from 5Volts to 15Volts & generates a double voltage as output ranges from 8 to 28V. For instance, if the input voltage of the circuit is 5V, then the output voltage of this circuit will be 1 0V approximately.
The required components of this circuit mainly include; 555 Timer IC, 1N4004 diodes – 2, 22uF capacitors- 2, 1nF capacitor, resistor-33K, a breadboard, 5 to 15V power supply, and connecting wires. Connect the circuit as per the circuit shown below.
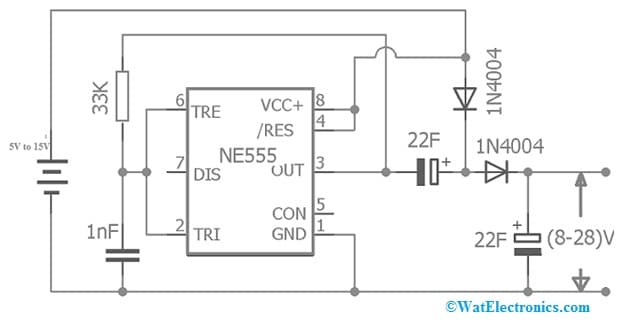
DC Voltage Doubler Circuit with 555 Timer IC
Working
The power supply of this circuit has positive rail (+) & negative rail (-). A diode in this circuit allows the flow of current in a single direction only. More specially, it allows the flow of current only whenever the voltage at the p-terminal of the diode is above the n-terminal through a certain value.
The circuit uses a 555 timer IC with the 33K resistor & 1nF capacitor and generates a square wave output signal at Pin-3. This signal changes between positive & negative voltages constantly.
For instance, if the input power supply is 5V, then the voltage at the 555 timer IC output will be at zero volts for some time, after that, it will change & stay at 5V for some time and changes back to zero volts.
In the above circuit, a 22uF capacitor negative terminal is added to the 555 timer IC output & its positive terminal is connected to the +ve terminal through a diode. Whenever the 555 timer IC output is at 0V, then the 22uF capacitor will charge throughout the diode. Once the 555 timer IC output is at a positive voltage, then the voltage across the capacitor will be within series by the voltage from the IC output.
Since the sources of two voltage within the series will add, the other end voltage of the capacitor will be equivalent to a voltage at the timer output & the voltage across the 22uF capacitor.
When the voltage at the 555 IC output & the voltage across the capacitor is equivalent to the +Ve voltage of the power supply, then the final voltage will be twice to the input voltage. In addition, the voltage at the diode’s n-junction is above than the voltage at the p-junction, so no current supplies back to the positive terminal.
Now we have a double voltage to the input voltage. To avoid the flow of current from flowing reverse to the capacitor from the o/p load, one more PN diode is added. A 22uF capacitor is connected at the end to smoothen the output.
In the above, the arrangement of diodes & capacitors is called a capacitor charge pump. This arrangement can be cascaded at the 555 timer IC output for generating high voltages. The resultant circuit is known as a voltage multiplier circuit that outputs a certain times i/p voltage as o/p voltage. Here, the factor where the o/p voltage is above the input voltage can be decided by the number of phases of the diode and capacitor charge pump blocks utilized.
The voltage doubler circuits are applicable in microwave ovens. These are used to generate voltages that produce very strong electric fields within CRTs. These are used in circuits that are powered by low-voltage sources.
Before selecting a diode there are few things that need to be taken care please read through point to be considered while selecting a diode and it is also important to have proper resistance value for the functioning of the diode. Please click here to know about it
Applications
The applications of the 1N4004 rectifier diode include the following.
- 1N4004 rectifier diode is used in a wide range of applications.
- These diodes are used for voltage blocking & rectification.
- These can be used easily in circuits below 400V.
- This diode can be used for building a diode rectifier to use in power supplies of appliances because its max repetitive reverse voltage is 400V.
- It can be used to block voltages for various purposes in circuits or electronics design.
- It avoids the reverse polarity problem.
- These are used in HWRs and FWRs.
- This diode can be used as a protection device
- These are used in power supplies, adapters, chargers of batteries, current flow regulators, AC – DC converters, voltage blocking, and protection of circuits.
Please refer to this link for the 1N4004 Diode Datasheet.
Thus, this is an overview of a 1N4004 Diode, features, specifications, circuit, working, and its applications. 1N4004 diode is a famous 1N400x series rectifier diode that is used in a broad range of applications that falls within its specifications.
The main difference between 1N4004 & 1N4007 diodes is the peak reverse voltage. For the 1N4007 diode, it is 1000Volts and 280Volts for the 1N4004 diode. Here is a question for you, what is 1N4007 Diode?